Manual displacement control (MDC)
The Manual Displacement Control (MDC) uses a mechanical input to operate the control spool in the
pump. A cam connects the input handle to the control spool allowing manipulation of the operating
curve using different cam profiles. The control spool modulates the pressure balance across the pump’s
servo piston. The angle of the swashplate is proportional to the angular position of the control input. A
mechanical feedback linkage moves the control spool toward neutral as the swashplate angle reaches
the commanded position. Mechanical feedback allows the pump to hold very accurately at the
commanded displacement. Centering springs and internal moments return the swashplate to neutral
position in the absence of control input.
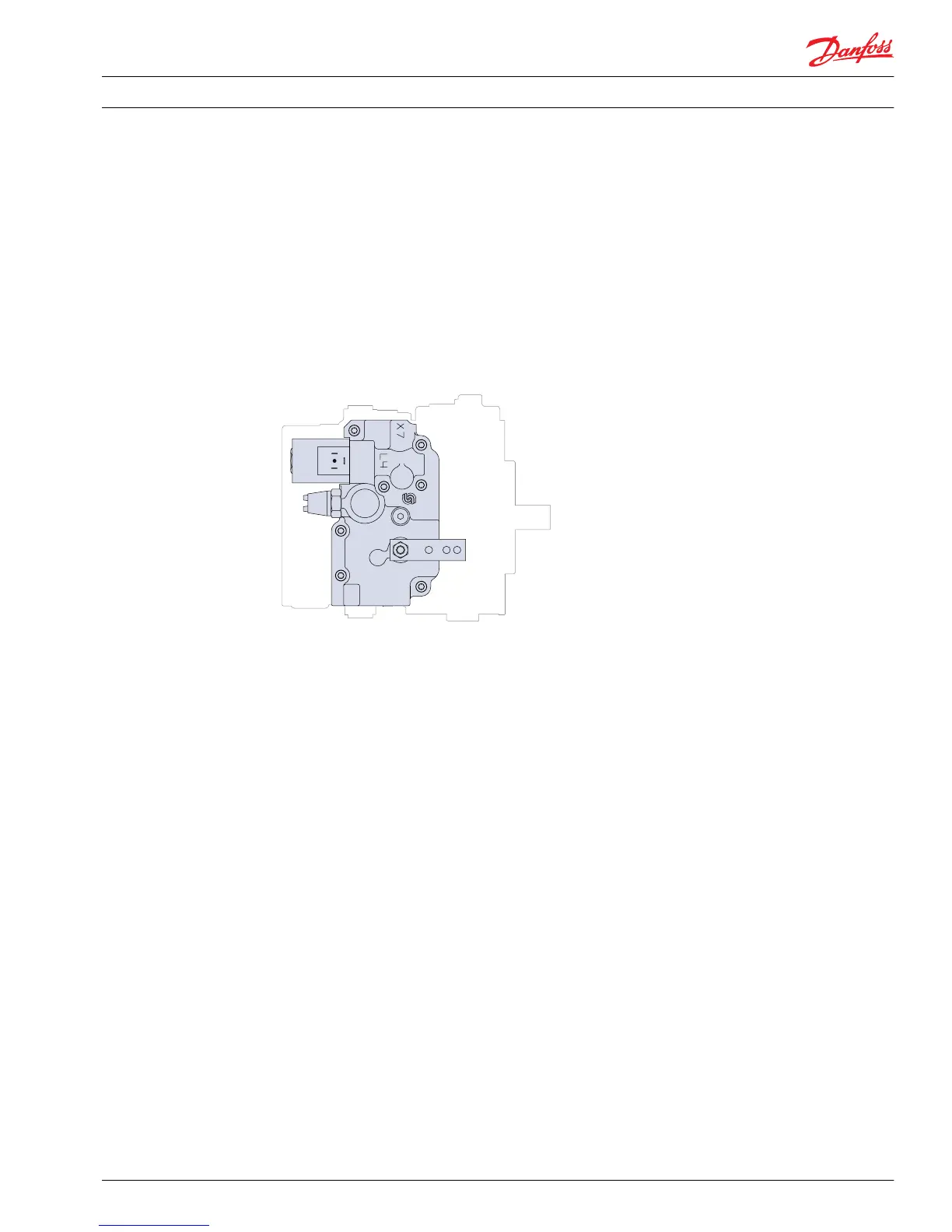
MDC on series 42 pump
Solenoid override valve
A solenoid override valve is available for the manual displacement control. This safety feature shunts the
servo piston allowing the pump to return to neutral when activated. Normally open or normally closed
options are available.
Neutral start switch (NSS)
The Neutral Start Switch (NSS) is an optional cam-operated ball-type microswitch. When connected
properly to the vehicle’s electrical system, the NSS ensures that the prime mover will start only when the
control input shaft is in the neutral position.
Back-up alarm switch (BAS)
The Back-up Alarm Switch (BAS) is available for the MDC and works in association with the NSS. When
connected properly to the vehicle’s electrical system, the BAS can sound an alarm when the control
commands the vehicle into reverse. One cam and switch assembly controls both functions. Repositioning
the cam accommodates both clockwise and counterclockwise control handle rotation to reverse
direction.
Electrical displacement control (EDC)
The Electrical Displacement Control (EDC) is a two-stage control using a DC input current to control
pump displacement. Stage one, the Pressure Control Pilot (PCP) valve, uses the DC input to operate a
torque motor which drives a flapper valve. The flap in the PCP blocks a portion of flow from one or the
other of two nozzles. The two nozzles modulate pressure balance across a sensing piston in the control.
The control piston is connected to the control spool in the pump by a pin and linkage. The control spool
modulates the differential pressure across the pump’s servo piston, this is stage two. The angle of the
swashplate is proportional to the input current. A mechanical feedback linkage moves the control spool
toward neutral as the swashplate angle reaches the commanded position. Mechanical feedback allows
Service Manual
Series 42 Axial Piston Closed Circuit Pumps
Control Options
520L0638 • Rev 0300 • July 2015 17

 Loading...
Loading...











