AD3000 5 – MODBUS TCP
NIDEC ASI S.P.A. – AD3000 COMMUNICATION MANUAL
IMAD30007EN 27
5.4.1 Function codes
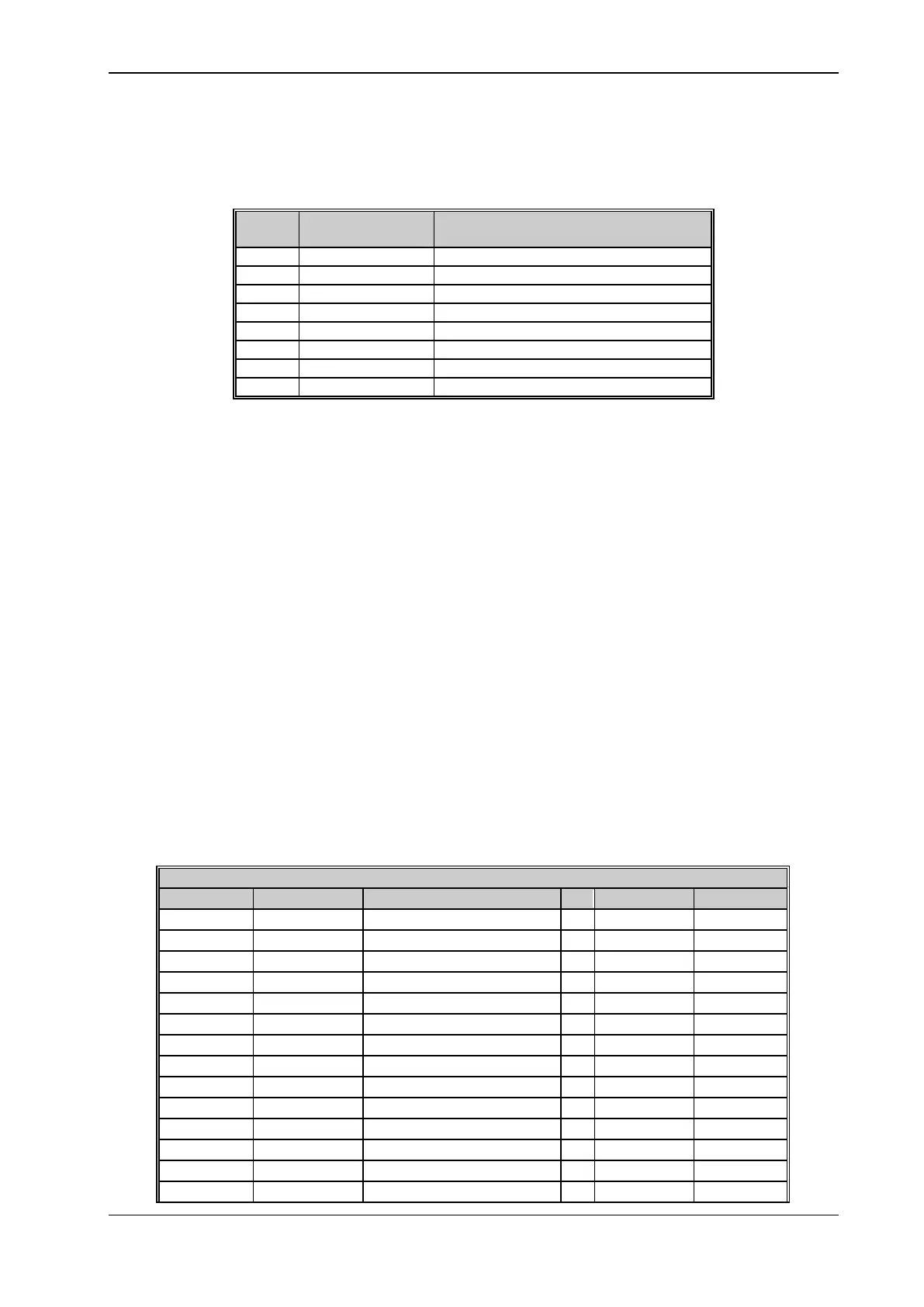
The table below shows the function codes available on the AD3000 drive.
Reading of one or more contiguous bits
Reading of one or more contiguous Holding Registers
Writing of only one Holding Register (single)
Writing of one contiguous group of bits
Writing of one group of Holding Registers (multiple)
Reading of string parameter
Writing of string parameter
Table 5.2 - Available function codes
5.4.2 Read holding register
The function code “Read Holding Register” reads the binary contents of maintenance registers (4XXXX references) in the slave (server). The broadcast
message is not supported.
All process data can be read by using 4+ID number as a Modbus address.
For example, to read Status Wd 1 [52.01] process data, the address will be 45201. For the data scaling refer to chapter 8 of the Programming
Manual.
Note: for some types of masters (client) it may not be necessary to place the number 4 before the ID and/or it may be necessary to set an address
incremented or decremented by 1 with respect to the value of the ID.
5.4.3 Write holding register
The function code “Write Holding Register” writes the binary contents of maintenance registers (4XXXX references) in the slav e. The broadcast
message is not supported.
The process data that can be written is listed in the following table, where the addresses are number 4+ID.
For example, to write Ext Cmd Wd 1 [51.02] process data, the address will be 45102. For the data scaling refer to chapter 8 of the Programming
Manual.
Note: for some types of masters (client) it may not be necessary to place the number 4 before the ID and/or it may be necessary to set an address
incremented or decremented by 1 with respect to the value of the ID.
Positiv e limit of torque reference
Negativ e limit of torque reference
Aux iliary speed reference
Additional speed reference
Reference 1 for Process PID
Feedback 1 for Process PID
Reference 2 for Process PID

 Loading...
Loading...











