Functions
2.1 General
SIPROTEC, 7SJ62/64, Manual
C53000-G1140-C207-2, Release date 01.2008
58
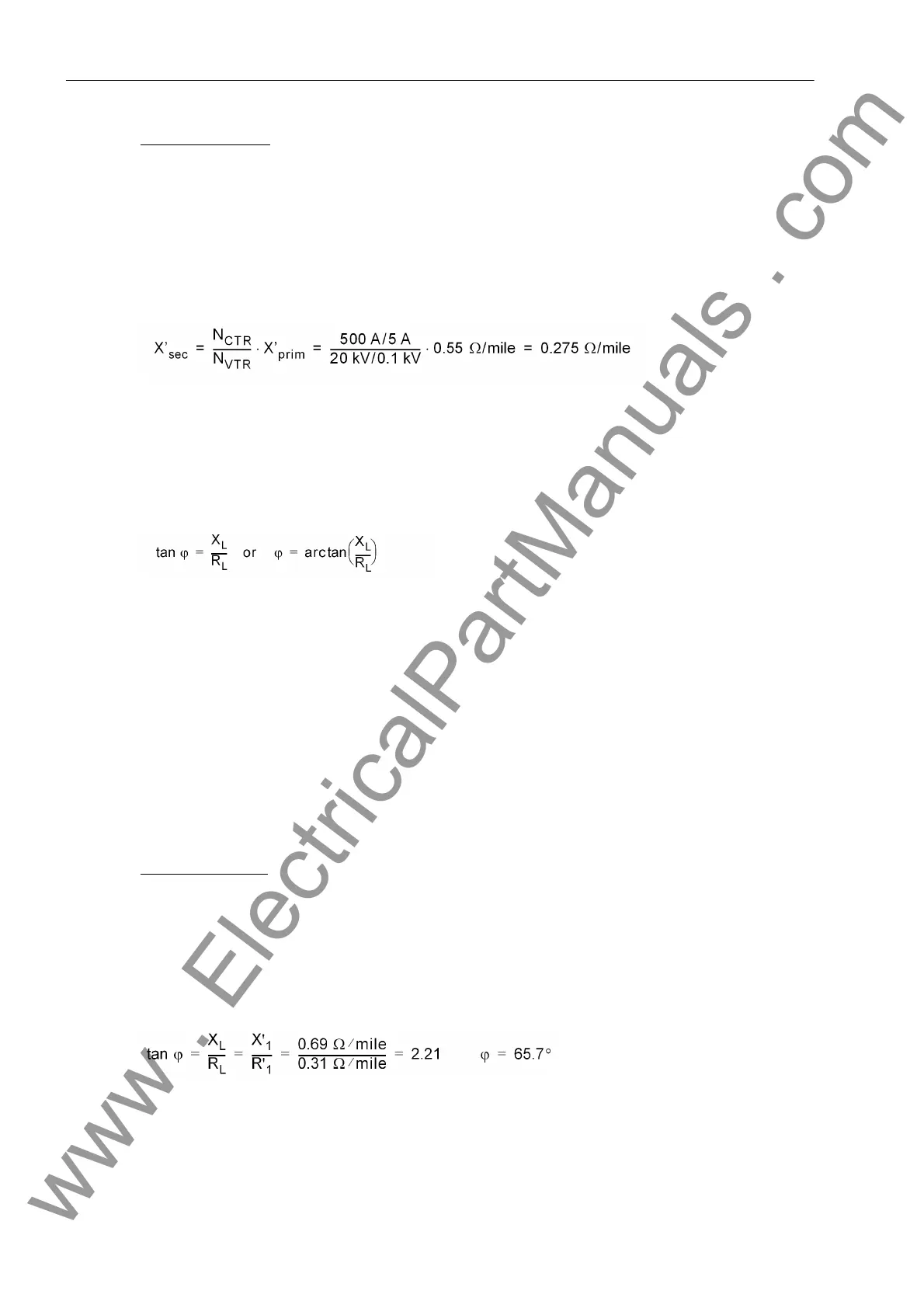
Calculation example:
In the following, the same line as illustrated in the example for ground impedance ratios (above) and additional
data on the voltage transformers will be used:
Current Transformers 500 A/5 A
Voltage Transformers 20 kV / 0.1 kV
The secondary reactance per unit length is calculated as follows:
Line Angle (only for Fault Location)
The setting of the line angle is only important for the utilization of the line fault location function. The line angle
can be derived from the line constants. The following applies:
with R
L
being the ohmic resistance and X
L
being the reactance of the line.
The value under address 1109 applies if only one line section is available and to all faults that occur outside
the defined line sections.
If several line sections are set, the following shall apply:
• for line section 1, address 6005
• for line section 2, address 6015
• for line section 3, address 6025
This data can be used for the entire line or line section, or as distance-related values, since the quotients are
independent of the distance. It is also irrelevant whether the quotients were derived from primary or secondary
values.
Calculation Example
:
110 kV free line 150 mm
2
with the following data:
R'
1
= 0.31 Ω/mile
X'
1
= 0.69 Ω/mile
The line angle is calculated as follows:
The respective address must be set to Line angle = 66°.
www . ElectricalPartManuals . com

 Loading...
Loading...











