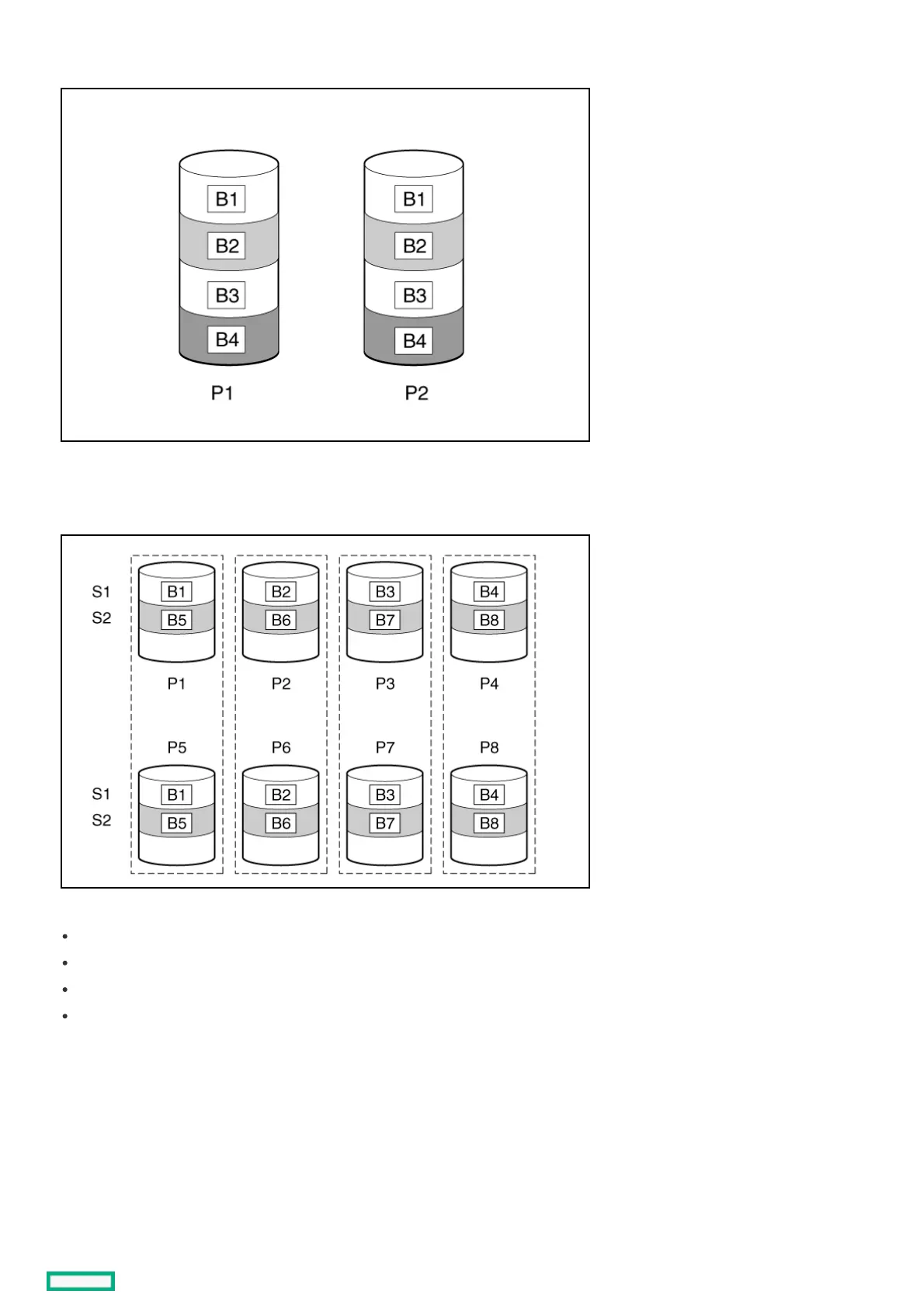
When the array contains only two physical drives, the fault-tolerance method is known as RAID 1.
The maximum number of drives supported for RAID 1 is 32.
When the array has more than two physical drives, drives are mirrored in pairs, and the fault-tolerance method is known as RAID 1+0 or RAID 10. If a physical
drive fails, the remaining drive in the mirrored pair can still provide all the necessary data. Several drives in the array can fail without incurring data loss, as long as
no two failed drives belong to the same mirrored pair. The total drive count must increment by 2 drives. A minimum of four drives is required.
The maximum number of drives supported for RAID 10 is 32.
This method has the following benefits:
It is useful when high performance and data protection are more important than usable capacity.
This method has the highest write performance of any fault-tolerant configuration.
No data is lost when a drive fails, as long as no failed drive is mirrored to another failed drive.
Up to half of the physical drives in the array can fail.
Read load balancingRead load balancing
In each mirrored pair or trio, the controller balances read requests between drives based upon individual drive load.
This method has the benefit of enabling higher read performance and lower read latency.
ParityParity

 Loading...
Loading...