FUJITSU PSWITCH User’s Guide
52 December/2018
3.1.2.3. Port Locator
The port locator identify ports that have network cabling errors and/or cabling
complications (mis-wiring) by providing a command that blinks a single interface’s
LED or the LEDs of multiple interfaces and turns off all other interface LEDs so that
the mis-wired interface can be easily identified.
In this TOR switch, one LED for link and a second for activity, only the link LED is used for
the port locator function. The other details refer the table below.
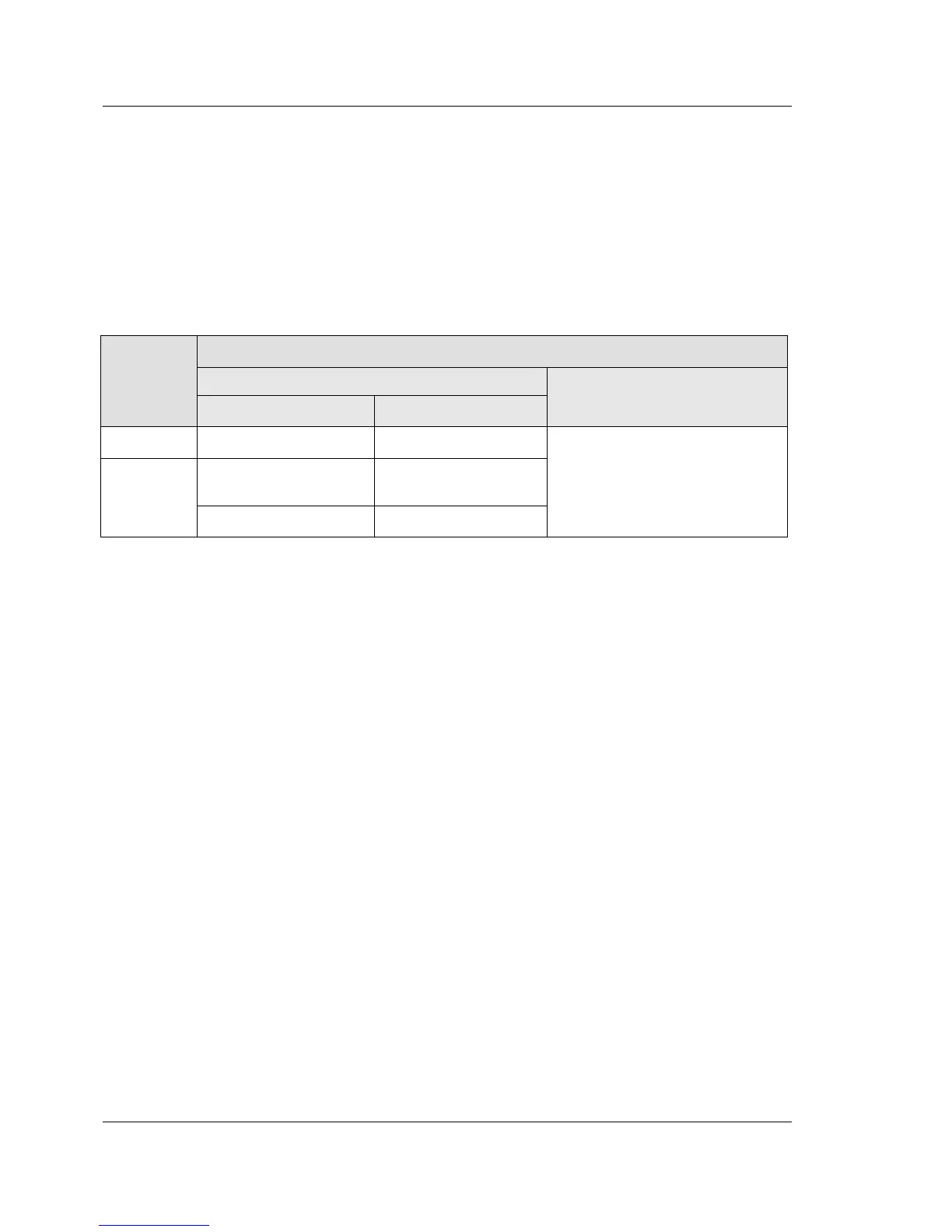
Table 3-2: Port-Locator
3.1.2.4. MAC Address Tables
3.1.2.4.1. Forwarding, Aging, Learning
Forwarding, Aging, and Learning are considered to be one component with three
related functions. Those functions are summarized as follows:
Forwarding
Forwarding occurs when a frame is processed completely by either the bridge
function or the routing function. At layer 2, frames are forwarded according to their
MAC address type, which is either unicast or multicast. A unicast frame is forwarded
in accordance with the address entry in the networking device’s address tables or
filtering database. The frame is forwarded to the port associated with the unicast
address in the address entry. Multicast frames are forwarded in accordance with
their address entry in the switch filtering database. If no entry exists, the frame is
forwarded to all ports in the associated VLAN.
Aging
An address aging time-out parameter based on the 802.1D specification is
included in the networking device. This parameter is a persistent input and output

 Loading...
Loading...