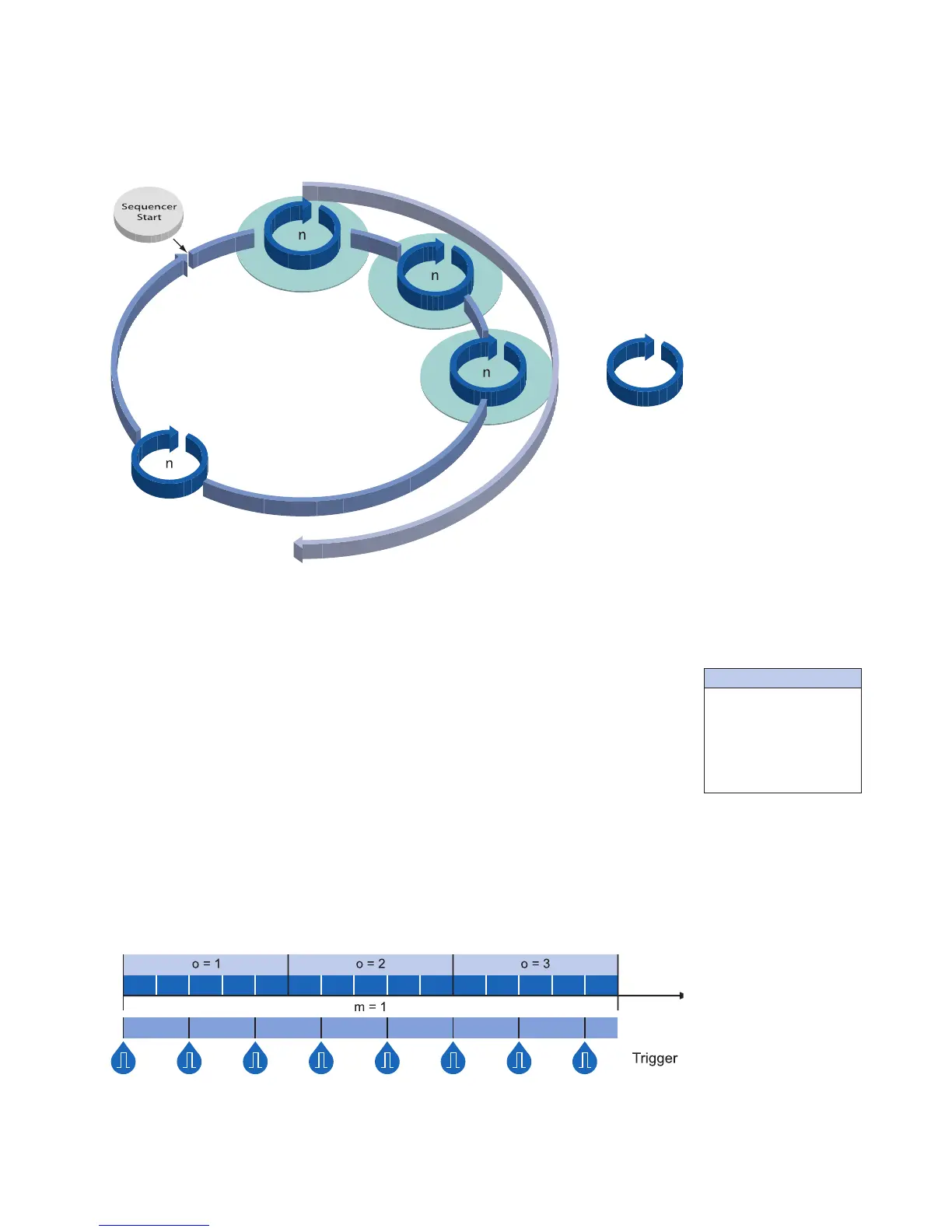
The gure above displays the fundamental structure of the sequencer module.
A sequence (o) is dened as a complete pass through all sets of parameters.
The loop counter (m) represents the number of sequence repetitions.
The repeat counter (n) is used to control the amount of images taken with the respective
sets of parameters.
The start of the sequencer can be realized directly (free running) or via an external event
(trigger).
The additional frame counter (z) is used to create a half-automated sequencer. It is ab-
solutely independent from the other three counters, and used to determine the number of
frames per external trigger event.
The following timeline displays the temporal course of a sequence with:
n = 5 repetitions per set of parameters ▪
o = 3 sets of parameters (A,B and C) ▪
m = 1 sequence and ▪
z = 2 frames per ▪ trigger
t
n = 1n = 2n = 3n = 4n = 5n = 1n = 2n = 3n = 4n = 5n = 1n = 2n = 3n = 4n = 5
ABC
z = 2z = 2z = 2z = 2z = 2z = 2z = 2
 Loading...
Loading...