61
Ste
Command
Remarks
5. Apply the ACL to an
SNMP community, group
or user.
• SNMPv1/v2c community:
snmp-agent community { read | write }
community-name [ mib-view view-name ]
[ acl acl-number | acl ipv6
ipv6-acl-number ] *
• SNMPv1/v2c group:
snmp-agent group { v1 | v2c }
group-name [ read-view read-view ]
[ write-view write-view ] [ notify-view
notify-view ] [ acl acl-number | acl ipv6
ipv6-acl-number ] *
• SNMPv3 group:
snmp-agent group v3 group-name
[ authentication | privacy ] [ read-view
read-view ] [ write-view write-view ]
[ notify-view notify-view ] [ acl acl-number
| acl ipv6 ipv6-acl-number ] *
• SNMPv1/v2c user:
snmp-agent usm-user { v1 | v2c }
user-name group-name [ acl acl-number |
acl ipv6 ipv6-acl-number ] *
• SNMPv3 user:
snmp-agent usm-user v3 user-name
group-name [ [ cipher ]
authentication-mode { md5 | sha }
auth-password [ privacy-mode { 3des |
aes128 | des56 } priv-password ] ] [ acl
acl-number | acl ipv6 ipv6-acl-number ] *
For more information about
SNMP, see Network
Management and
Monitoring Configuration
Guide.
SNMP login control configuration example
Network requirements
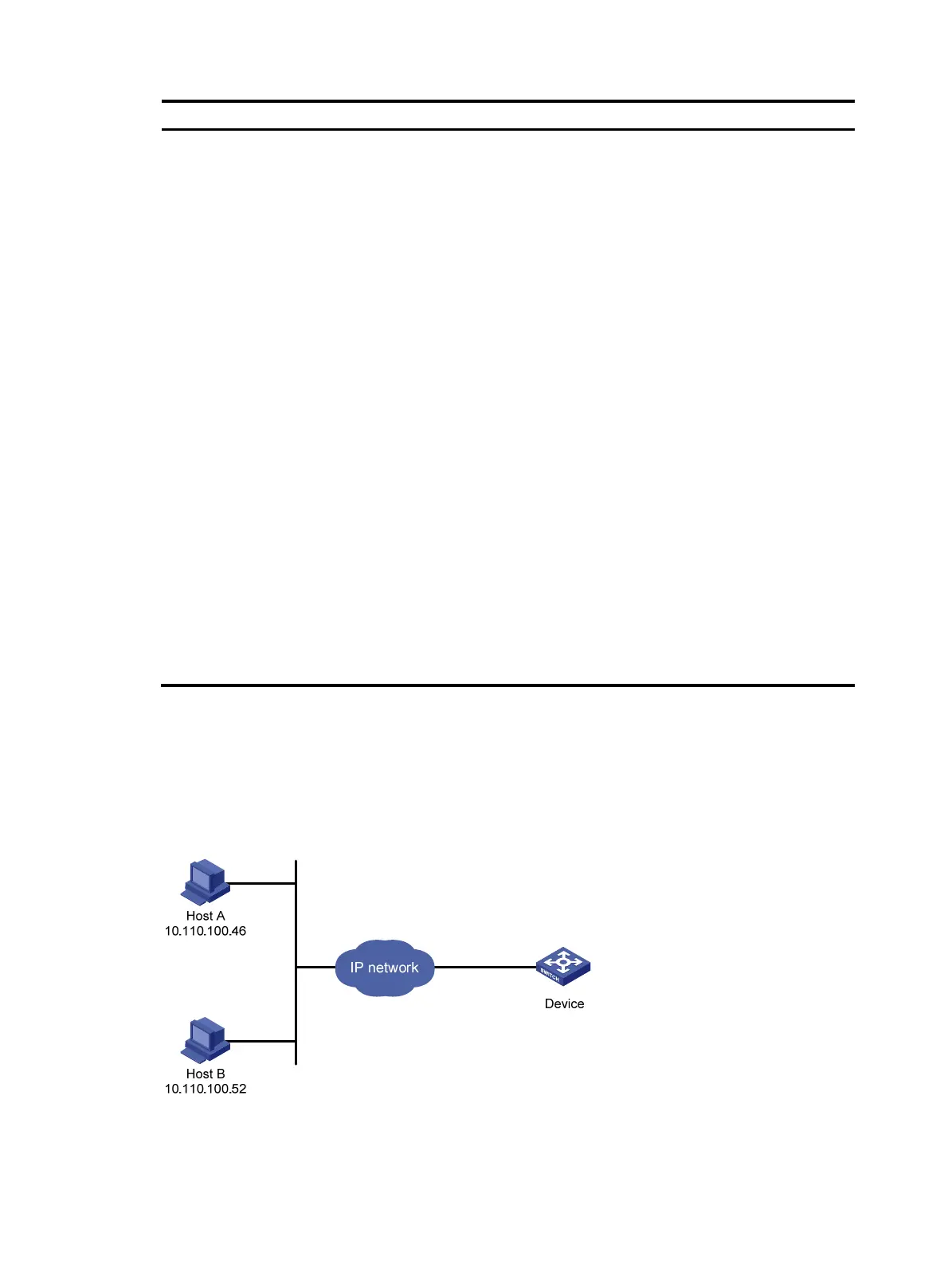
As shown in Figure 24, configure the device to allow only NMS users from Host A and Host B to access.
Figure 24 Network diagram

 Loading...
Loading...