3-4 Input Range Verification Chapter 3 — Performance Verification
3-4 PN: 13000-00164 Rev. K ML248xx, ML249xA MM
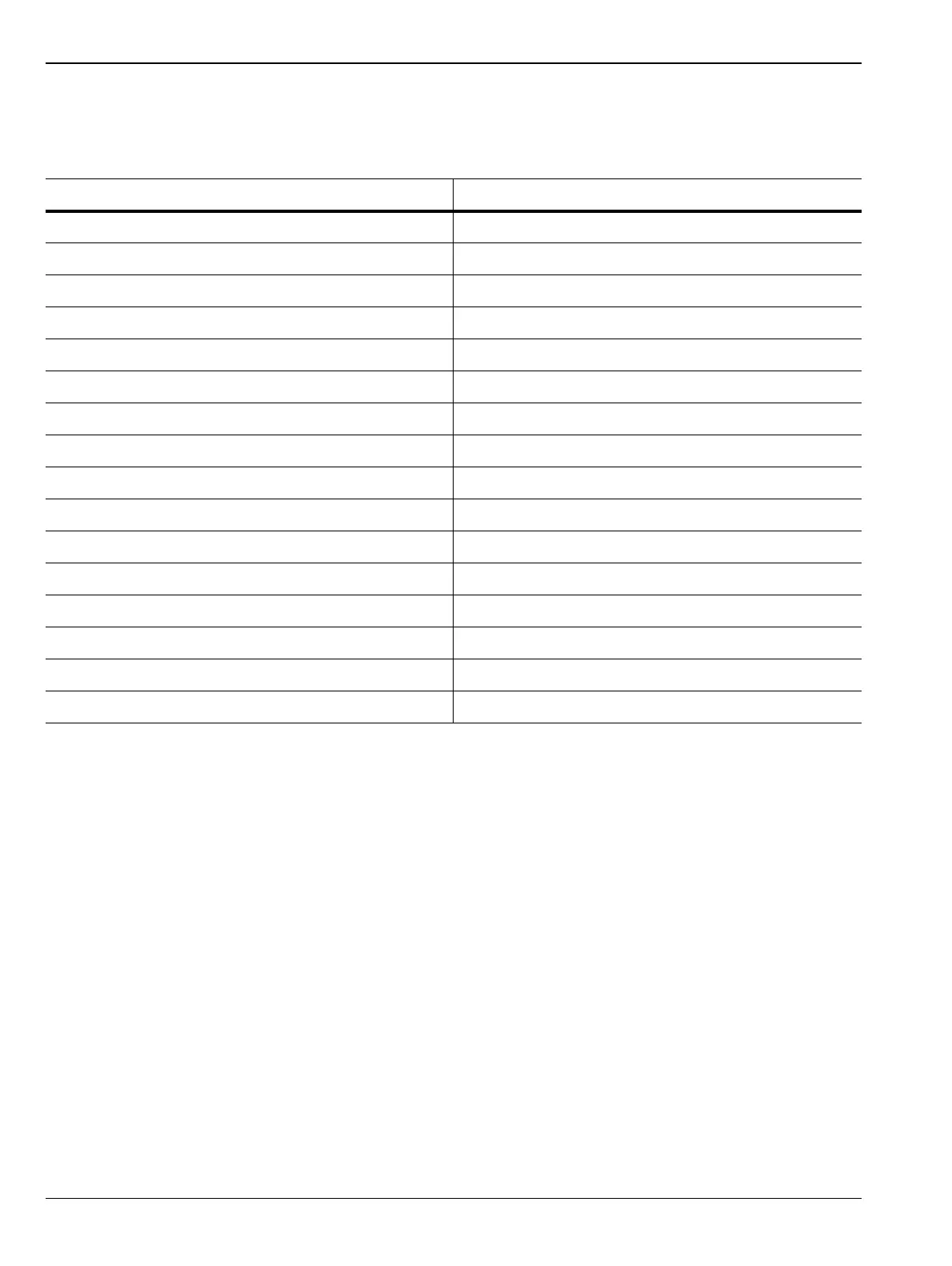
Pass/Fail Criteria
The meter should be accepted as PASSED if it meets the error and linearity statistics listed in Table 3-2.
Absolute Error
The absolute error is the difference between the measured level and expected level. For example, from the
readout shown in Figure 3-2, the calculated absolute error for Range 1 Upper (R1U) is:
R1
upper
– R1
expected
= (–0.955) – (–0.9540) = –0.0010 dB
The calculated absolute error in this case should be ≥ –0.020 dB and ≤ 0.020 dB which are the limits
shown in Table 3-2.
Linearity
The linearity is the difference between the upper range error and the lower range error. For example, from the
absolute error calculations above, the calculated linearity is:
Error R1U – Error R1L = (0.0010) – (0.0002) = 0.0008 dB
The calculated linearity in this case should fall between –0.040 and 0.040 dB as shown in Table 3-2.
Range Change
The range change error is the difference between the errors for the two dB levels at the overlap between any
two ranges. This should be ≥ –0.030 dB and ≤ 0.030 dB as shown in Table 3-2. For example, the maximum
range change error between R1L–R2U is:
R1L
error
– R2U
error
= (0.0002) – (–0.0008) = 0.0010 dB
Table 3-2. Pass/Fail Criteria
Range Specifications (dB)
Range 1 Absolute Error –0.020 ≤ R1U ≤ 0.020
Range 1 Linearity –0.040 ≤ R1U–R1L ≤ 0.040
Ranges 1-2 Change –0.030 ≤ R1L–R2U ≤ 0.030
Range 2 Linearity –0.040 ≤ R2U–R2L ≤ 0.040
Ranges 2-3 Change –0.030 ≤ R2L–R3U ≤ 0.030
Range 3 Absolute Error –0.020 ≤ R3U ≤ 0.020
Range 3 Linearity –0.040 ≤ R3U–R3L ≤ 0.040
Ranges 3-4 Change –0.030 ≤ R3L–R4U ≤ 0.030
Range 4 Linearity –0.040 ≤ R4U–R4L ≤ 0.040
Range 4-5 Change –0.030 ≤ R4L–R5U ≤ 0.030
Range 5 Linearity –0.040 ≤ R5U–R5L ≤ 0.040
Range 7 Absolute Error –0.030 ≤ R7U ≤ 0.030
Range 8 Absolute Error –0.030 ≤ R8U ≤ 0.030
Range 8 Linearity –0.085 ≤ R8U–R8L ≤ 0.085
Range 9 Absolute Error –0.050 ≤ R9U ≤ 0.050
Range 9 Linearity –0.18 ≤ R9U–R9L ≤ 0.18

 Loading...
Loading...