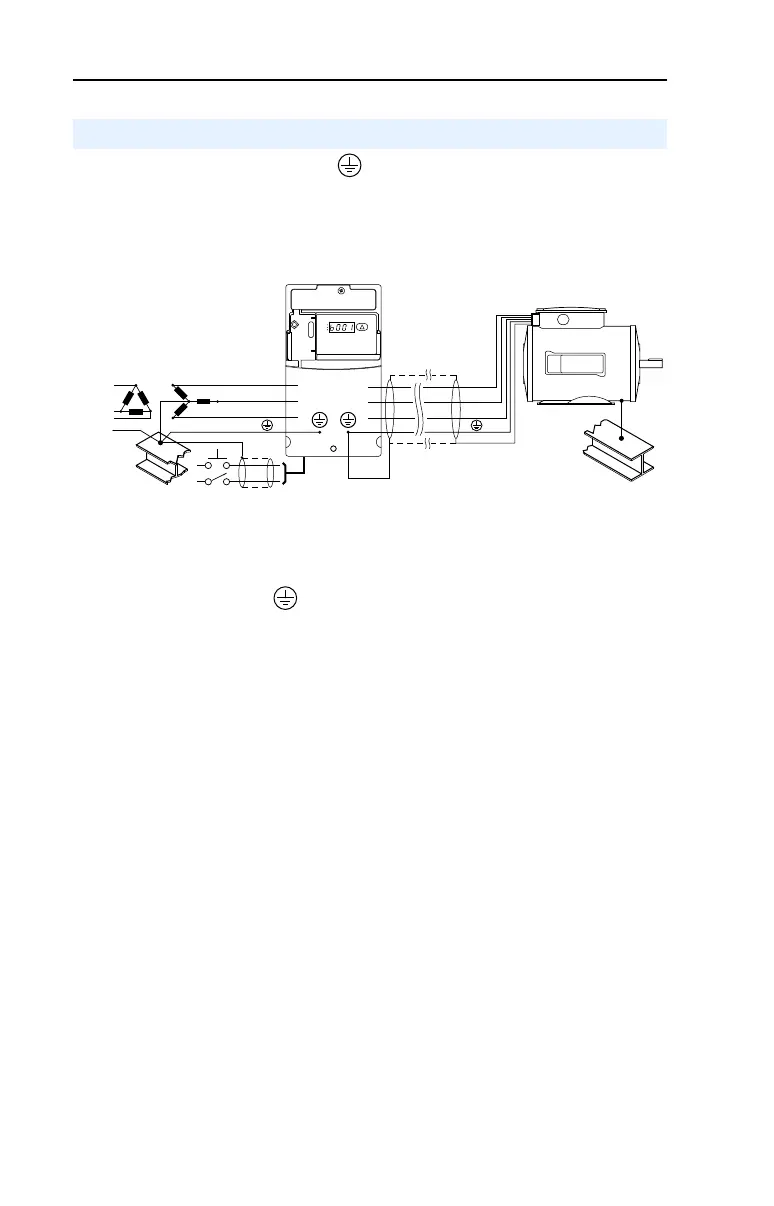
1-6 Installation/Wiring
The drive Safety Ground - (PE) must be connected to system
ground. Ground impedance must conform to the requirements of
national and local industrial safety regulations and/or electrical codes.
The integrity of all ground connections should be periodically checked.
Figure 1.3 Typical Grounding
Ground Fault Monitoring
If a system ground fault monitor (RCD) is to be used, only Type B
(adjustable) devices should be used to avoid nuisance tripping.
Safety Ground - (PE)
This is the safety ground for the drive that is required by code. One of
these points must be connected to adjacent building steel (girder, joist), a
floor ground rod or bus bar. Grounding points must comply with national
and local industrial safety regulations and/or electrical codes.
Motor Ground
The motor ground must be connected to one of the ground terminals on
the drive.
Shield Termination - SHLD
Either of the safety ground terminals located on the power terminal
block provides a grounding point for the motor cable shield. The motor
cable shield connected to one of these terminals (drive end) should also
be connected to the motor frame (motor end). Use a shield terminating or
EMI clamp to connect the shield to the safety ground terminal. The
conduit box option may be used with a cable clamp for a grounding point
for the cable shield.
When shielded cable is used for control and signal wiring, the shield
should be grounded at the source end only, not at the drive end.
General Grounding Requirements
SHLD
U/T1
V/T2
W/T3
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3
RUN
REV
FAULT

 Loading...
Loading...











