SM-Applications Modules & Motion Processors User Guide 97
Issue Number: 4
Safety
Information
Introduction Installation
Getting
Started
Parameters
DPL
Programming
Communications
Freeze and
Marker
CTSync
Inter-option
Synchronization
Diagnostics
Migration
Guide
Quick
Reference
Index
9CTSync
9.1 Overview
Please see Features section on pages 8, 9 & 10 for availability of CTSync on your
Second Processor.
The Second Processor may be used to synchronize two or more drives. This will ensure
that the drives run their internal functions at exactly the same frequency and time
meaning all actions are performed at the same instant.
Also, 3 data values can be passed from one module (the Master) to others (Slaves) on
the CTSync network. This comprises 2 x signed 32bit integers and 1 x Unsigned 8bit
integer.
Only one Second Processor should be configured as the Master and all others
configured as Slaves if they need to participate in the CTSync scheme. The Master
generates reference data which is transmitted to all Slaves on the network. The Master
can be set to operate as a Slave, if for instance two drives need to be synchronized. In
this case the Master will be generating the reference data as well as following that
reference data. The slave will also be following that reference data.
9.2 Connections
CTSync operates via a connection between the EIA-RS485 ports of the Second
Processors on the network in either 2-wire or 4-wire. Refer to section 3.7 EIA-RS485
Connections on page 18 for information on how to connect the SM-Applications
Modules & Motion Processors RS-485 ports.
To simplify wiring the Slave transmit and Master receive signal line connections can be
omitted in 4-wire mode (See Figure 9-1). This is because the Master does not receive a
response from the Slave.
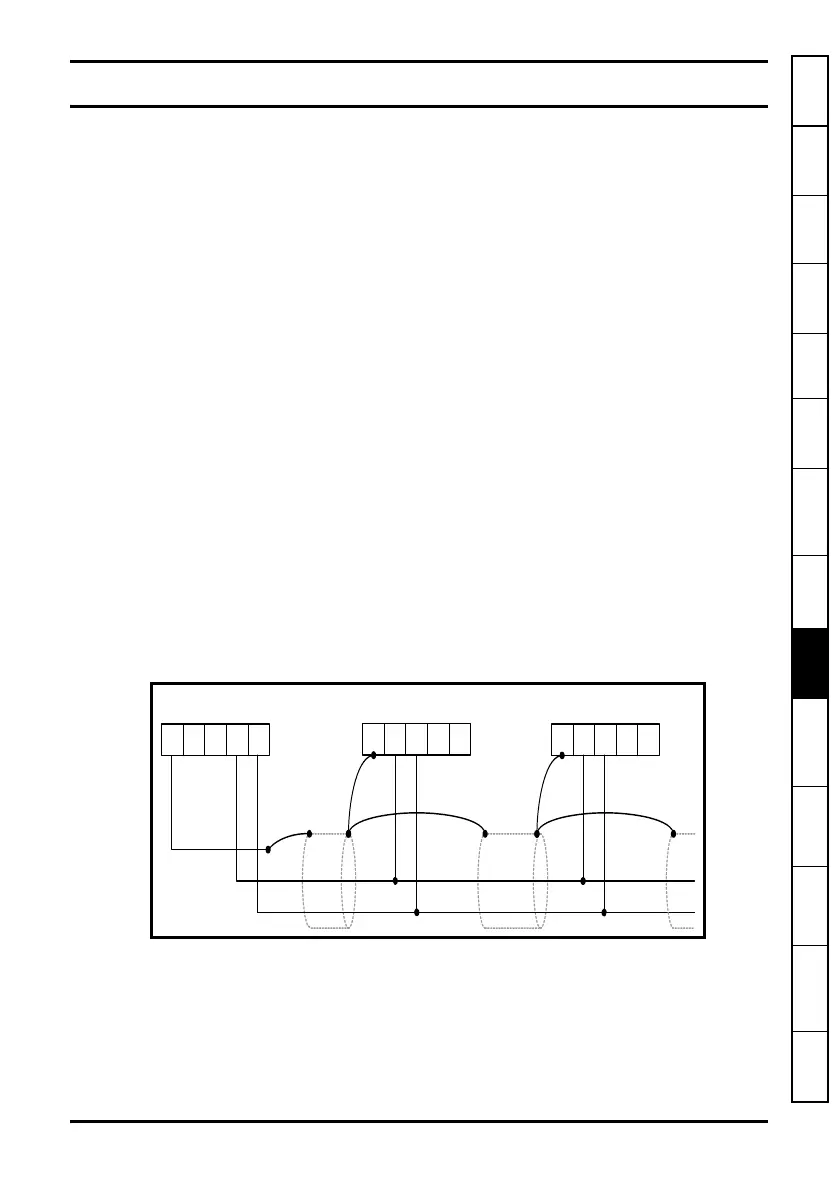
Figure 9-1 CTSync Wiring Example for SM-Applications
0V / Rx Rx / Tx Tx
12345
SM-Appli cati ons Modul e
Sl a ve
Sl a ve
0V / Rx Rx / Tx Tx
12345
Mast er
0V / Rx Rx / Tx Tx
12345
SM-Applicati ons Modul e
SM-Applications Modul e

 Loading...
Loading...