38
Network Configuration Section 2-2
cable alone. Use the following formulae to calculate the max. network length
based on the lengths of thick and thin cable in the line.
L
THICK
: Length of thick cable in the maximum network length
L
THIN
: Length of thin cable in the maximum network length
Example Calculation
L
THICK
+ L
THIN
= 175 m ≥ 100 m 500 kbps not allowed
L
THICK
+ 2.5 × L
THIN
= 250 m ≤ 250 m 250 kbps OK
L
THICK
+ 5 × L
THIN
= 375 m ≤ 500 m 125 kbps OK
The results of the above formulae indicate that 250 kbps and 125 kbps can be
used as the baud rates for this configuration example.
Even when the above conditions are met, however, the current flowing
through the cables must not exceed the permissible current capacity. (Refer to
SECTION 3 Communications Power Supply Methods.)
Applications Requiring
Thin Cable
Thin cable must be used in applications where space is restricted and thick
cable cannot be bent enough. In particular, use thin cable when wiring
devices mounted to DIN Track and the area between the DIN Tracks is limited.
In conclusion, we recommend the following usage:
Baud rate Max. network length
500 kbps L
THICK
+ L
THIN
≤ 100 m
250 kbps L
THICK
+ 2.5 × L
THIN
≤ 250 m
125 kbps L
THICK
+ 5 × L
THIN
≤ 500 m
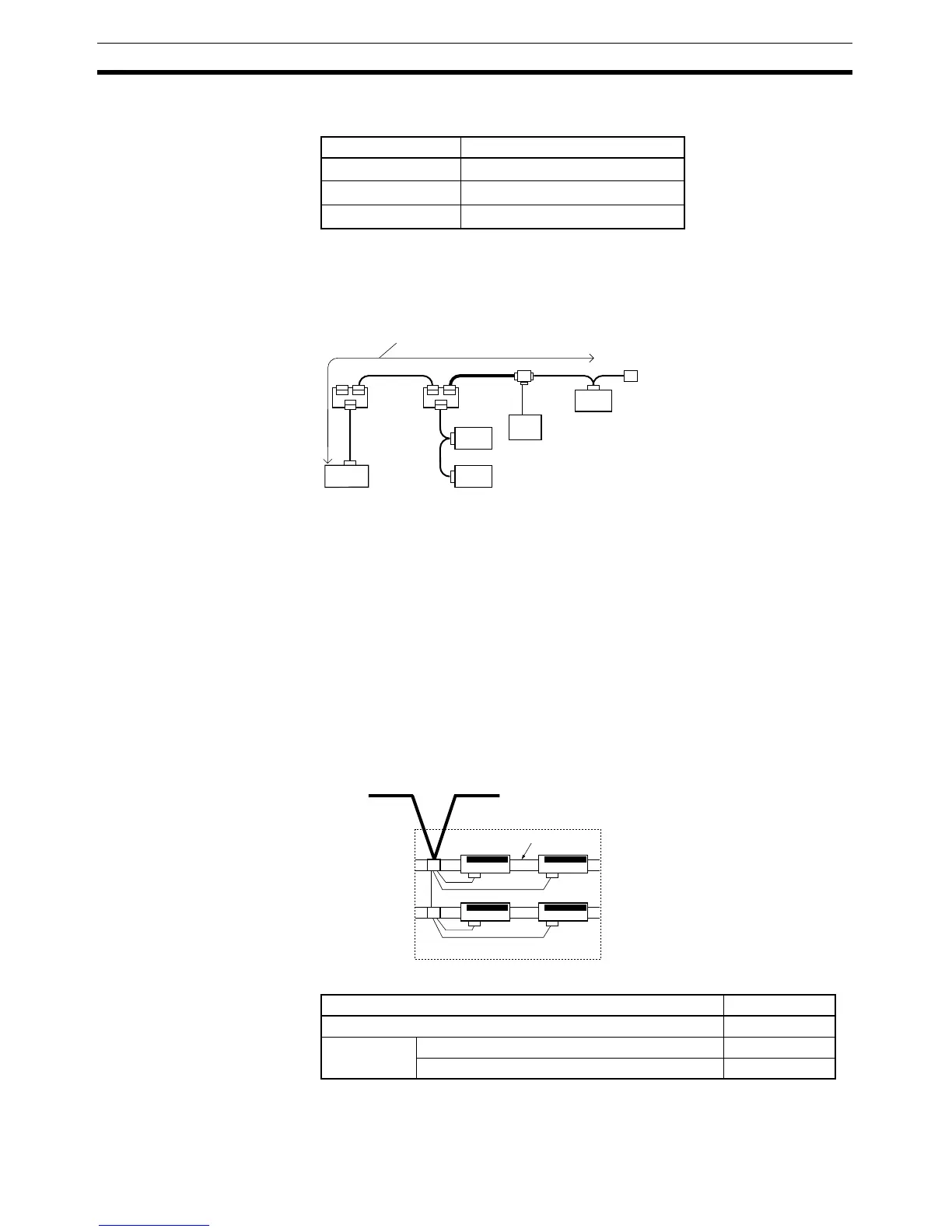
6 m
24 m 125 m 20 m 1 m
Max. network length
Terminal-block
Terminating Resistor
Node
Node
Node
Node
PS
Thick
Thin
Thin Thin
Application Cable type
Trunk line Thick cable
Branch lines Unrestricted spaces such as outside panels Thick cable
Restricted spaces such as within panels Thin cable
Sub-panel
Thin cable
Thin cable
DIN Track
Thick cable
 Loading...
Loading...











