▶
30
Duecanali User Guide
▶
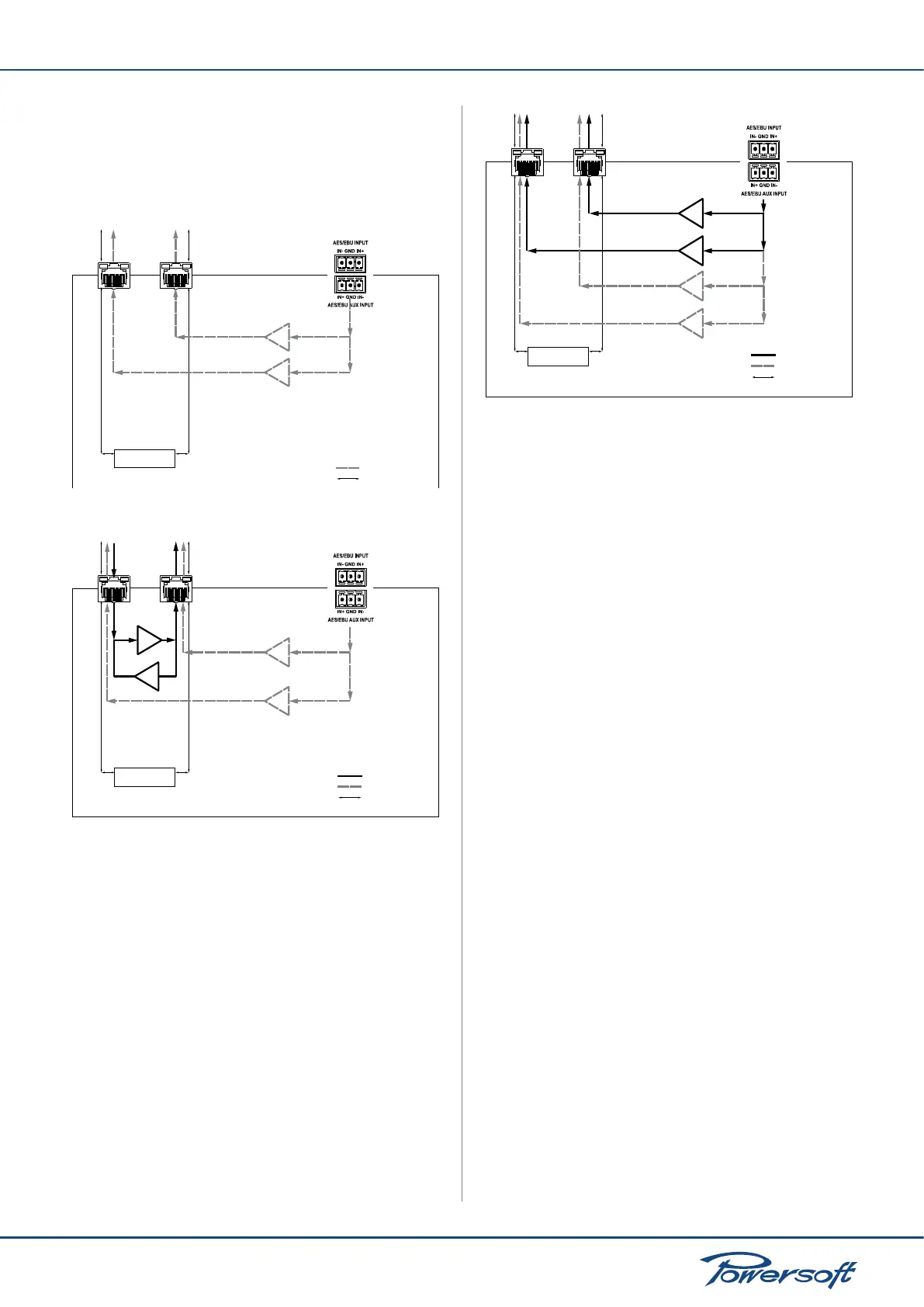
Forward to AES3-B:
the amplier behaves just as in the “forward to AES3-A” mode
but with respect to the AES3-B stream. The AES3 stream coming
from the rear panel Phoenix connector will be routed to the
AES3-B stream on both RJ45 ports 1 and 2. The AES3-A stream,
if present will be repeated from/to RJ45 ports 1 and 2.
AES3-B stream
Control data stream
Port 1 Port 2
Ethernet switch
FIGURE 45: Forward to AES3-B signal path. No AES3-A stream
present
AES3-A stream
AES3-B stream
Control data stream
Port 1 Port 2
Ethernet switch
FIGURE 46: Forward to AES3-B signal path and simultaneous AES3-A
stream in repeater mode.
▶
Forward to both:
the amplier’s rear panel AES input via the Phoenix connector will
be routed to both AES3 stream A and AES3 stream B on both
main ports 1 and 2. Repeater functionality will be disabled.
AES3-A stream
AES3-B stream
Control data stream
Port 1 Port 2
Ethernet switch
FIGURE 47: AES3 stream coming from the rear Phoenix stream is
routed to both AES3 streams A and B via the master RJ45 ports.
IMPORTANT: when an amplier is set to forward the Phoenix
AES3 signal to either the AES3-A or AES3-B stream, the
amplier can accept as the sole AES3 input signal the one coming
from the Phoenix connector. The RJ45 ports cannot, when the
amplier is in forwarding mode on both streams, input an AES3
signal to the amplier.
9.2 Network robustness
Duecanali Series ampliers equipped with a KAESOP are capable
of being connected each to the other via a network: using a single
sound source, each amplier in the network can be, for example,
dedicated to providing power audio signal to a given subsection
of a large venue. In dealing with networks of ampliers, one of
the most important aspects to consider, especially when working
in a critical application such as large venue sound distribution, is
the robustness of the network itself. Data and audio connections
can be made “fault proof”: this means that if for some reason
one audio or data connection should fail, the whole system is not
compromised. The degree of redundancy expresses how many
network connections can break before sound is interrupted in
any one amplier part of the system. A “zero degree” redundant
system is not robust: the rst connection to jump (either from a
cable failure or even from an amplier problem) means the whole
system goes down. A “one degree” redundancy system, on the
other hand, will continue working automatically if one (but no
more than one) connection fails. This happens because Duecanali
Series ampliers can sense a connection failure and automatically
(and almost instantaneously) invert the audio feed direction to
allow the source signal to remain uninterrupted.
The following section illustrates and analyzes some common
amplier networks divided by redundancy degrees.
9.3 Network connections
▶
Daisy chain
The following diagrams show a daisy chain connection of 4
ampliers.

 Loading...
Loading...











