Measurement Methods
2CMC48001M0201 85 A43/A44
Revision: C User Manual
The following illustration shows a vector diagram for resistive, inductive and ca-
A load that consumes both reactive and active energy can be divided into active
and reactive components. The angle between the apparent power (U*I) vector and
the active power component is described as phase displacement angle or power
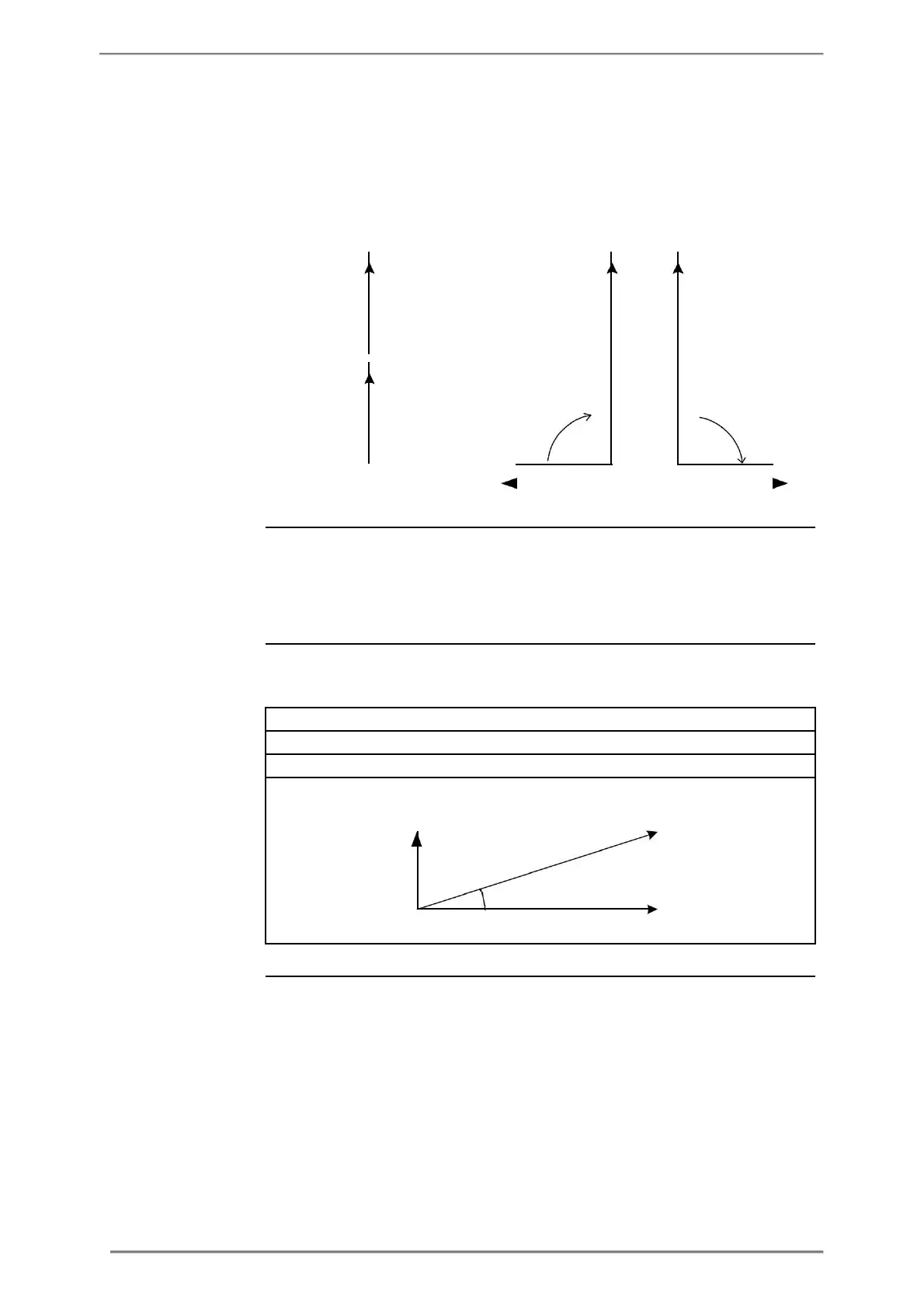
The following illustration shows a vector diagram for a load with an active and a
Active power = P = U x I x cos (unit W)
Reactive power = Q = U x I x sin (unit var)
Apparent power = S = U x I (unit VA)
The type of load can be represented geometrically by for quadrants. In the first
quadrant the load is inductive and active and energy is imported (energy is deliv-
ered from the utility to the customer). In the second quadrant the load is capacitive
and active energy is exported and reactive energy is imported. In the third quad-
rant the load is inductive and active and reactive energy is exported. In the last
quadrant the load is capacitive and active energy is imported and reactive
energy exported.
 Loading...
Loading...