411
COM
1
2
3
4
4
6
7
8
7.6 Structure creation instructions
7.6.10 COM
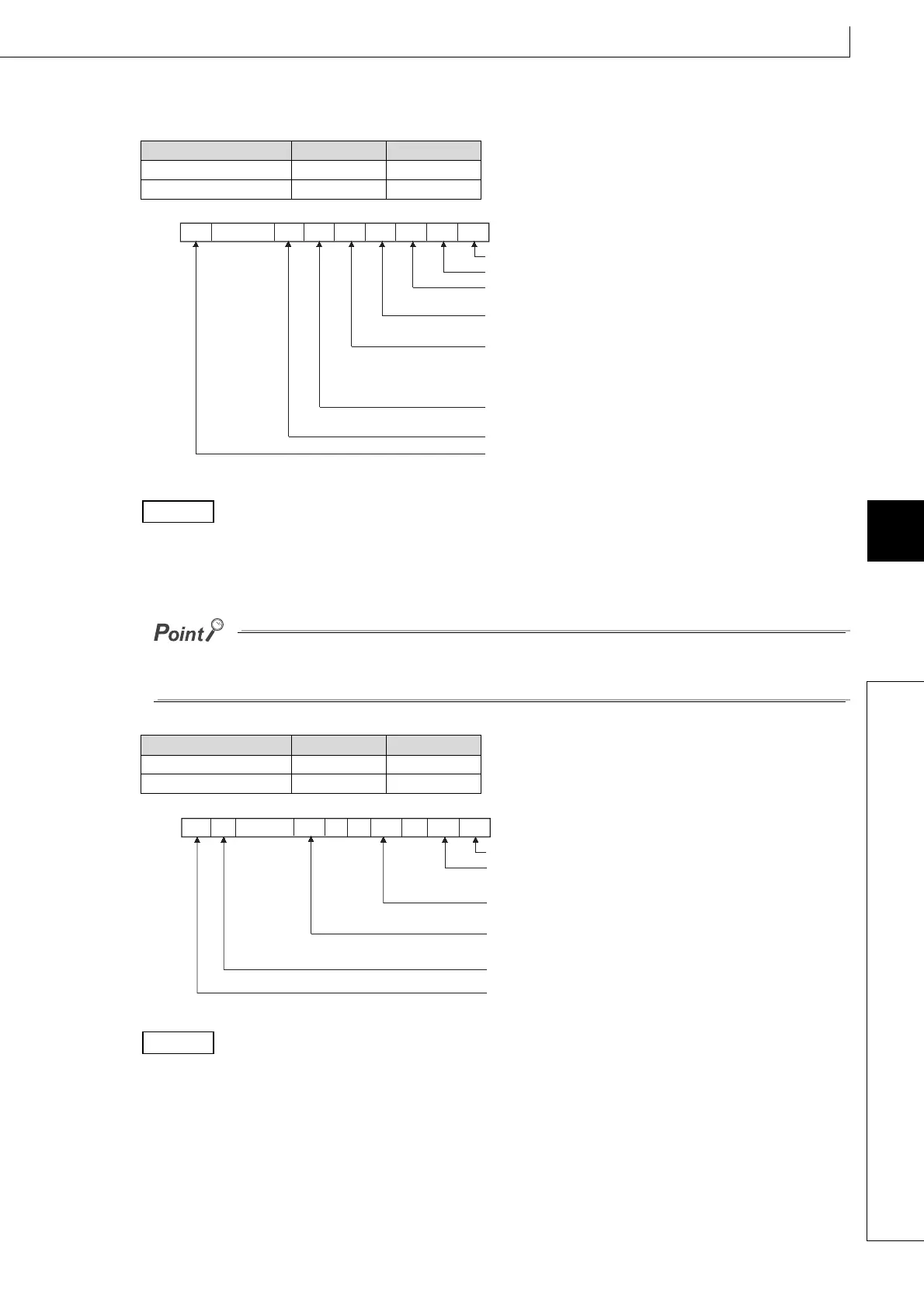
(b) Set an execution status for each processing in SD778.
Set an execution status for each bit of SD778 as shown below.
[ QCPU]
To make only the send/receive processing with the remote I/O station faster, designate MELSECNET/H refresh
only.
(Set only b2 and b15 of SD778 to 1 (SD778: 8004
H
).)
Refresh between the multiple CPUs by the COM instruction is performed under the following condition.
• Receiving operation from other CPUs: When b4 of SD778 (auto refresh in the CPU shared memory) is 1.
• Sending operation from host CPU: When b15 of SD778 (execution status of service processing) is 0.
[ LCPU]
To speed up processing of the display unit only, specify communication with the display unit only. (Write "1" to bits
b14 and b15 of SD778 (SD778:C000
H
).)
Bit of SD778 Executed Not Executed
b0 to b6 1 0
b15 0 1
Bit of SD778 Executed Not Executed
b0, b1, b3, b6, b14 1 0
b15 0 1
b15
b0
b1b2
b3
b4b5b6b14 to
CC-Link IE Controller Network,
MELSECNET/H refresh
1/0 1/01/01/01/01/001/0
SD778
Auto refresh of
intelligent function module
Auto refresh using QCPU standard
area of multiple CPU system
Reading inputs/outputs from the outside
of the multiple CPU system group
Auto refresh using the multiple CPU high speed
transmission area of multiple CPU system
Service processing
(communication with programming tool,
GOT, or other external devices)
I/O refresh
CC-Link refresh
1/0
CC-Link IE Field Network refresh
Example
b15
b0
b1b2
b3
b4b14b13
Auto refresh by intelligent function module
to
001/0 1/0 1/01/0 1/0
SD778
Communication with display unit
Service processing (communication with
programming tool, GOT, or external devices)
I/O refresh
Refresh via CC-Link
1/0 00
b5
b6
Refresh via CC-Link IE Field Network
Example

 Loading...
Loading...











