536
(2) Floating-point operation instructions for the Universal model QCPU
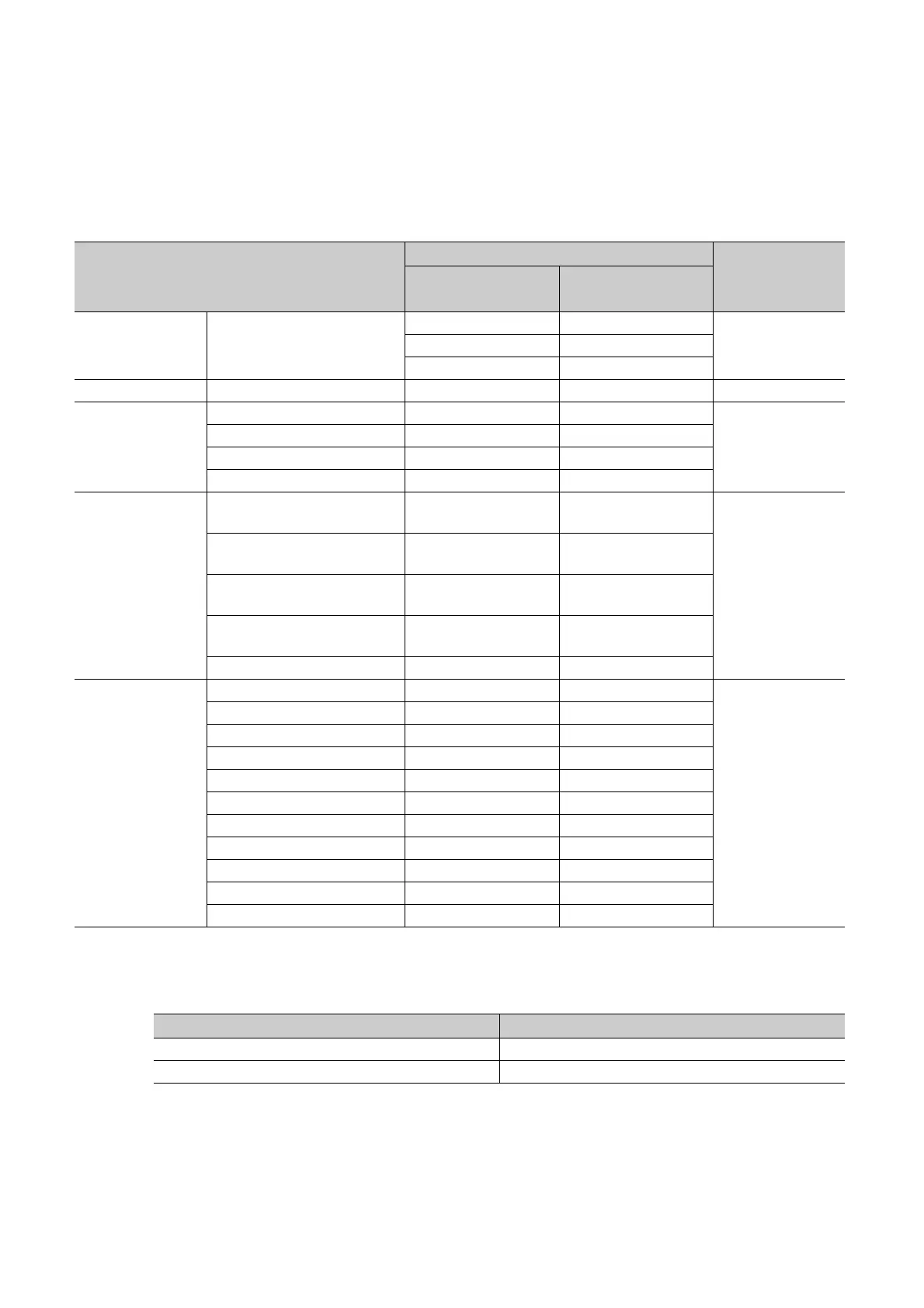
The following table lists floating-point operation instructions for the Universal model QCPU.
Specifications of the single-precision floating-point operation instructions are compatible with those for the High
Performance model QCPU.
Floating-point data can be converted mutually between single precision and double precision using instructions in
the following table.
Instruction name
Instruction symbol
Remarks
Single-precision
floating-point data
Double-precision
floating-point data
Comparison Floating-point data comparison
LDE LDED
indicates one of
the following;
<>,=,<,>,<=,>=.
ANDE ANDED
ORE ORED
Data transfer Floating-point data transfer EMOV(P) EDMOV(P) ---
Four arithmetic
operation
Floating-point data addition E+(P) ED+(P)
---
Floating-point data subtraction E-(P) ED-(P)
Floating-point data multiplication E*(P) ED*(P)
Floating-point data division E/(P) ED/(P)
Data conversion
Conversion from BIN 16-bit data
to floating-point data
FLT(P) FLTD(P)
---
Conversion from BIN 32-bit data
to floating-point data
DFLT(P) DFLTD(P)
Conversion from floating-point
data to BIN 16-bit data
INT(P) INTD(P)
Conversion from floating-point
data to BIN 32-bit data
DINT(P) DINTD(P)
Floating-point sign inversion ENEG(P) EDNEG(P)
Special function
SIN operation SIN(P) SIND(P)
---
COS operation COS(P) COSD(P)
TAN operation TAN(P) TAND(P)
SIN-1 operation ASIN(P) ASIND(P)
COS-1 operation ACOS(P) ACOSD(P)
TAN-1 operation ATAN(P) ATAND(P)
Conversion from angle to radian RAD(P) RADD(P)
Conversion from radian to angle DEG(P) DEGD(P)
Square root SQR(P) SQRD(P)
Exponential operation EXP(P) EXPD(P)
Natural logarithm operation LOG(P) LOGD(P)
Instruction name Instruction symbol
Single precision to double precision conversion ECON(P)
Double precision to single precision conversion EDCON(P)

 Loading...
Loading...











