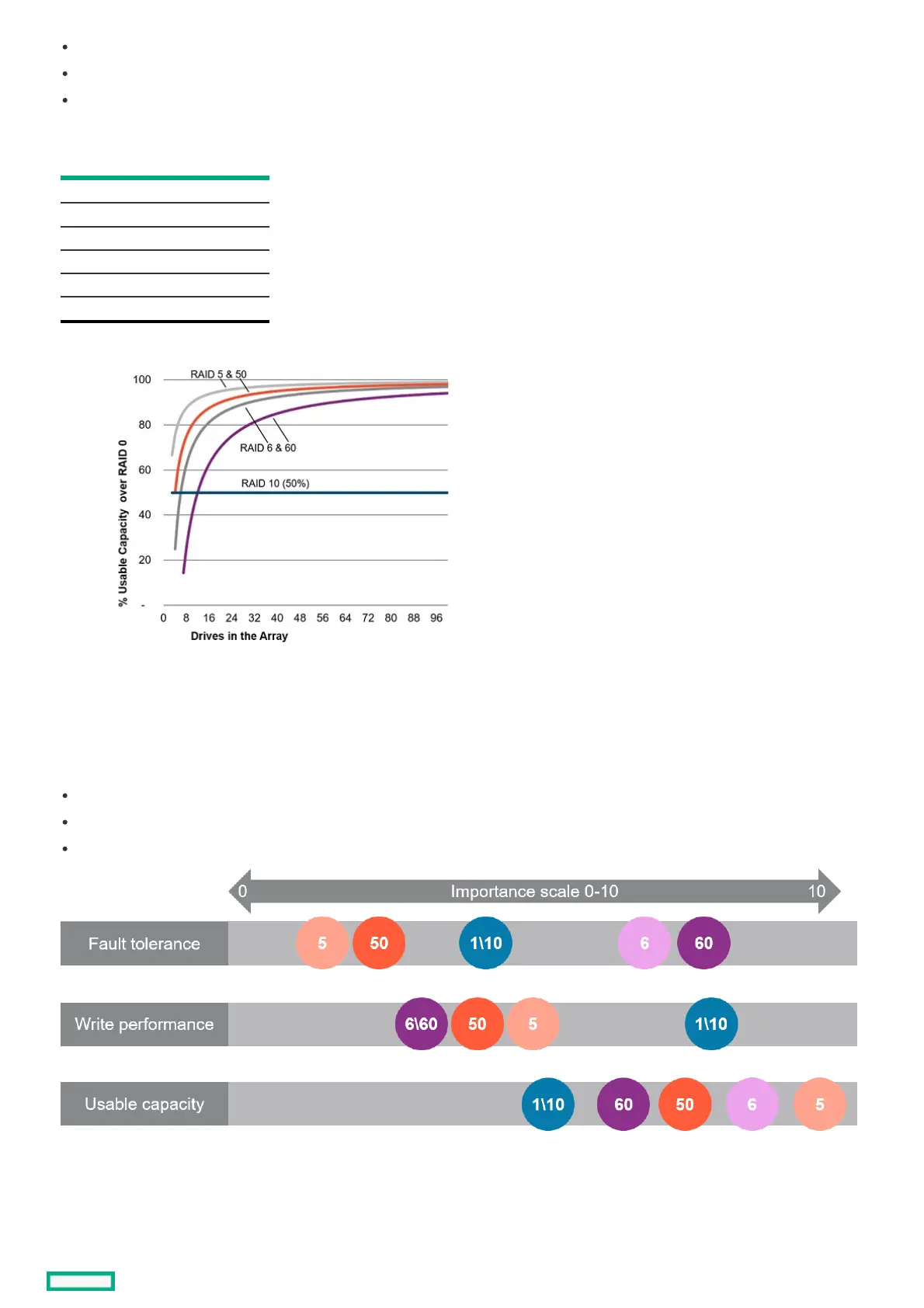
The usable capacity for RAID 10 remains flat with larger arrays.
The usable capacity for RAID 5, 50, 6, and 60 increases with larger arrays.
RAID 50 and RAID 60 assumes two parity groups.
Note the minimum drive requirements for the RAID types, as shown in the table below.
RAID typeRAID type Minimum number of drivesMinimum number of drives
RAID 0 1
RAID 10 2
RAID 5 3
RAID 6 4
RAID 50 6
RAID 60 8
Supported RAID levels may vary based on the controller model.
Selecting RAID for the storage solutionSelecting RAID for the storage solution
The chart in this section shows the relevance of the RAID type to the requirements of your environment. Depending on your requirements, you should optimize the
RAID types as follows:
RAID 6/60: Optimize for fault tolerance and usable capacity.
RAID 1/10: Optimize for write performance.
RAID 5/50: Optimize for usable capacity.
Mixed mode (RAID and JBOD)Mixed mode (RAID and JBOD)
Mixed mode allows for any drive to be a member of a logical drive (logical volume or RAID volume), unconfigured and hidden from the operating system, or in a

 Loading...
Loading...