5 Exhaust Venting
Exhaust Venting
28 Site Preparation Guide
Exhaust Venting
During normal operation, the GC exhausts hot oven air. Depending on the installed inlet and
detector types, the GC can also exhaust (or vent) uncombusted carrier gas and sample. Proper
venting of these exhausts is required for operation and safety.
Venting hot air
Do not place temperature-sensitive items (for example, gas cylinders, chemicals, regulators,
and plastic tubing) in the path of the heated exhaust. These items will be damaged and
plastic tubing will melt. Be careful when working behind the instrument during cool-down
cycles to avoid burns from the hot exhaust.
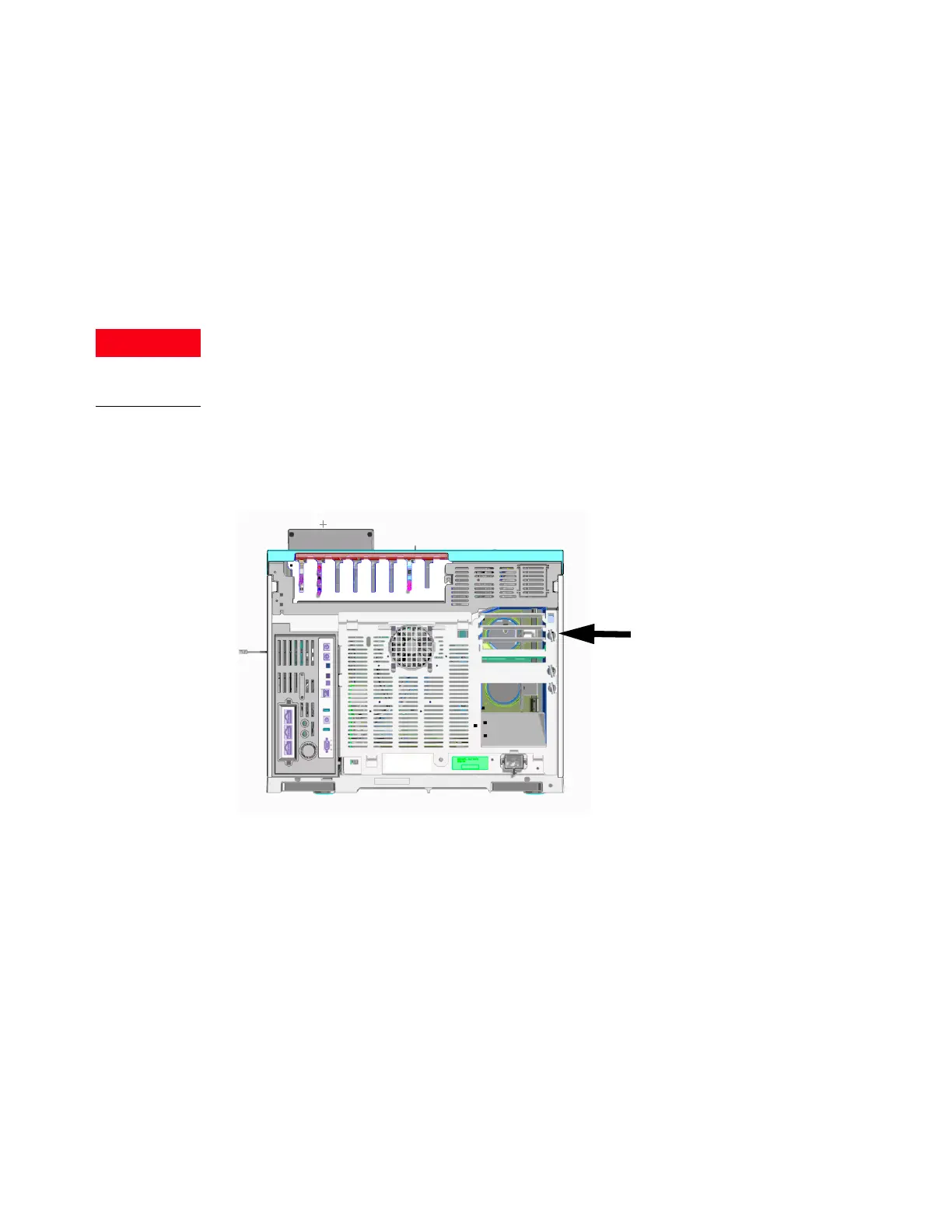
1 Hot air (up to 450 °C) from the oven exits through a vent in the rear of the instrument. Allow
at least 25 cm (10-inch) clearance behind the instrument, or 30 cm (12-inch) behind a
Q-TOF GC/MS to dissipate this hot air. See Figure 4.
Figure 4. Exhaust outlet.
2 For most applications, an optional oven exhaust deflector is available. The exhaust
deflector allows for less bench depth than a GC without the exhaust deflector installed.
• The GC exhaust deflector is included if GC option 306 is ordered. The exhaust deflector
requires 14 cm (5.5 inches) behind the instrument. For GCs with the exhaust deflector
option installed, the exhaust rate is about 65 ft
3
/min (1.84 m
3
/min). Without the
deflector, the exhaust rate is about 99 ft
3
/min (2.8 m
3
/min). The deflector outlet
diameter is 10 cm (4 in). See Figure 5.
• For part numbers for the exhaust deflectors, see Table 9.

 Loading...
Loading...











