1. Scope
The PC·1600 has been designed with the following versatile
features:
1. The most of PC·1500 BASIC software and the PC·1500
hardware options are compatible with the PC·1600,
2. Advanced technology gives the PC·1600 new features
not available on the PC·1500.
1-1. Compatibility with the PC-1500 BASIC
simulation mode
For compatibility with succeeding models, most of soft-
ware created in BASIC for the PC·1500 can also run on the
PC·1600.
(a) For display in the simulation mode, a single line on the
bottom of the display rows is subject for execution.
(b) In the simulation mode, the same character codes of
the PC-1500 are used.
(c) The PC·1600 must work with a variety of PC·1500
software programs that include an option control-
ling system, and the PC·1600 system bus signals are
upper grade compatible with the PC·1500 system bus.
(Consideration is given for the use of the CE·150, 158,
and 162E.)
(d) The slot signals are also upper grade compatible; th is
allows the use of the PC·1500 memory module on
-the PC·1600.
2. Specifications
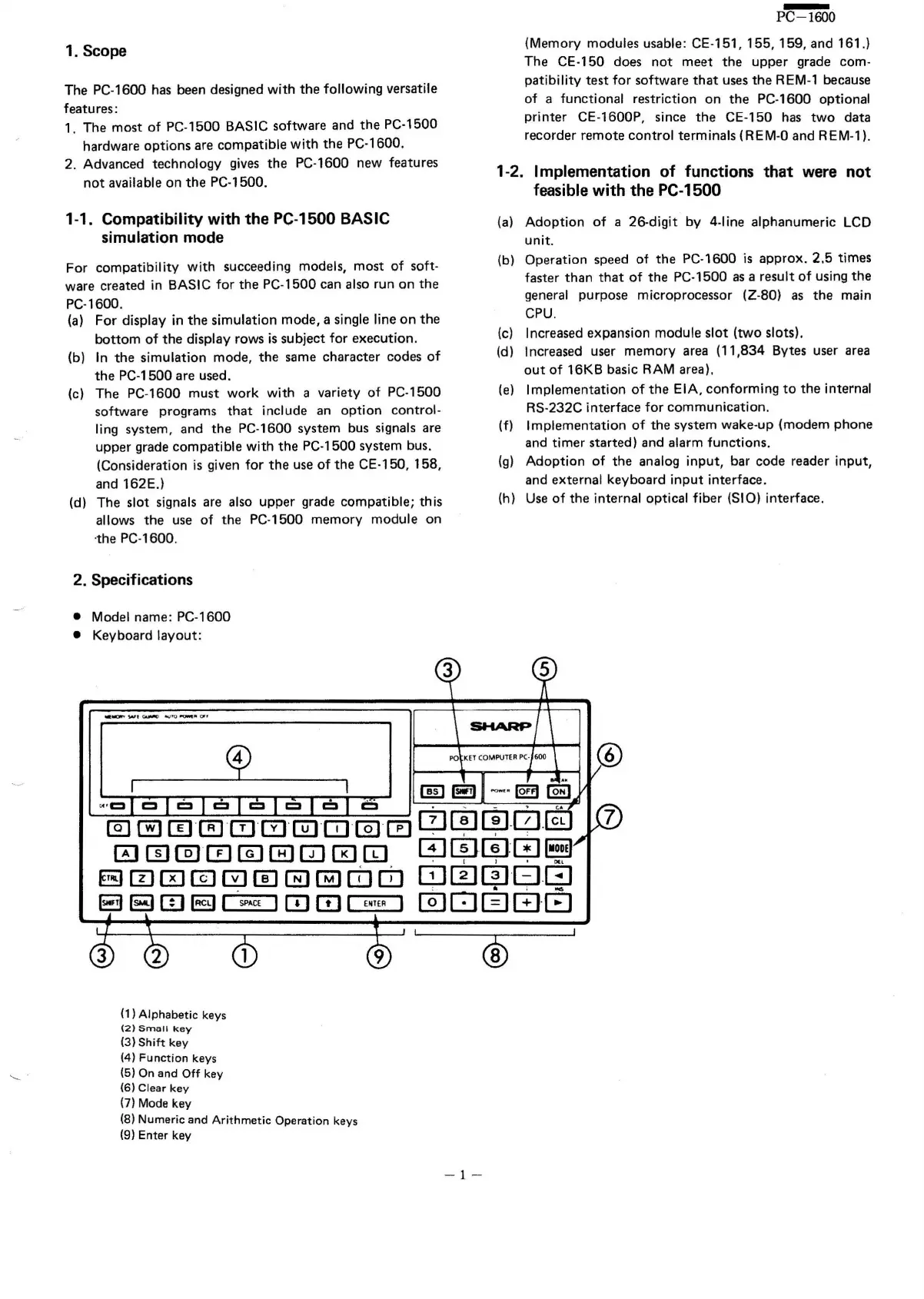
• Model name: PC·1600
• Keyboard layout:
-
PC-1600
(Memory modules usable: CE·151, 155, 159, and 161.)
The CE·150 does not meet the upper grade corn-
patibility test for software that uses the REM-1 because
of a functional restriction on the PC·1600 optional
printer CE·1600P, since the CE·150 has two data
recorder remote control terminals (REM·O and REM·1).
1-2. Implementation of functions that were not
feasible with the PC·1500
(a) Adoption of a 26-digit by 4·line alphanumeric LCD
unit.
(b) Operation speed of the PC·1600 is approx. 2.5 times
faster than that of the PC·1500 as a result of using the
general purpose microprocessor (Z·80) as the main
CPU.
(c) Increased expansion module slot (two slots).
(d) Increased user memory area (11,834 Bytes user area
out of 16KB basic RAM area),
(e) Implementation of the EIA, conforming to the internal
RS·232C interface for communication.
(fl Implementation of the system wake-up (modem phone
and timer started) and alarm functions.
(g) Adoption of the analog input, bar code reader input,
arid external keyboard input interface.
(h) Use of the internal optical fiber (SIO) interface.
(1) Alphabetic kevs
(2) Small key
(3)
Shift key
(4) Function keys
(5) On and Off key
(6) Clear key
(7) Mode key
(8) Numeric and Arithmetic Operation keys
(9) Enter key
-1-
 Loading...
Loading...