Multi-DENCO Commissioning
FläktGroup DC-2013-0101-GB • Subject to modifications • R5-08/2020 107
8.3.6 Commissioning water circuits
The following procedure applies to any water circuit used within a Multi-DENCO sys-
tem (C-Version, CombiCool circuit, O-Version, F-Version, W-Version, P-Version etc).
Procedure
• Check for an established water flow
• Check that any temperature sensors are securely fastened to the correct pipework
• Take readings of water temperature sensors and compare these values with the
values displayed on the C5-12 controller: all probes and sensors MUST be
calibrated
• Check for correct rotation in the water pump and any air within the water system is
being removed by the pump or by air purge valves
• (If applicable) add as required pressure to any expansion vessels
• (If applicable) sample and check Glycol concentration (more details below)
• Record all details to the commissioning report
Glycol and corrosion inhibitors
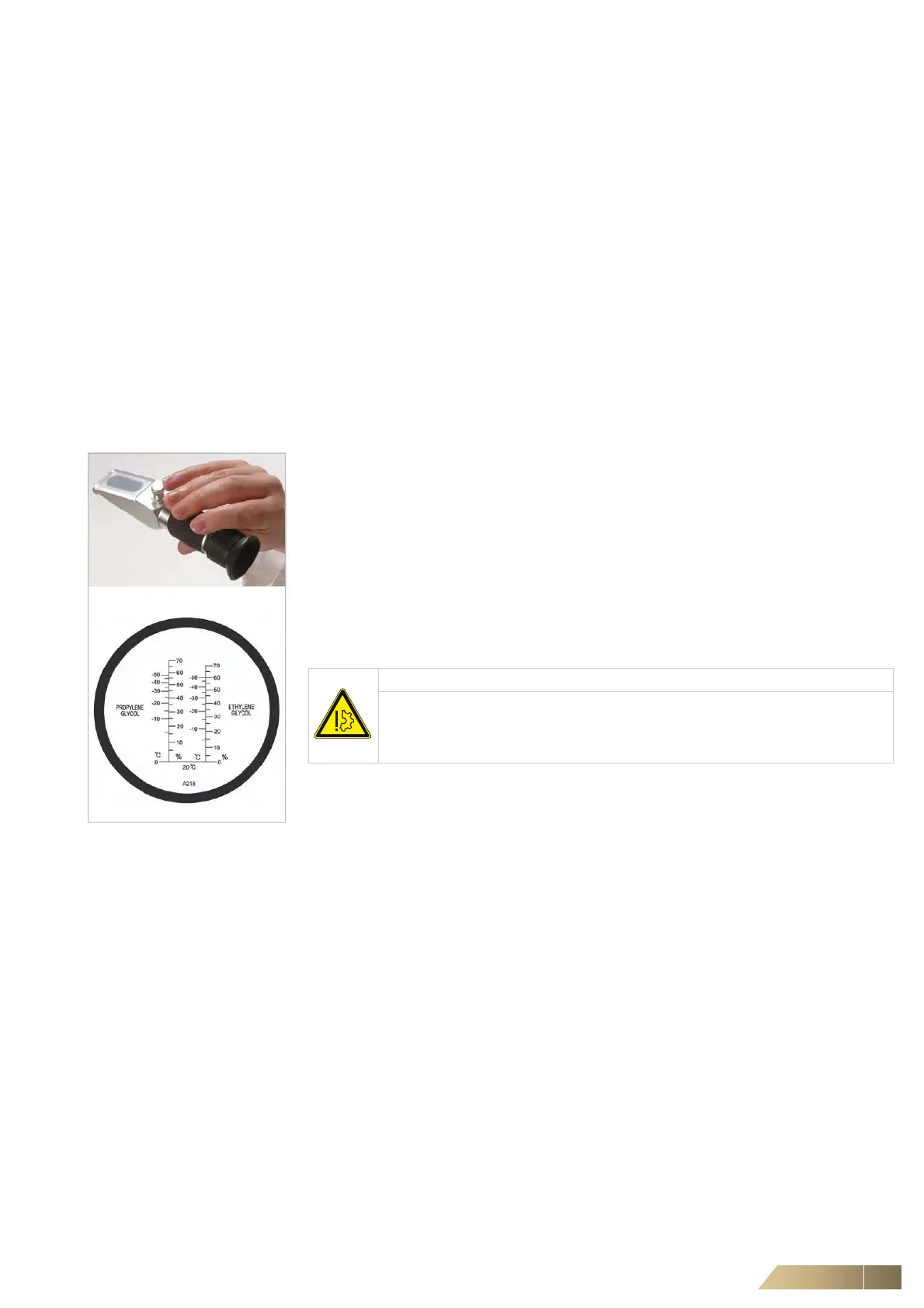
We recommend using a hand held refractometer (for example Kittiwake, RHA-21ATC)
for measuring glycol concentrations. It is able to give accurate readings from a very
small sample of fluid and covers both Ethylene Glycol and Propylene Glycol.
It is important to ascertain the quality and quantity of any glycol and corrosion inhibitors
(see chapter 6.6.4 'Glycols' on page 81). Pumps must never have a negative pressure
or vacuum on their inlet.
Automotive inhibitors and anti-freeze MUST NOT BE USED as nearly all automotive
anti-freeze contains silicate-based inhibitors, which gel and foul, coating heat
exchanger surfaces and reducing energy efficiency. These silicates have also been
shown to significantly reduce the lifespan of pump seals.
Coolant concentrations are determined by first deciding what freeze and/or burst pro-
tection is appropriate for the application, based on operating temperatures or ambient
temperatures.
Fig. 8-1: Kittiwake hand held
refractometer
Freeze protection This is imperative when a system requires pumping. It is achieved when glycol concen-
trations in a system are sufficient to prevent ice crystals from forming when the fluid
experiences the lowest temperature for its application.
Burst protection This is achieved when the concentration of glycol in a system is high enough to prevent
the fluid from freezing solid. The glycol concentration will be lower than that of a 'Freeze
Protected' system, therefore it can form ice crystals at low temperatures (being a semi-
fluid state) and will no longer be pump-able. When ice crystals being to form the solu-
tion will expand.
NOTICE
Low levels of glycol or inhibitors can cause corrosion of steel or iron
components.
• Ensure minimum concentration of inhibitor is above 20%.
 Loading...
Loading...