Basics of program execution
10.3 Events and OBs
S7-1500R/H redundant system
328 System Manual, 01/2024, A5E41814787-AF
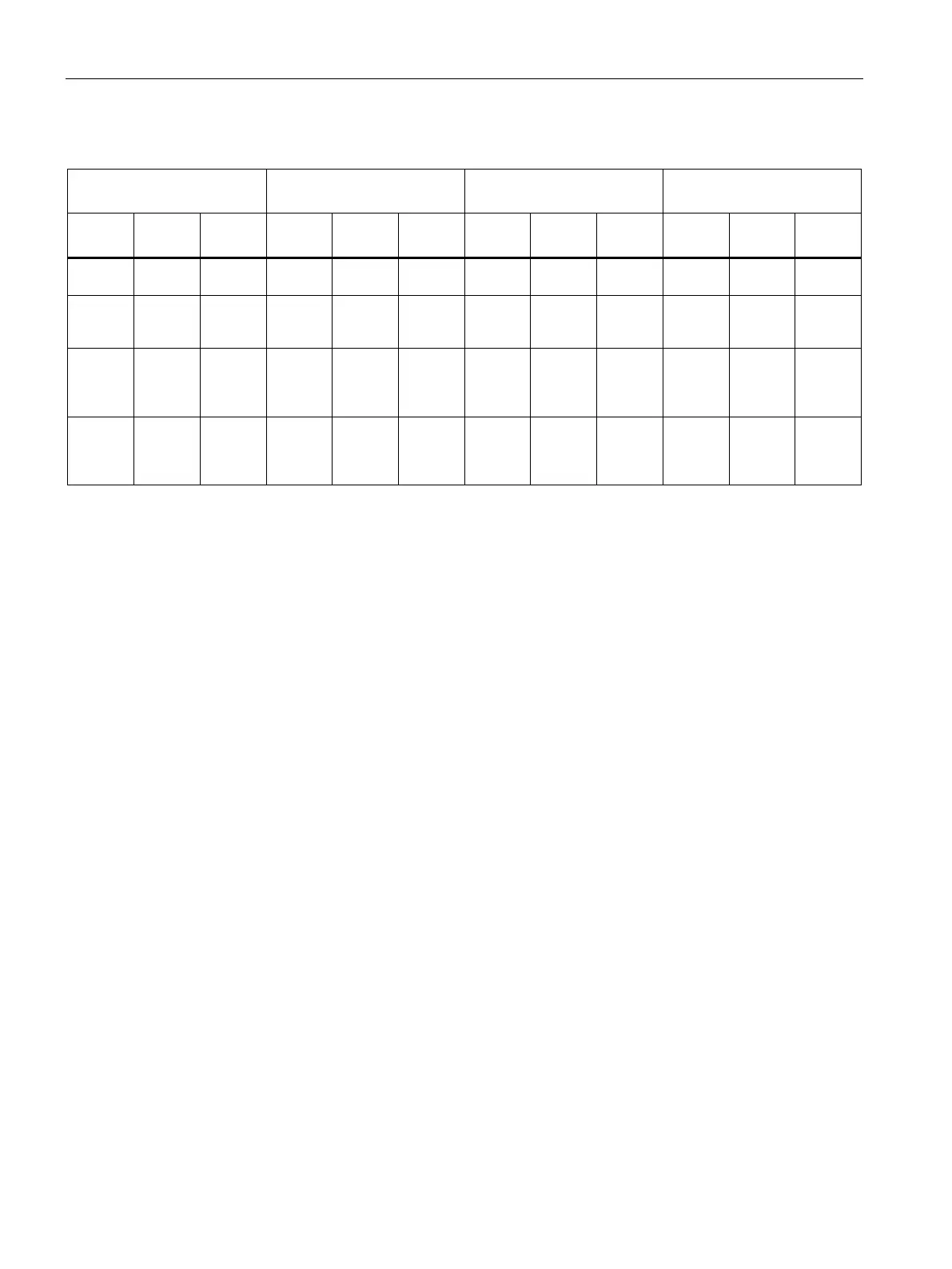
Table 10- 5 Response of S7-1500R/H redundant system when cycle time is exceeded with OB 80
Initial situation 1st time cycle time is ex-
2nd time cycle time is ex-
3rd time cycle time is ex-
System Primary
Backup
System Primary
Backup
System Primary
Backup
System Primary
Backup
1)
Syncup
Syncup
2)
Syncup
Syncup
+ OB 80
+ OB 80
Solo
+ OB 80
Redun-
dant
Redun-
dant
Redun-
dant
Redun-
dant
Redun-
dant
Redun-
dant
Solo
+ OB 80
1)
SYNCUP until snapshot of the work memory contents
2)
SYNCUP after snapshot of the work memory contents
Assignment between event source and OBs
The type of OB determines where you assign OB to event source:
• For hardware interrupts: Assignment in hardware configuration
• For all other OB types: Assignment when the OB is created, where applicable after you
have configured the event source
OB priority and runtime behavior
If you have assigned an OB to the event, the OB has the priority of the event. S7-1500R/H
CPUs support the priorities 1 (lowest) to 26 (highest). The following items are essential to the
execution of an event:
• Call and execution of the assigned OB
• The update of the process image partition of the assigned OB
The user program processes the OBs exclusively on a priority basis. This means the program
processes the OB with the highest priority first when multiple OB requests occur at the same
time. If an event occurs that has a higher priority than the currently active OB, this OB is
interrupted*. The user program processes events of the same priority in order of occurrence.

 Loading...
Loading...