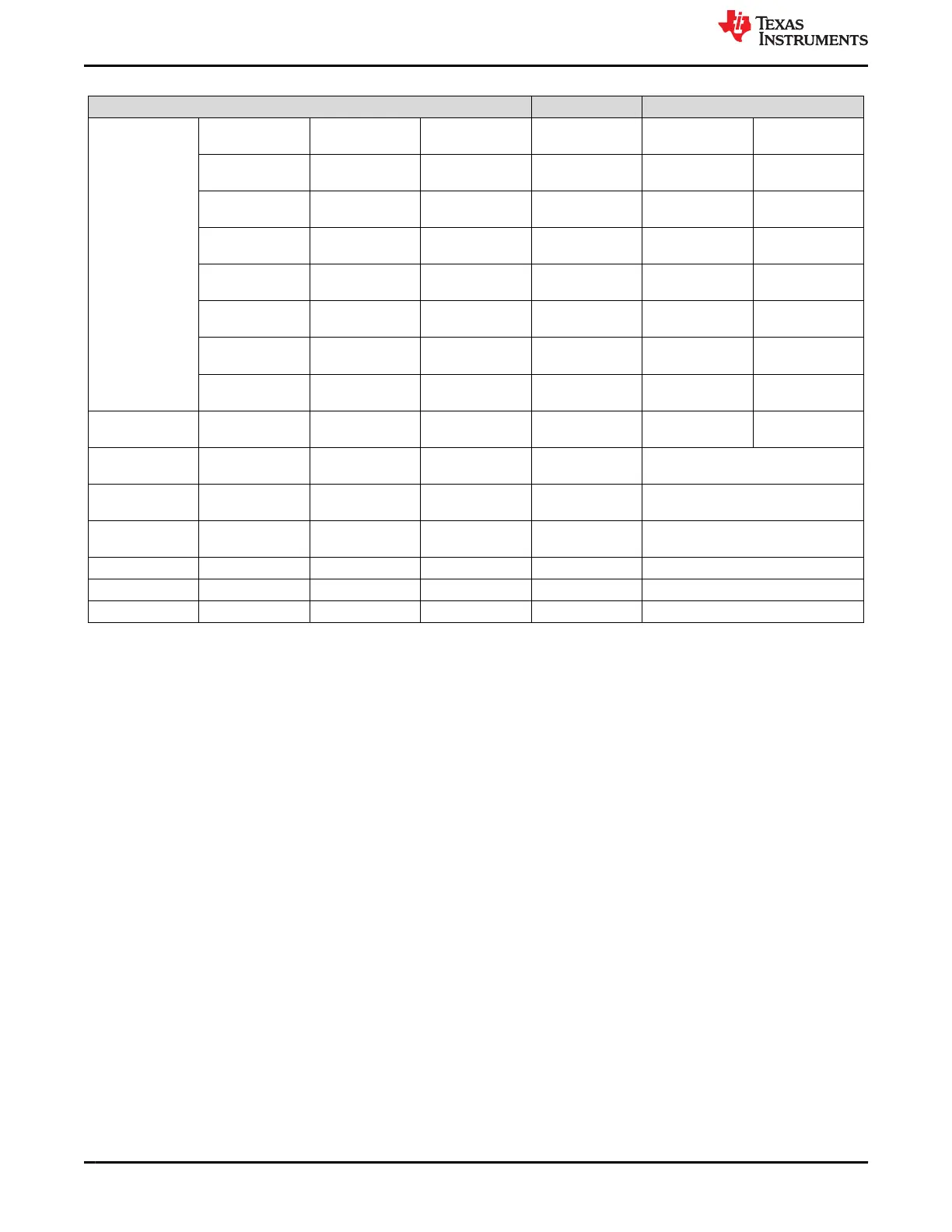
Table 4-2. Power Monitoring Safety Features (continued)
ASIL-B ASIL-D Adds
TPS65941421-Q1
(PMIC-B)
BUCK1 VDD_IO_1V8 SOC PMIC-B - OV &
UV
PMIC-B -CM PMIC-B -RVM
BUCK3 VDD_PHY_1V8 SOC PMIC-B - OV &
UV
PMIC-B -CM PMIC-B -RVM
BUCK4 VDD_DDR_1V1 SOC PMIC-B - OV &
UV
PMIC-B -CM PMIC-B -RVM
BUCK5 VDD_RAM_0V85 SOC PMIC-B - OV &
UV
PMIC-B -CM PMIC-B -RVM
LDO1 VDD_WK_0V8 SOC PMIC-B - OV &
UV
PMIC-B -CM PMIC-B -RVM
LDO2 VDD_GPIORET_3
V3
SOC PMIC-B - OV &
UV
PMIC-B -CM PMIC-B -RVM
LDO3 VDA_DLL_0V8 SOC PMIC-B - OV &
UV
PMIC-B -CM PMIC-B -RVM
LDO4 VDA_PLL_1V8 SOC PMIC-B - OV &
UV
PMIC-B -CM PMIC-B -RVM
LP876411B5-Q1 BUCK1-4 VDD_CORE_0V8 SOC PMIC-C - OV &
UV
PMIC-C -CM PMIC-C -RVM
TPS22965-Q1 Ld Sw A VDD_MCUIO_3V3 MCU PMIC-A (FB_B3) -
OV & UV
(5)
NA
(3)
(4)
TPS22965-Q1 Ld Sw B VDD_IO_3V3 SOC PMIC-C (FB_B4) -
OV & UV
(5)
NA
(3)
(4)
TLV3318P-Q1 LDO-A VDD1_DDR_1V8 SOC PMIC-C (FB_B3)
-OV & UV
(5)
NA
TLV7103318-Q1 LDO-B VDD_SD_DV None NA
(2)
NA
(2)
TLV73333P-Q1 LDO-C VDDA_3P3_USB None NA
(2)
NA
(2)
TLV73318P-Q1 LDO-D VDD_EFUSE_1V8 None NA
(2)
NA
(2)
(1) Rail Group settings for the TPS65941120-Q1, TPS65941421-Q1 and LP876411B5-Q1 are found in Table 5-7.
(2) Power rails VDDSHV5, VPP_CORE, VPP_MCU, VDDA_3P3_USB, and VDD1_LPDDR4_1V8 are not safety critical.
(3) Power rails VDD_IO_1V8/3V3 are typically not safety critical since other means are available (for example, black-channel checkers) to
provide diagnostic coverage to detect faults in SoC signaling interfaces (for example, CAN, UART, and SPI).
(4) If an SoC GPIO control signal is used in a safety critical interface, then adding voltage and current monitoring to specific VIO power rail
may be needed per customer's end product design.
(5) PMIC-C, Buck3 and 4 have unused remote sense feedback inputs that can be assigned to provide OV and UV voltage monitoring
after SoC SW boot for 2x external power rails per desired functional safety needs. Optional OV/UV monitoring of VDD_DDR_1V1 and
VDD_IO_3V3 power rails are examples.
5 Static NVM Settings
The TPS6594-Q1 and LP8764-Q1 devices consist of user register space and an NVM. The settings in NVM,
which are loaded into the user registers during the transition from INIT to BOOT BIST, are provided in this
section. Note: The user registers can be changed during state transitions, such as moving from STANDBY to
ACTIVE mode. The user register map is described in the TPS6594-Q1 and LP8764-Q1 data sheets.
5.1 Application-Based Configuration Settings
In the TPS6594-Q1 data sheet, there are seven application-based configurations for each BUCK to operate
within. The following list includes the different configurations available:
• 4.4 MHz VOUT Less than 1.9 V, Multiphase or High COUT Single Phase
• 2.2 MHz Single Phase for DDR Termination
• 4.4 MHz VOUT Less than 1.9 V, Low COUT, Single Phase Only
• 4.4 MHz VOUT Greater than 1.7 V, Single Phase Only
• 2.2 MHz Full VOUT Range and VIN Greater than 4.5 V, Single Phase Only
• 2.2 MHz VOUT Less than 1.9 V Multiphase or Single Phase
• 2.2 MHz Full VOUT and Full VIN Range, Single Phase Only
In the LP8764-Q1 data sheet, there are also seven application-based configurations:
• 4.4MHz Single-Phase and Multi-Phase Configuration
Static NVM Settings www.ti.com
14 TPS65941120-Q1, TPS65941421-Q1 and LP876411B5-Q1 PMIC User Guide
for J721S2, PDN-0A
SLVUCJ9 – FEBRUARY 2023
Submit Document Feedback
Copyright © 2023 Texas Instruments Incorporated

 Loading...
Loading...











