Examples GE 800
58 1.1/1209
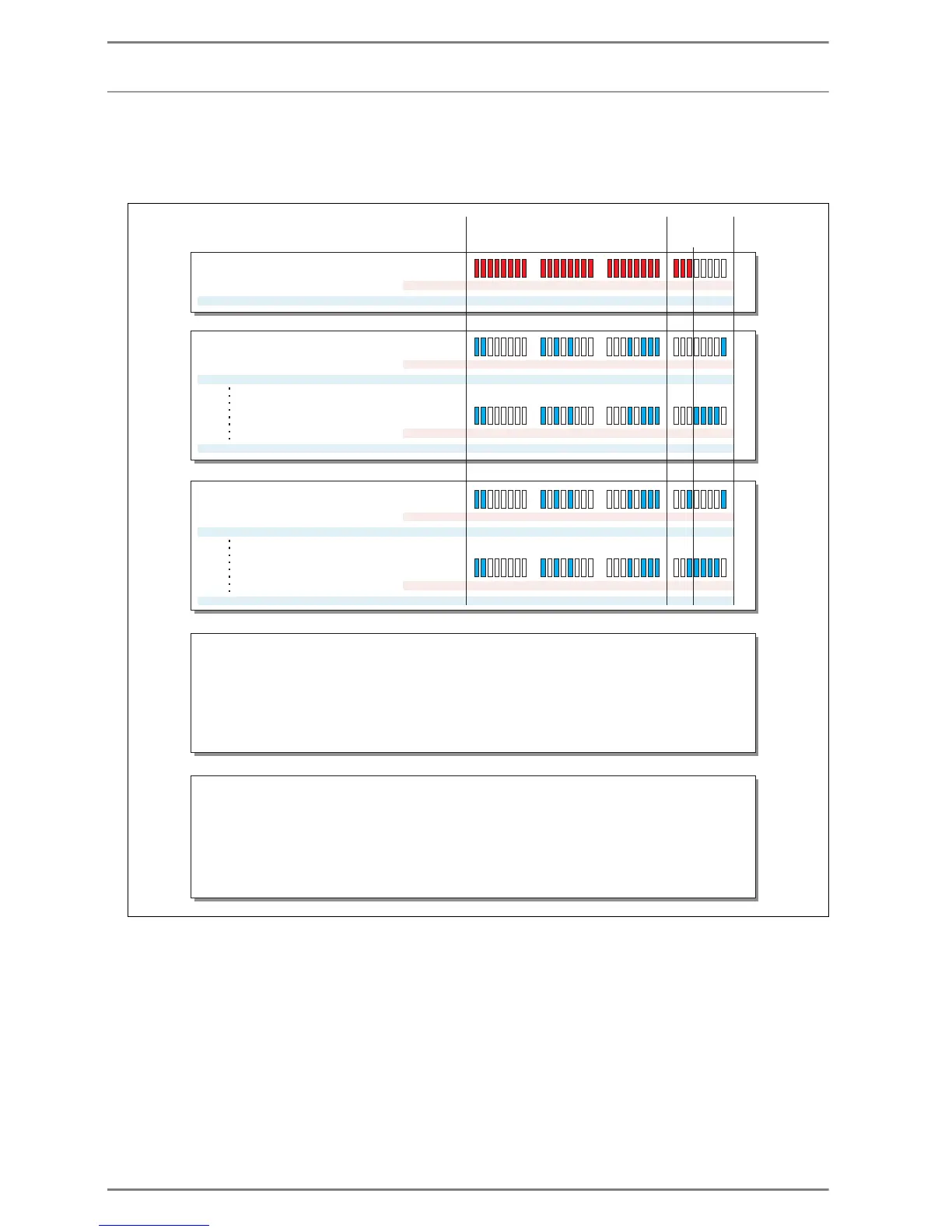
IP-Addresses with Subnetting
The subnet mask specifies which portion of an IP-address represents the network ID (for identification
of the subnet) and which portion represents the host ID (for identification of single network compon-
ents). “Subnetting“ is e.g. using single bits from the host ID for forming further subnets.
11111111
255
11111111
255
11111111
255
111 00000
224
255.255.255.224
11000000
192
10101000
168
00010111
23
00000001
1
00011110
192.168.23.1 (2)*
11000000
192
10101000
168
00010111
23
30192.168.23.30 (29)*
11000000
192
10101000
168
00010111
23
00100001
33
00111110
192.168.23.33 (34)*
11000000
192
10101000
168
00010111
23
62192.168.23.62 (61)*
Subnet mask:
IP addresses for subnet 1:
IP addresses for subnet 2:
Network ID Host ID
Reserved addresses in the host ID (cannot be used for IP-Terminals):
Subnet 1:
0 .......
31 ..... : 1
Network address: all “host bits" are 0 (the 5 bits at the right)
Broadcast address all “host bits" are (the 5 bits at the right)
Subnet 2:
32 .....Network address: all “host bits" are 0 (the 5 bits at the right)
63 .....Broadcast address: all are 1 (the 5 bits at the right)“host bits"
* Usually already taken addresses in the host ID:
Subnet 1:
1 .......for Router:
30 .....for Switch:
all are 0 (the 5 bits at the right), only the last is 1
all are 1 (the 5 bits at the right), only the last is 0
Subnet 2:
33 .....for Router: all are 0 (the 5 bits at the right), only the last is 1
62 .....for Switch: all are 1 (the 5 bits at the right), only the last is 0
“host bits"
“host bits"
“host bits"
“host bits"
binary:
decimal:
binary:
binary:
binary:
binary:
decimal:
decimal:
decimal:
decimal:
 Loading...
Loading...