General pipe connections
Pipe installation must be carried out in accordance with
current norms and directives.
The system requires a low-temperature design of the
radiator circuit. At lowest dimensioned outdoor tem-
perature (DOT) the highest recommended temperat-
ures are 55 °C on the supply line and 45 °C on the re-
turn line.
Overflow water from the evaporator collection tray
and safety valves goes via non-pressurised collecting
pipes to a drain so that hot water splashes cannot cause
injury. The entire length of the overflow water pipe
must be inclined to prevent water pockets and must
also be frost proof.
NOTE
The pipe system needs to be flushed out be-
fore the heat pump is connected so that any
debris cannot damage component parts.
Maximum boiler and radiator volumes
The volume of the pressure expan-
sion vessel (CM1) is 10 litres and it
is pressurised as standard to 0.5
bar ((5 mvp). As a result, the max-
imum permitted height "H"
between the vessel and the
highest radiator is 5 metres; see
figure.
If the standard initial pressure in
the pressure vessel is not high
enough it can be increased by
adding air via the valve in the ex-
pansion vessel. The initial pressure
of the expansion vessel must be
stated in the inspection document. Any change in the
initial pressure affects the ability of the expansion vessel
to handle the expansion of the water.
The maximum system volume excluding the boiler is
219 litres at the above pre-pressure.
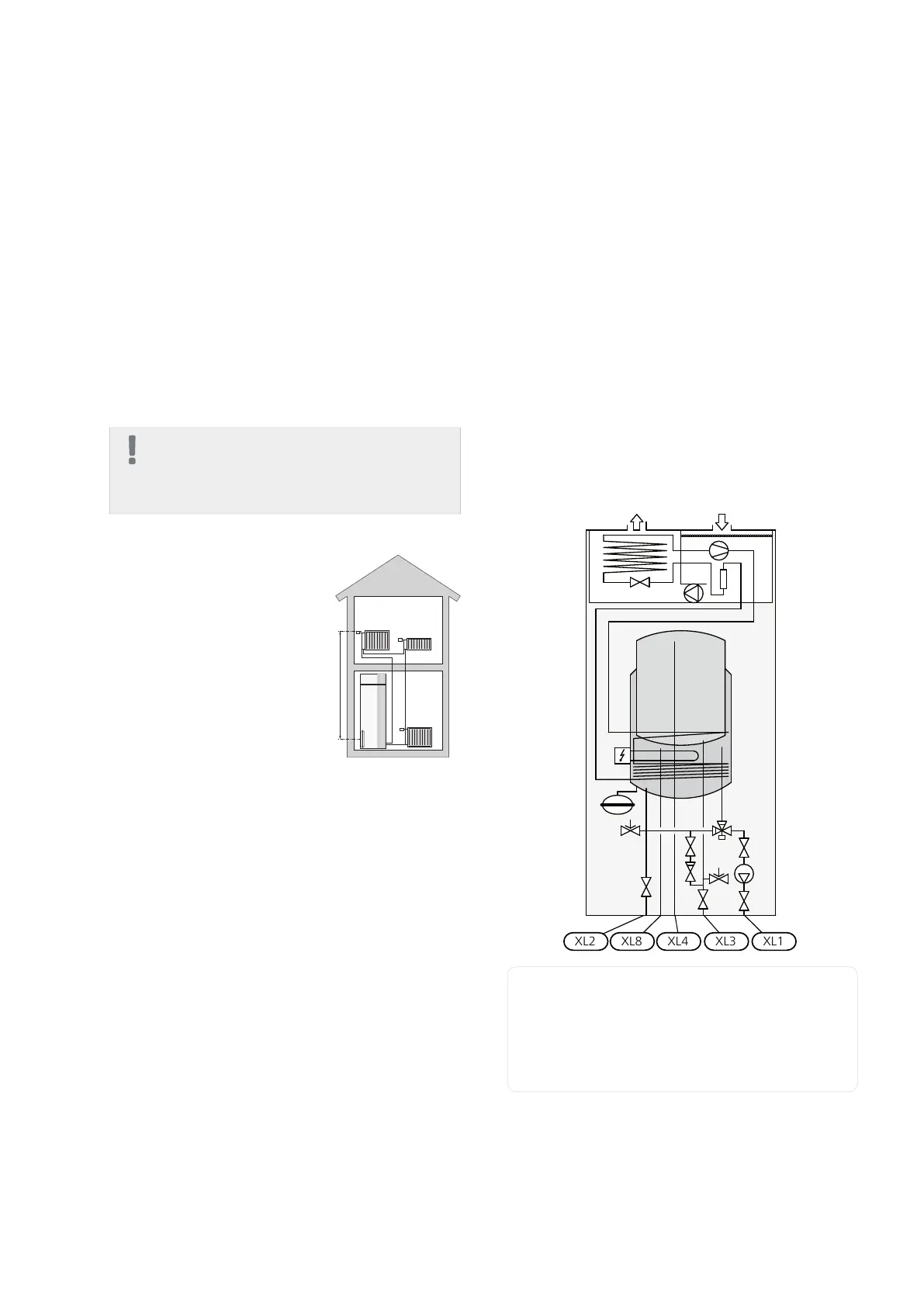
System diagram
F370 consists of a heat pump, water heater, immersion
heater, fan, circulation pump and control system.F370
is connected to the ventilation system and heating
medium circuits.
When the exhaust air at room temperature passes
through the evaporator, the refrigerant evaporates
because of its low boiling point. In this way the energy
in the room air is transferred to the refrigerant.
The refrigerant is then compressed in a compressor,
causing the temperature to rise considerably.
The warm refrigerant is led to the condenser. Here the
refrigerant gives off its energy to the boiler water,
whereupon the refrigerant changes state from gas to
liquid.
The refrigerant then goes via filters to the expansion
valve, where the pressure and temperature are reduced.
The refrigerant has now completed its circulation and
returns to the evaporator.
Connection, heating medium flowXL 1
Connection, heating medium returnXL 2
Connection, cold waterXL 3
Connection, hot waterXL 4
Connection, dockingXL 8
NIBE™ F370Chapter 4 | Pipe and ventilation connections14
4 Pipe and ventilation connections

 Loading...
Loading...