space of the instance, because the command device interprets as assignment
of the instance from CCI.
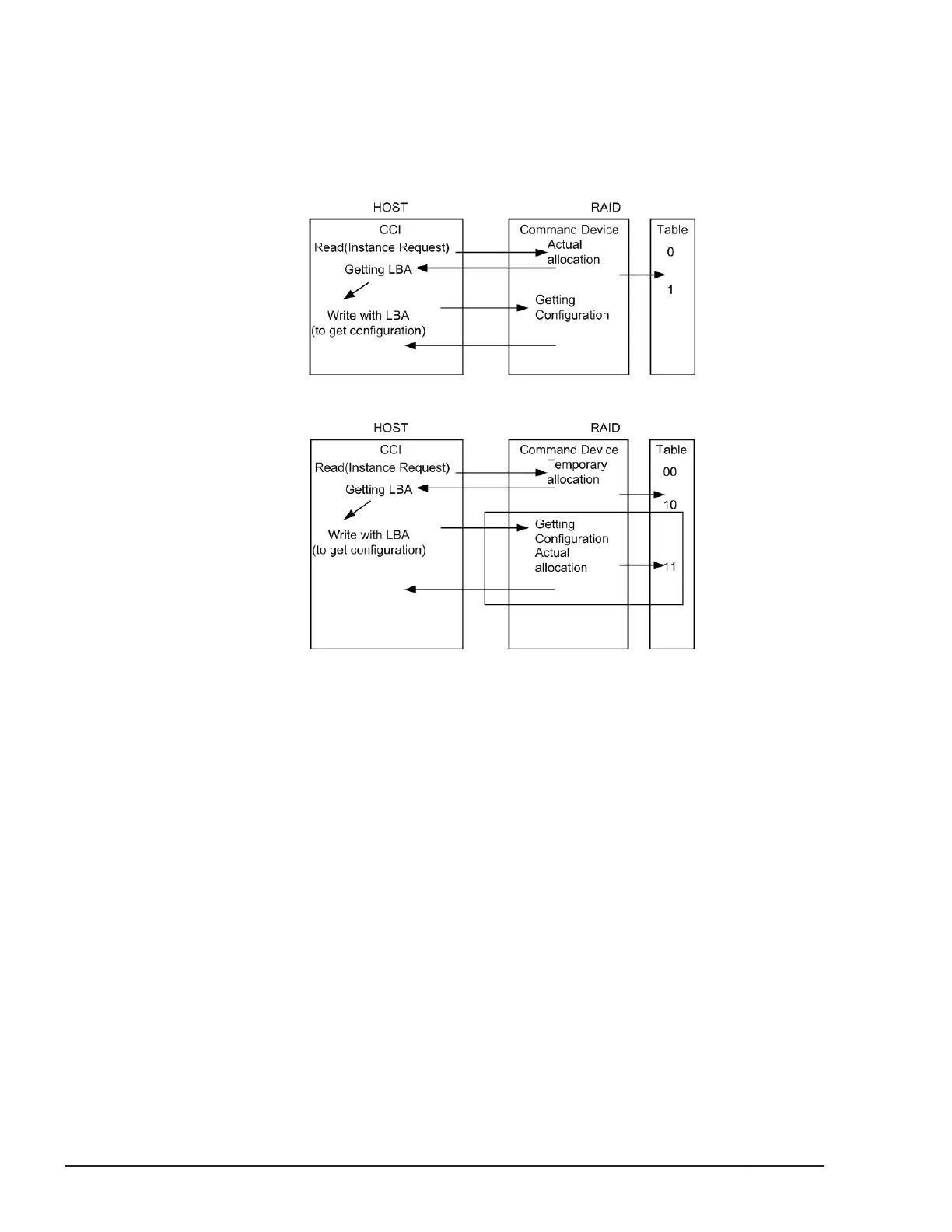
CCI has TWO phases that it reads to acquire usable LBA, and writes with the
acquired LBA in attaching sequence to the command device, so the command
device can confirm whether it was required as the assignment for CCI or not,
by detecting and adding two status bits to the instance assignment table.
Figure 2-1 Current assignment sequence
Figure 2-2 Improved assignment sequence
The command device performs the assignment of an instance through TWO
phases that have "temporary allocation (1 0)" and "actual allocation (1 1)" to
the instance assignment table.
If the command device is attacked, the instance assignment table is filled
with "temporary allocation (1 0)" status. After that, the command device will
detect a fault of full space as the instance assignment, clear up all
"temporary allocation (1 0)", and then reassign the required instance
automatically.
This does not require a service representative to switch the command device
"OFF/ON" to clear up the instance table.
Verifying the CCI instance number
CCI provides a way to verify the number of "temporary allocations (1 0)" and
"actual allocations (1 1)" on the instance table so that you can confirm
validity of the CCI instance number in use. The horcctl -DI command
shows the number of CCI instances since HORCM was started as follows.
Example without command device security:
2-4
CCI software environment
Command Control Interface User and Reference Guide

 Loading...
Loading...











