458
HABIN, HABINP, DHABIN, DHABINP
DHABIN
(1) Converts hexadecimal ASCII data stored in the area starting from the device number designated by into BIN 32-bit
data, and stores it in the device number designated by .
For example, if the ASCII code of 5CB807E1
H
is designated for the area starting from , the operation result would be
stored at +1 and in the following manner:
(2) The ASCII data designated by to +3 can be in the range of from 00000000
H
to FFFFFFFF
H
.
(3) The ASCII codes can be in the range of "30
H
" to "39
H
" and from "41
H
" to "46
H
".
Operation Error
(1) In any of the following cases, an operation error occurs, the error flag (SM0) turns ON, and an error code is stored into
SD0.
Program Example
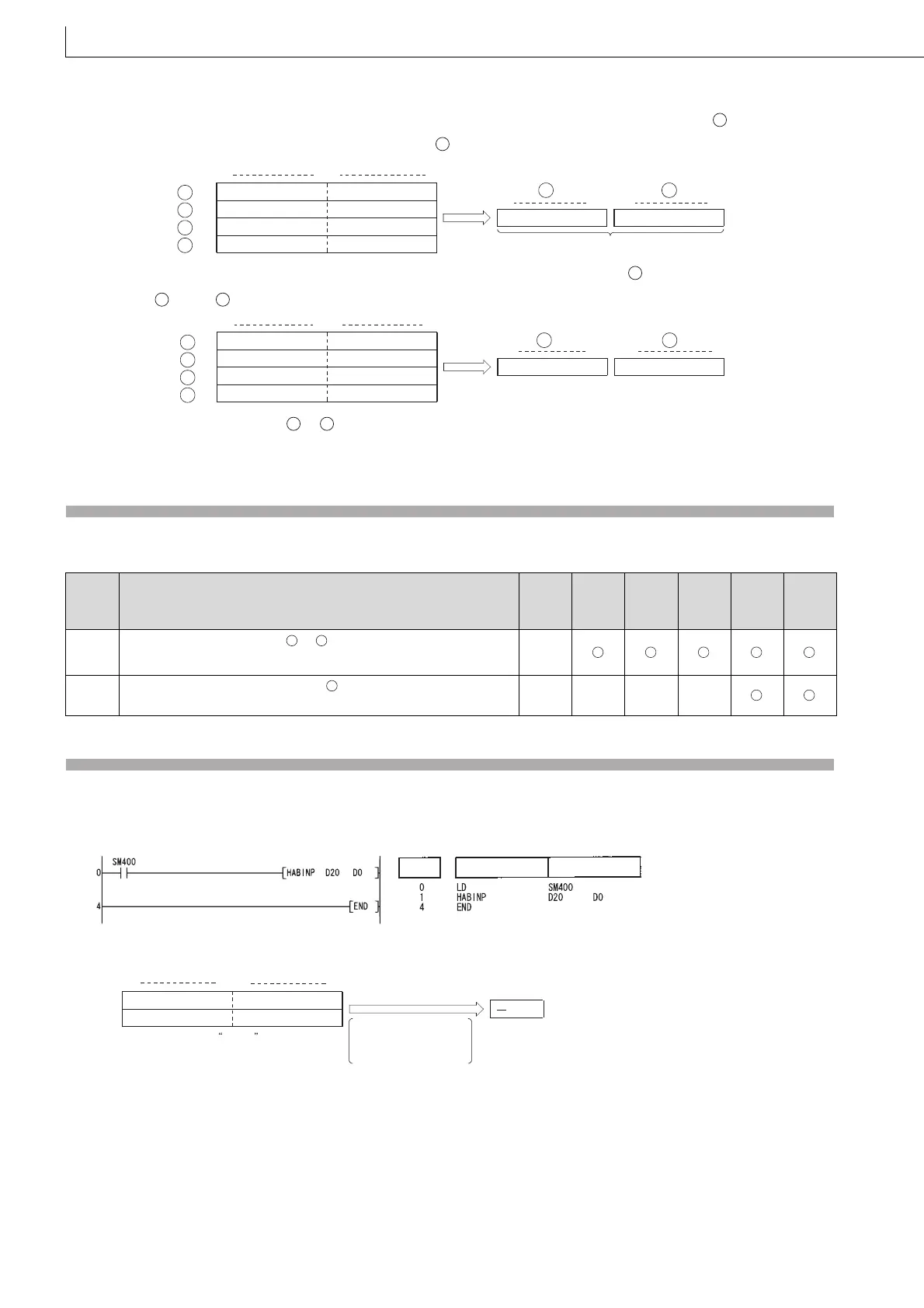
(1) The following program converts the hexadecimal, 4-digit ASCII data set at D20 and D21 to BIN data, and stores the
result at D0.
[Ladder Mode] [List Mode]
[Operation]
Error
code
Error details
Q00J/
Q00/
Q01
QnH QnPH QnPRH QnU LCPU
4100
The ASCII codes specified in to +3 are other than "30
H
" to "39
H
"
and from "41
H
" to "46
H
".
––
4101
The range of the device specified in exceeds the range of the
corresponding device.
–– –– –– ––
S
D
+1
ASCII code for the 8th digitASCII code for the 7th digit
ASCII code for the 6th digitASCII code for the 5th digit
b15 b8b7 b0
+2
ASCII code for the 4th digitASCII code for the 3rd digit
ASCII code for the 2nd digit
ASCII code for the 1st digit
+3
Upper 16 bits Lower 16 bits
BIN 32 bits
+1
b31 b16 b15 b0
S
D
S
S
S
D
S
D D
35
H
(5)43
H
(C)
42
H
(B)38
H
(8)
b8b7 b0
30
H
(0)37
H
(7)
45
H
(E)31
H
(1)
5CB8H 07E1H
+1
b31 b15 b0
D
b15
D
b16
+1
+2
+3
S
S
S
S
S S
S S
S
Step Instruction Device
D21
41
H
(A)36
H
(6)
33
H
(3)46
H
(F)
b8b7 b0
D20
D0
BIN value
22977
A63F
b15
Regarded as A63FH
(-22977 in decimal
value)

 Loading...
Loading...











