Communication with Modbus
A43/A44 100 2CMC48001M0201
User Manual Revision: C
9.2 About the Modbus Protocol
General
Supported
function codes
Modbus
request frame
Message types
Modbus is a master-slave communication protocol that can support up to 247
slaves organized as a multidrop bus. The communication is half duplex.
Services on Modbus are specified by function codes.
The function codes are used to read or write 16 bit registers. All metering data,
such as active energy, voltage or firmware version, is represented by one or more
such registers. For further information about the relation between register
number and metering data, refer to “Mapping Tables” on page - 103.
The Modbus protocol is specified in its entirety in Modbus Application Protocol
Specification V1.1b. The document is available at http://www.modbus.org
The following function codes are supported:
• Function code 3 (Read holding registers
• Function code 6 (Write single register)
• Function code 16 (Write multiple registers)
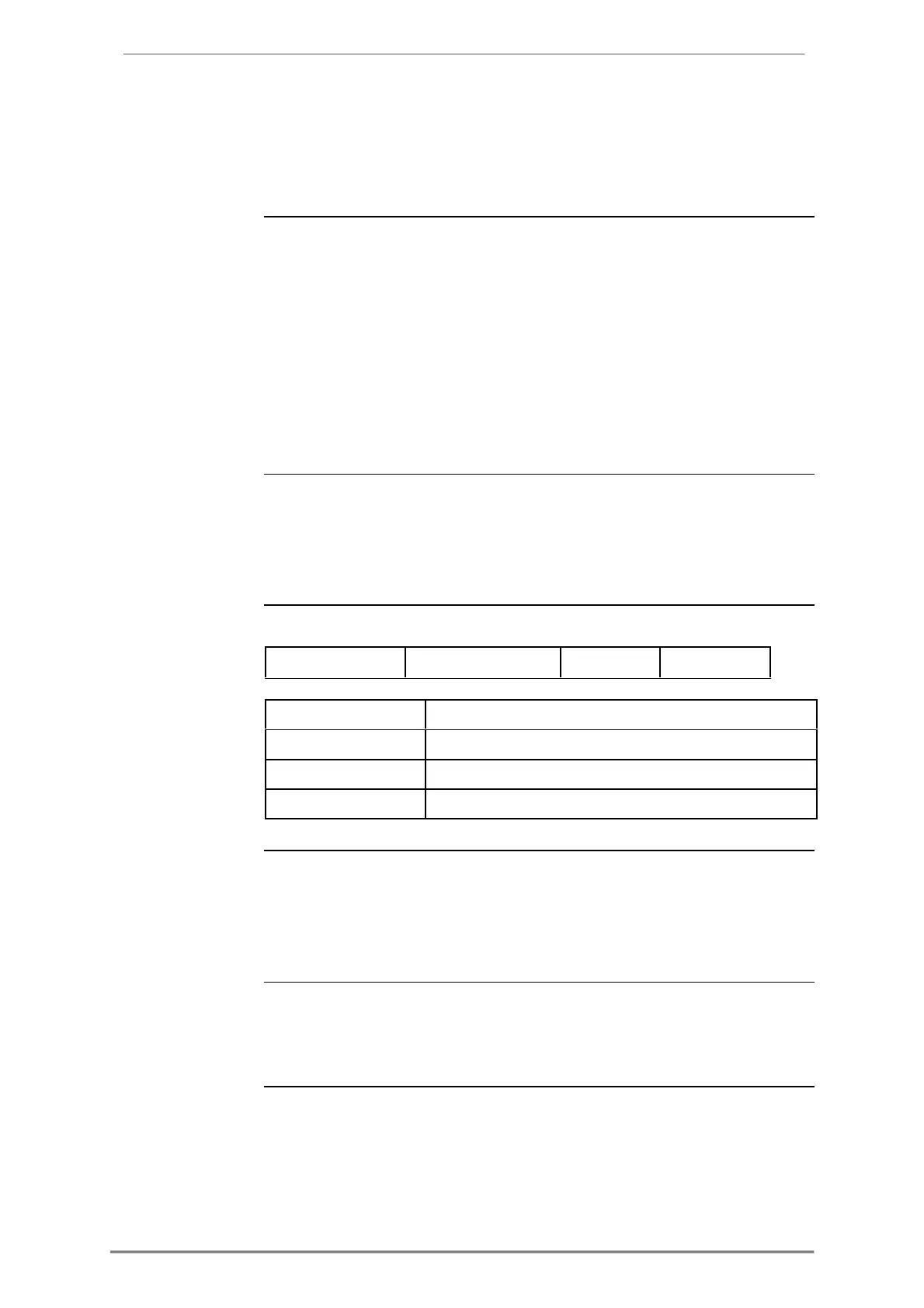
A Modbus request frame generally has the following structure:
Modbus slave address, 1 byte.
Decides the service to be performed.
Dependent on the function code. The length varies.
The network messages can be query-response or broadcast type. The query-
response command sends a query from the master to an individual slave and
is generally followed by a response.
The broadcast command sends a message to all slaves and is never followed by
a response. Broadcast is supported by function code 6 and 16.
9.2.1 Function Code 3 (Read holding registers)
General Function code 3 is used to read measurement values or other information from the
electricity meter. It is possible to read up to 125 consecutive registers at a time.
This means that multiple values can be read in one request.
 Loading...
Loading...