90
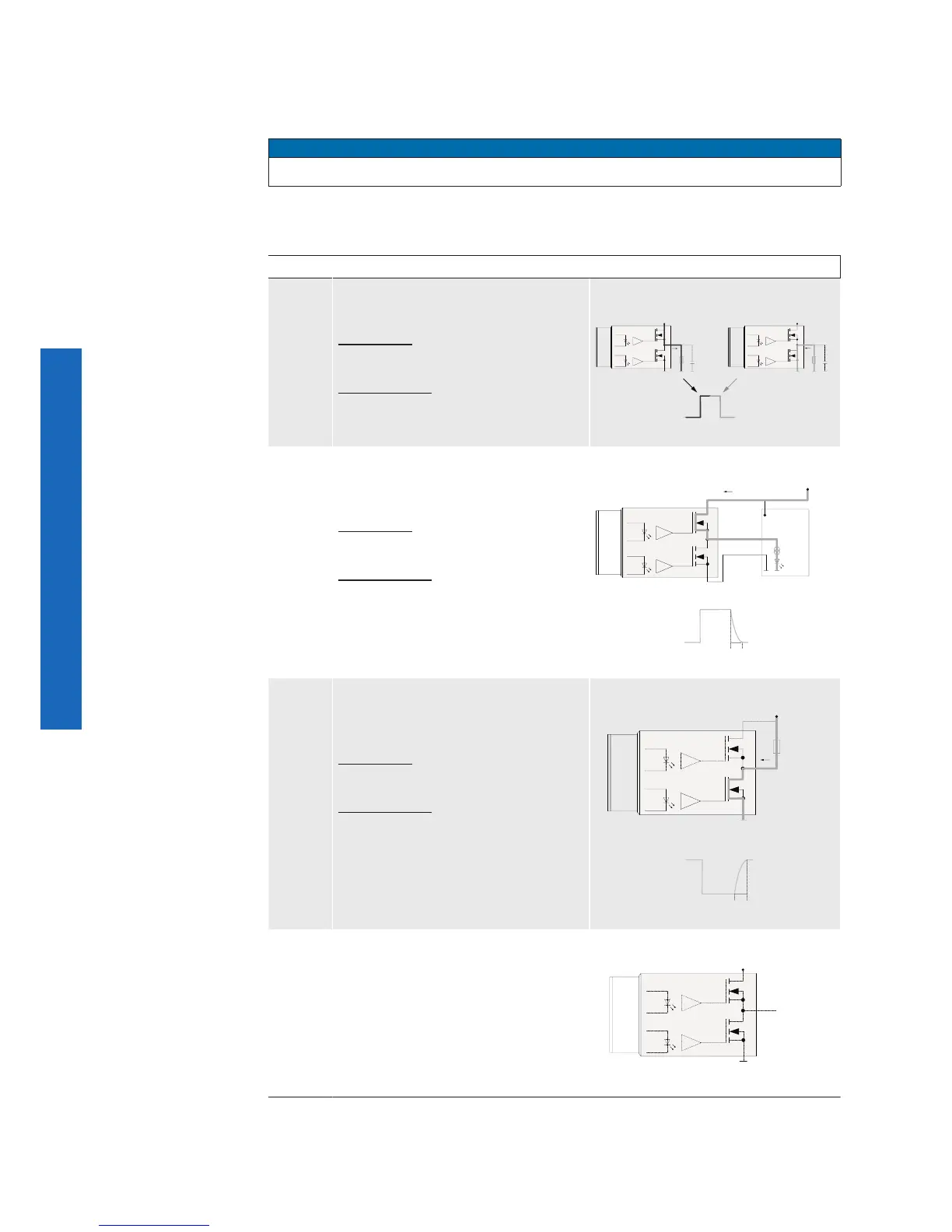
7.6.1.4 Modes of Outputs (only VCXG.I / .XT)
By switching the modes, the behavior of the outputs can be adapted to the respective
installation.
Notice
In all modes the supply voltage for the outputs (Pin 11, 12) must to be connected!
The following modes are available for each of the 4 outputs:
Modes Description Circuit
Push-
Pull
This mode is used to generate sharp
edges for fast switching processes.
Advantage: Sharp edges in both direc-
tions.
Disadvantage: For long cable more
susceptible to ground bounce and po-
tential differences.
Power (IO)
GND (IO)
Camera
Output
I
Power (IO)
GND (IO)
Camera
Output
I
Open-
Source
Typical applications for this mode are:
PLC input, control of illumination con-
nected to ground.
Advantage: Stable at long cable
lengths and potential differences.
Disadvantage: The falling edge has
a lower slope due to parasitic capaci-
tances. Switching off is slower due to
this lower slope.
Open-
Drain
A typical case of application for this
mode is a illumination control con-
nected to plus.
Advantage: Stable at long cable
lengths and potential differences.
Disadvantage: The rising edge has a
lower slope due to parasitic capaci-
tances. Switching off is slower due to
this lower slope.
Power (IO)
GND (IO)
Camera
Output
t
off
t
on
I
Tri-
State
In this mode, the output is disabled.
Power (IO)
GND (IO)
Camera
Output
 Loading...
Loading...