C-Nav Hardware Reference Guide
92
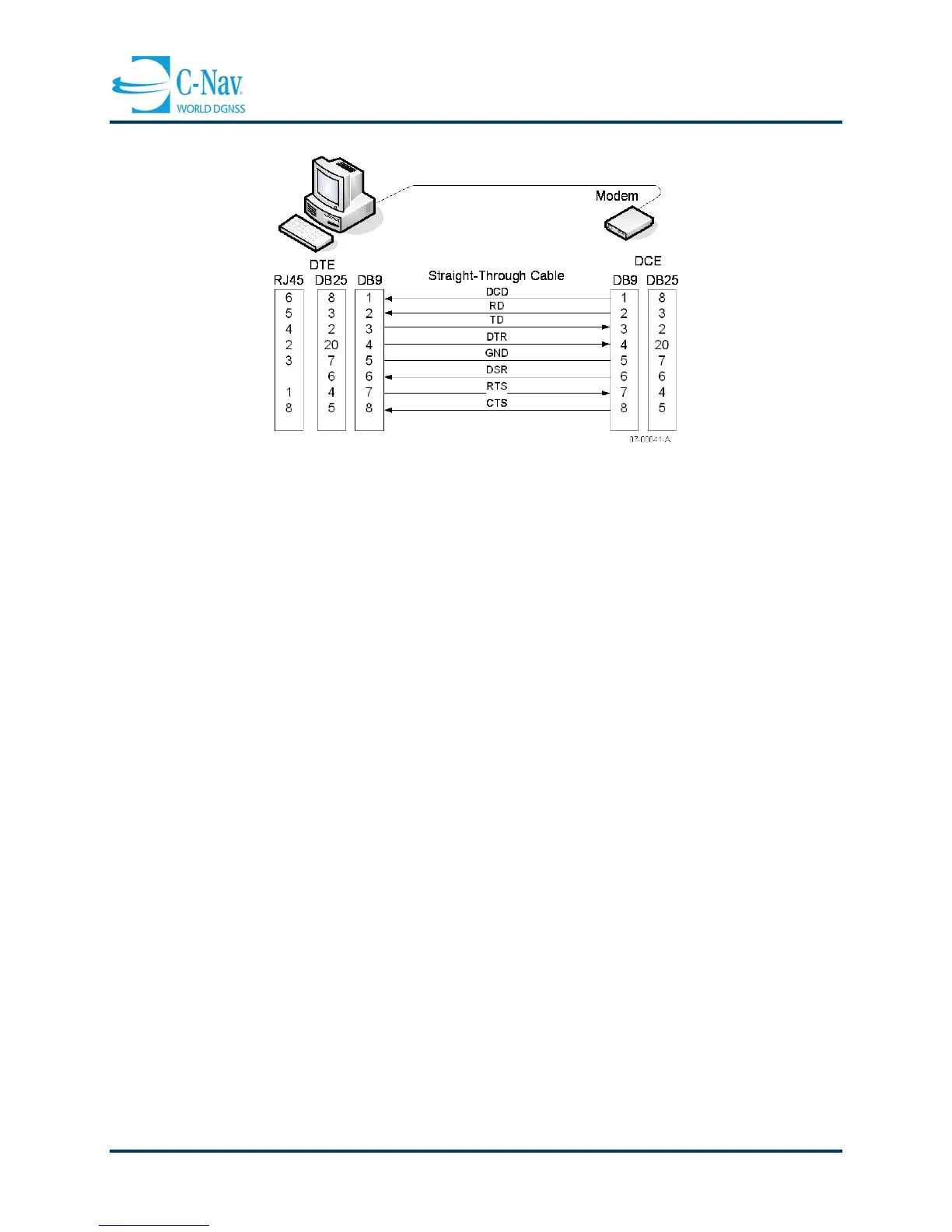
Figure 6-1: DTE to DCE RS-232 Pin Assignments
Deflection of the Vertical is the angle between the perpendicular to the geoid (plumb line) and
the perpendicular to the ellipsoid.
DGPS see Differential GPS.
Differencing is a technique used in baseline processing to resolve the integer cycle ambiguity
and to reduce a number of error sources including oscillator variations and atmospheric and
orbital modeling errors. This technique “differences” the measurement of the carrier beat phase
across time, frequency, receivers, satellites, or any combination of these. The most popular
differences are single, double and triple.
Differential GPS (DGPS) is a positioning procedure that uses two receivers, a rover at an
unknown location and a reference station at a known, fixed location. The reference station
computes corrections based on the actual and observed ranges to the satellites being tracked.
The coordinates of the unknown location can be computed with sub-meter level precision by
applying these corrections to the satellite data received by the rover.
Dilution of Precision (DOP) is a class of measures of the magnitude of error in GPS position
fixes due to the orientation of the GPS satellites with respect to the GPS receiver. There are
several DOP’s to measure different components of the error. Note: this is a unit-less value. See
also PDOP.
Doppler Aiding is a signal processing strategy that uses measured Doppler shifts to help the
receiver smoothly track the GPS signal, allowing more precise velocity and position
measurement.
Doppler Shift is the apparent change in frequency of a received signal due to the rate of
change of the distance between the transmitter and receiver.
Double Difference between receivers and between satellites is found by differencing the single
difference for one satellite with the single difference for another satellite where both single
differences are from the same epoch.
Dual-Frequency is a type of GPS receiver that uses both L1 and L2 signals from GPS
satellites. A dual-frequency receiver can compute more precise position fixes over longer
distances and under more adverse conditions because it compensates for ionospheric delays.
 Loading...
Loading...