4 IR COMP/RPC
4.1
{IR COMP}
»
The remote
commands are CT/ for selecting feedback or sampled and
CC/
for
selecting
IR COMP on/off. Refer
to
Chapter
4,
Section 6.8.
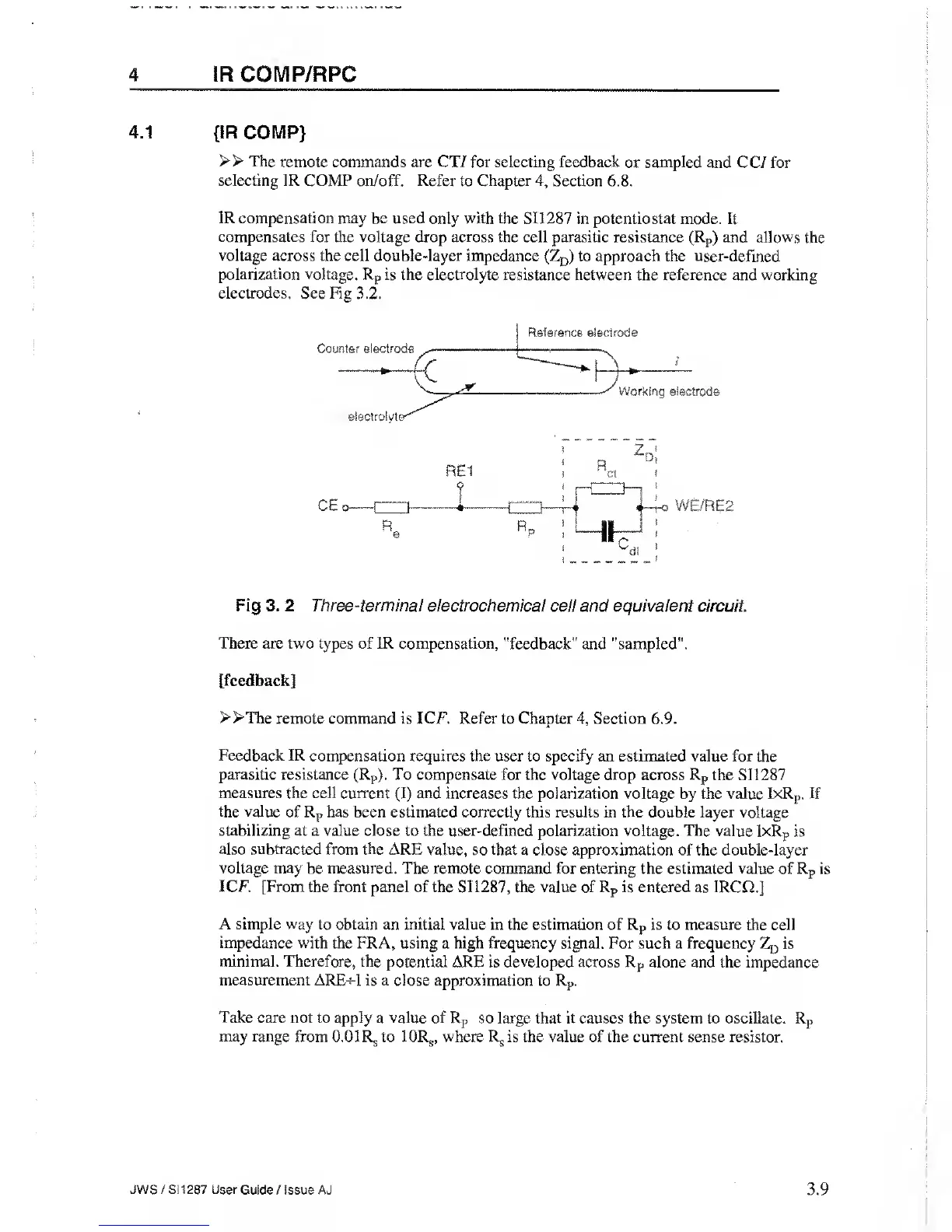
IR
compensation may be used only with the SI1287 in
potentiostat mode. It
compensates for the voltage
drop
across
the cell parasitic resistance (R
p
)
and allows
the
voltage
across the cell double-layer impedance (Z
D
)
to approach the
user-defined
polarization voltage. R
P
is the electrolyte
resistance between the reference and working
electrodes.
See Fig 3.2.
Fig 3. 2 Three-terminal
electrochemical cell and equivalent circuit.
There are two
types of IR compensation, "feedback" and "sampled".
[feedback]
>>The remote
command is IGF. Refer to Chapter
4,
Section 6.9.
Feedback IR compensation requires
the user to specify an estimated
value
for the
parasitic resistance
(R
p
).
To compensate for the voltage drop across R
p
the
SI1287
measures the cell current
(I)
and increases
the polarization
voltage
by the
value IxR
p
. If
the value
of
R
P
has been estimated correctly this results in the double layer voltage
stabilizing
at a value close to the user-defined polarization voltage.
The
value IxR
p
is
also subtracted from the ARE
value, so that a close approximation of the double-layer
voltage
may be measured. The remote command for entering the estimated value
of R
p
is
ICF. [From the front panel of the SI1287, the value of
R
p
is entered as IRCQ.]
A simple way
to obtain an initial value in the estimation of R
P
is
to
measure
the cell
impedance with the FRA, using
a
high frequency
signal. For such a frequency Z
D
is
minimal. Therefore, the
potential ARE is
developed
across
R
p
alone and the impedance
measurement ARE-s-I
is a close approximation to R
p
.
Take care not to apply
a
value of
R
p
so large that it causes the system to oscillate. R
p
may range
from 0.01 R
s
to 1 0R
S
,
where
R
s
is the value of the current sense resistor.
JWS /
SI
1287 User
Guide ! Issue AJ
3.9
 Loading...
Loading...