Chapter 11 Basic Configuration Examples
132 Aerohive
If the HiveAP does not have any network settings, check that it can reach the DHCP server. To check
if a DHCP server is accessible, enter interface mgt0 dhcp-probe vlan-range <number1>
<number2>, in which <number1> and <number2> indicate the range of VLAN IDs on which you
want the HiveAP to probe for DHCP servers. The results of this probe indicate if a DHCP server is
present and has responded. If the probe succeeds, check the DHCP server for MAC address filters or
any other settings that might interfere with delivery of network settings to the HiveAP.
• Are the HiveAPs in the same subnet as HiveManager?
HiveAPs must be in the same subnet and the same VLAN as HiveManager for their broadcast CAPWAP
Discovery messages to reach it. If you can move the HiveAPs or HiveManager so that they are all in the
same subnet, do so. If they must be in different subnets from each other, it is still possible for the
HiveAPs to contact HiveManager, but not by broadcasting CAPWAP messages. For a list of other
connection options, see "How HiveAPs Connect to HiveManager" on page 133.
• Can the HiveAPs ping the IP address of the HiveManager MGT interface?
Enter the ping <ip_addr> command on the HiveAP, where the variable <ip_addr> is the IP
address of the HiveManager MGT interface. If it does not elicit any ICMP echo replies from HiveManager,
make sure that HiveManager is connected to the network through its MGT interface, not its LAN
interface, and that the IP address settings for the MGT interface are accurate (see HM Admin >
HiveManager Settings > Interface Settings in the HiveManager GUI).
• What is the status of the CAPWAP client running on the HiveAP?
To check the CAPWAP status of a HiveAP, enter the show capwap client command. Compare the
"RUN state" with the CAPWAP states explained in Figure 4 on page 130. Check that the HiveAP has an IP
address for itself and the correct address for HiveManager. If for some reason, the HiveAP does not have
the correct address for HiveManager, you can set it manually by entering the capwap client server
name <ip_addr> command, in which <ip_addr> is the HiveManager MGT interface IP address.
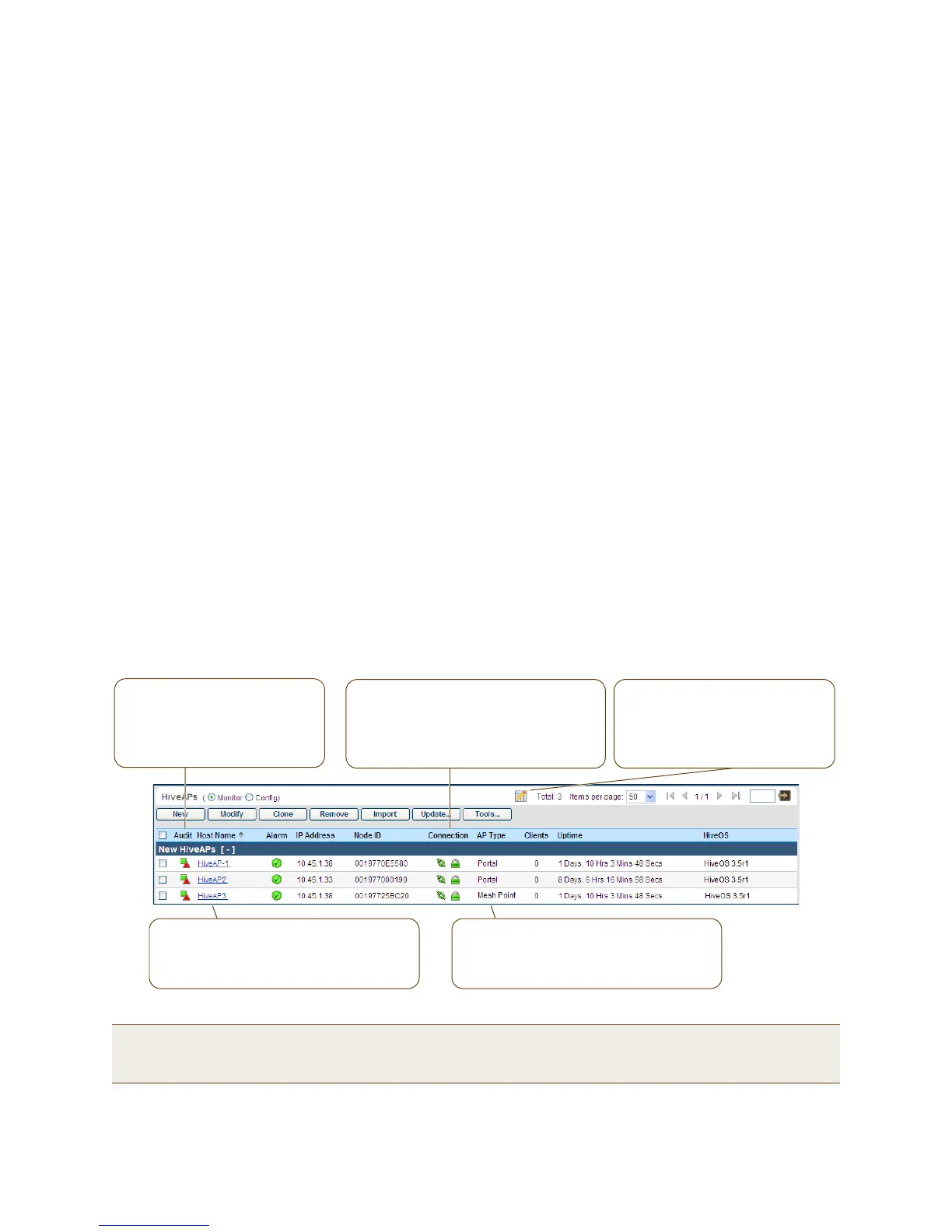
When HiveAPs have contacted HiveManager, they appear in the Monitor > Access Points > HiveAPs page, as
shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5 Monitor > Access Points > HiveAPs (view mode: Monitor)
Note: If you see a different group of HiveAP settings, make sure that Monitor is selected as the view mode at the
top of the HiveAPs page. The GUI provides two view modes for HiveAPs, one that focuses on monitoring
HiveAPs (Monitor) and another that focuses on configuring them (Config).
The AP type for HiveAP1 and HiveAP2 is
"Portal"; they have Ethernet connections to
the network. HiveAP3 is "Mesh Point"; it
connects to the network through a portal.
The host names have been changed to match
those in the example. By default, the host
name is AH- + the last six bytes of its MAC
address. (Example: AH-0E5580)
Audit icon
Green square + red triangle: The
configuration on a HiveAP does not
match that on HiveManager.
Two green squares: They match.
CAPWAP connection and security icons:
Green linked chain/red unlinked chain: The
HiveAP is connected or disconnected.
Green locked padlock/red unlocked padlock:
Connection is secured through DTLS or not.
You can customize the table contents
by clicking the Edit Table icon. You
can add more columns (radio
channels and power for example),
remove columns, and reorder them.
 Loading...
Loading...