UHP SCPC MODEM
USER MANUAL, v3.2
© ROMANTIS 2015 36 www.uhp.net
Beam diameter in degrees (10) or in miles (10m) or in kilometers (10k);
EIRP value in range of 0-100.
6.4 Interaction with Mobile Antenna Controller
Configuration of the interface between UHP router and the mobile antenna controller is centralized in a special
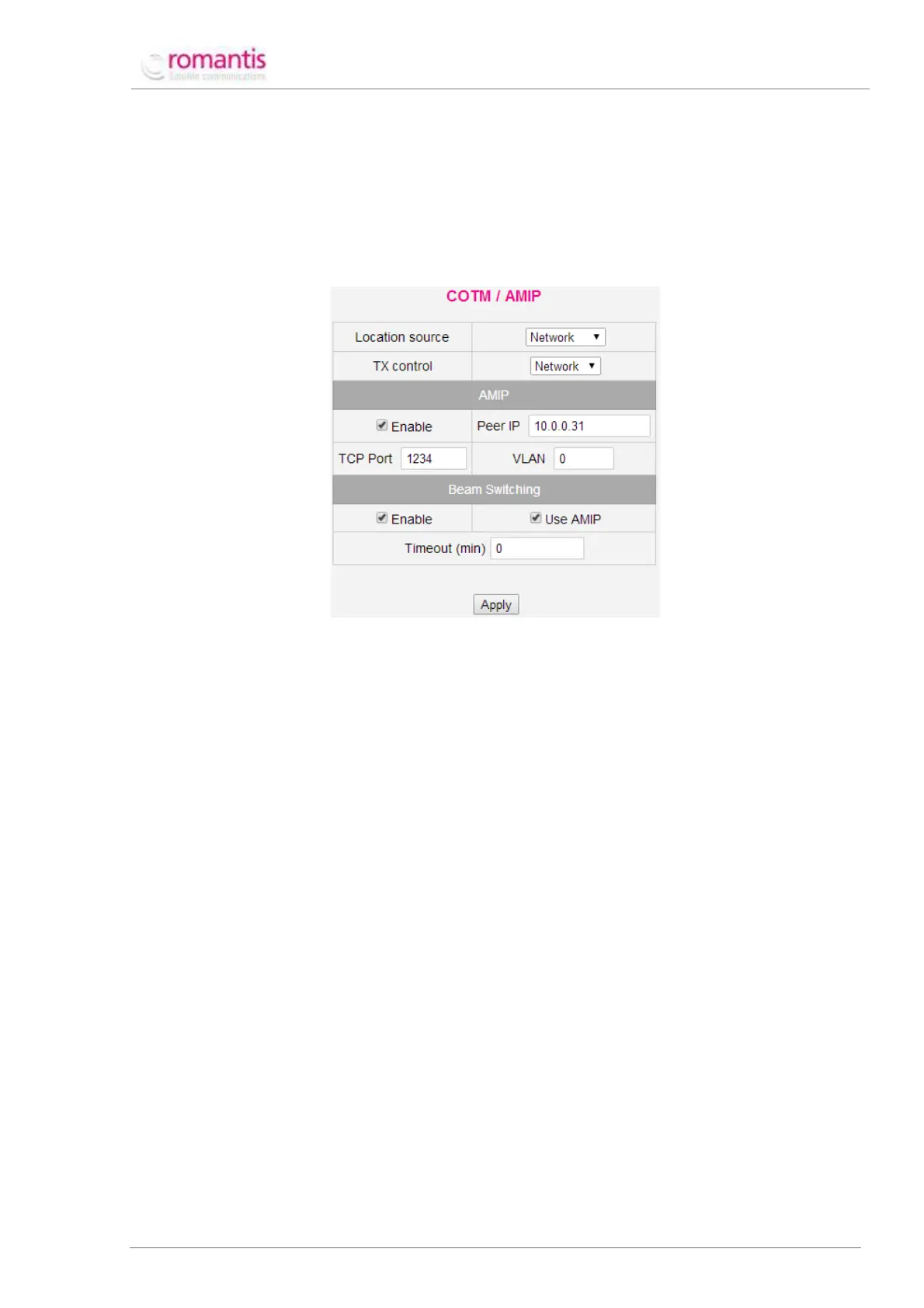
editor Advanced –> Network –> COTM/AMIP (See Figure 40).
Figure 40 COTM configurator
This section defines the method to retrieve actual coordinates by UHP router:
UHP router uses coordinates defined in its Site Setup section;
UHP router retrieves actual coordinates from the controller of the mobile antenna using
OpenAMIP or SNMP protocols;
UHP router retrieves actual coordinates using serial console port.
This section defines management of UHP transmission:
By setting via its HTTP/telnet/NMS interfaces;
By commands from the antenna controller using OpenAMIP or SNMP protocols;
By an electric relay circuit.
This section configures OpenAMIP/SNMP protocols:
Enables OpenAMIP protocol; When disabled UHP router uses SNMP protocol instead;
IP-address of the mobile antenna controller;
TCP-port number of the mobile antenna controller;
VLAN number of the mobile antenna controller.
Automatic Beam Switching configuration:
Activation of the Beam Switching;
Use OpenAMIP commands for switching between satellites;
Max time required by a mobile antenna to repoint to the requested satellite.
When SNMP protocol is used for communication between UHP router and the mobile antenna controller it
requires respective configuration and permissions Advanced –> IP protocols –> SNMP (See Figure 41).

 Loading...
Loading...