F R O N T C O N S O L E C H A P T E R 3
XIT (Transmit Incremental Tuning): Click to enable XIT. XIT may be used as a quick way to
operate split at a specific offset. When enabled, the transmit frequency is increased from the
VFO A frequency by the amount shown in Hz while leaving the receive frequency intact. With
SPLT activated, XIT modifies the VFO B frequency. Click the 0 button next to the XIT button to
clear the XIT control to 0.
RIT (Receive Incremental Tuning): Click to enable RIT. When enabled, the receive
frequency is increased from the VFO A frequency by the amount shown in Hz while leaving the
transmit frequency intact. Click the 0 button next to the RIT button to clear the RIT control to
0.
(13) CPU %
This displays your computer's total CPU load as seen in the Windows Task Manager under the
Performance Tab. Note that running other applications will cause the CPU load to increase. If your CPU
load is peaking at close to100%, audio and possibly video artifacts will become noticeable. In this case
closing additional applications and turning down some of the functions may improve the performance.
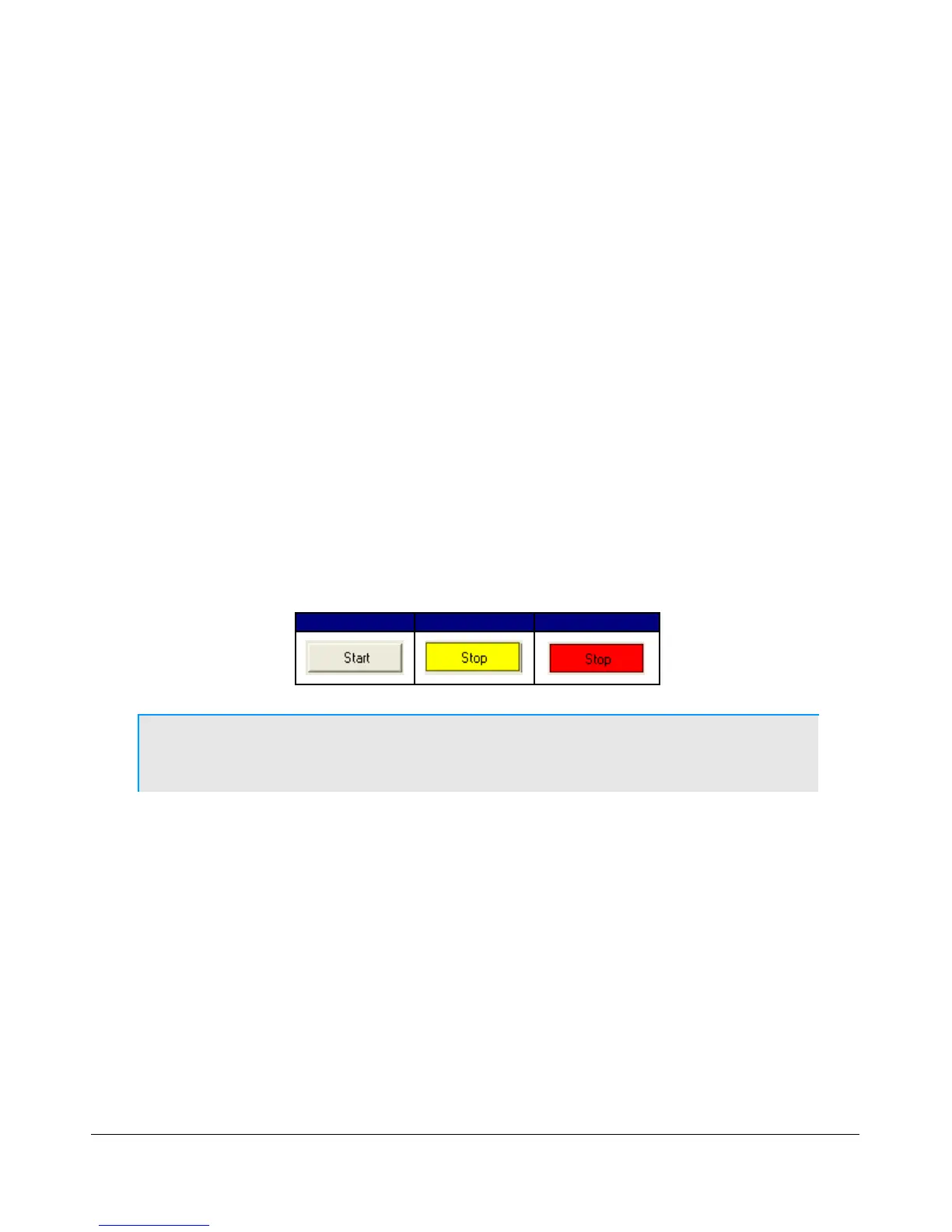
(14) Start/Stop Button
Click Start to activate PowerSDR, click Stop to deactivate it. As Figure 55 shows, the button also acts
as a RX/TX indicator.
Start Stop Stop/Transmit
Figure 55: Power Button States
Note: Please see also the Power-Up/Down procedures described on page
132 for information on best practices.
(15) MON (Monitor)
When enabled, the transmitted audio is monitored through the receiver’s speakers. The MON function
is not available in AM, SAM, or FM modes as those modes are transmitted at the Intermediate
Frequency (IF, usually 9kHz). In voice operation the MON feature will allow you to hear the effects of
MIC gain, TX equalization, compression and compansion and to adjust them in real time. The AF
control can be used to adjust the monitor volume.
[The rest of this page has been left blank intentionally]
56 2003-2009 FlexRadio Systems

 Loading...
Loading...