PCMx Operation Manual
© 2021 Radiodetection Ltd 27
Theory and
Application
This section demonstrates measurement taking and
possible results from surveying various pipe
systems.
7.1 Basic technique
‘Tie-ins’ and Loops
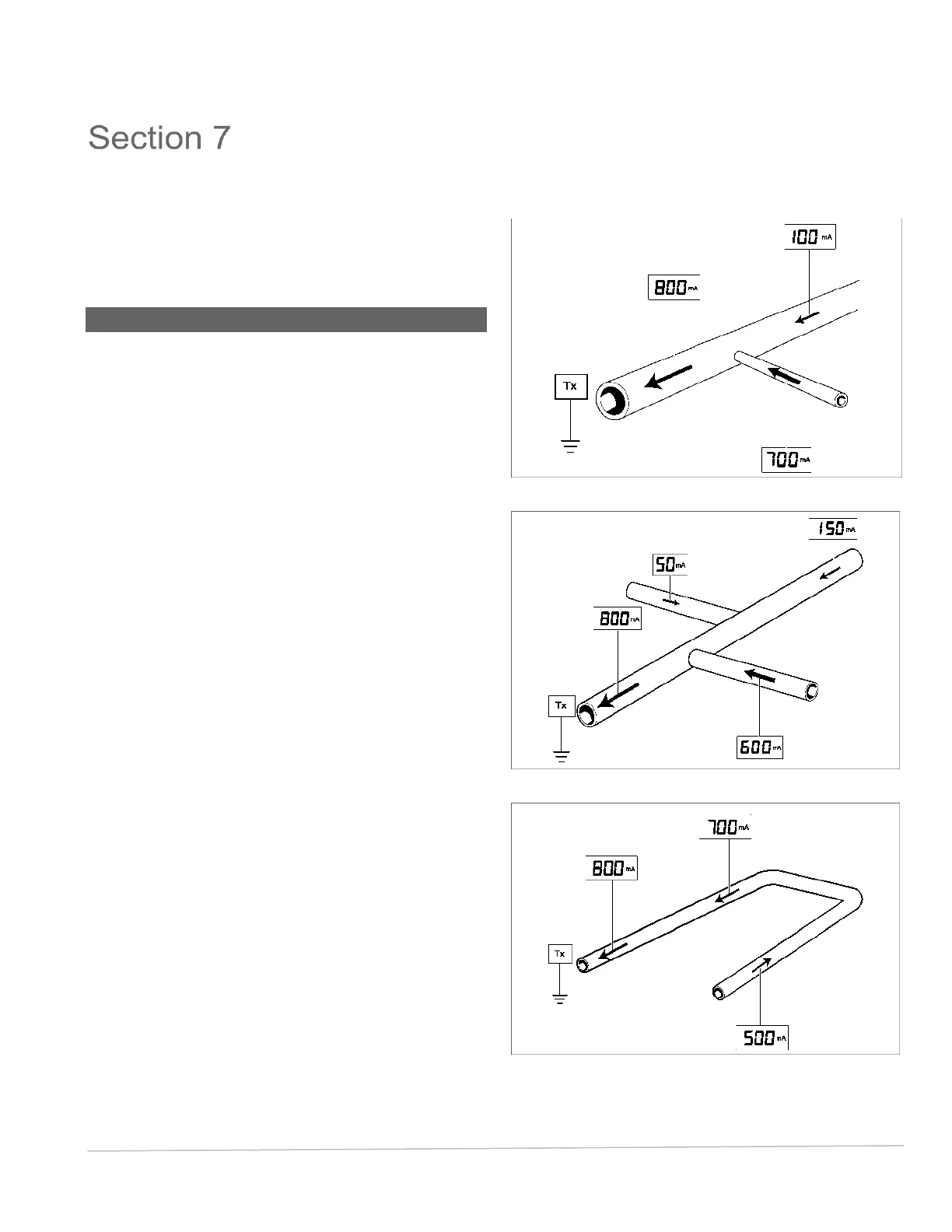
Fig 7.1 shows current split between two lines.
i.e. 800 = 700 + 100
The pipeline with the greatest reading indicates where the
majority of current is flowing from and is the direction to
follow in order to locate the fault (short or poor coating).
Fig 7.2 shows current split between three lines.
i.e. 800 = 600 + 150 + 50
The pipeline with the greatest reading indicates where the
majority of current is flowing from and is the direction to
follow in order to locate the fault (short or poor coating).
Loops
If the current arrow changes direction it could indicate the
pipe has changed location. Use the PCMx in locate mode
to relocate it – see Fig 7.3.
Current flow within a Loop system
If all distances and coatings are equal, and the rate of loss is
constant, the current measured at Point A will be zero – see
Fig 7.4.
In practice, with pipes of different ages and coating the points
reading zero (0) could be anywhere. The respective current
readings will indicate the direction to follow – see Fig 7.5.
Fig. 7.1: Tie line 1
Fig. 7.2: Tie line 2
Fig. 7.3: Loop

 Loading...
Loading...










