Service Manual UHF3 (350-400MHz) Information
215
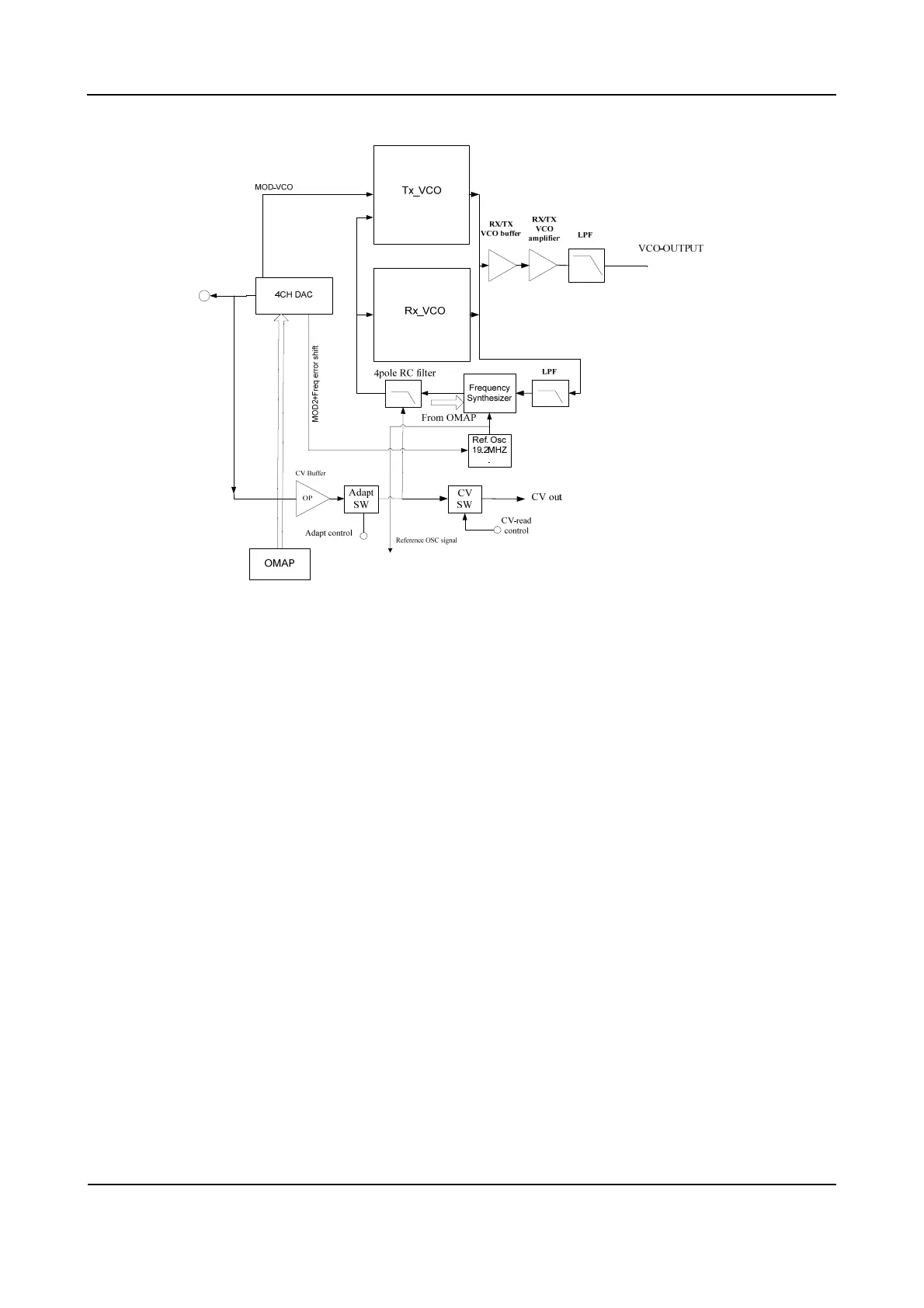
Figure 9-4 Diagram of FGU
9.3.1 Working Principle of PLL
The 19.2MHz frequency generated by the reference crystal oscillator goes to PLL for division,
generating the reference frequency (i.e. step frequency f1). Meanwhile, the frequency generated by
VCO generates another frequency (f2) through the frequency divider in PLL. Then frequencies f1 and
f2 are compared in the phase detector (PD), to generate continuous pulse current. The current goes to
the loop filter for RC integration, and is then converted to CV voltage. Then the CV voltage is sent to
the varactor of VCO. It adjusts the output frequency of VCO directly until the CV voltage becomes
constant. Then the PLL is locked, and the stable frequency output by VCO goes to the TX-RX channel
after passing through two buffer amplifiers.
9.3.2 Working Principle of VCO
VCO employs Colpitts oscillator circuit (the RX oscillator circuit is composed of D102, D103, D106,
D107 and L112; the TX oscillator circuit is composed of D108, D109, D110, D101 and L117). It obtains
different output frequencies by changing the varactor's control voltage (i.e. CV voltage).
There are two types of VCO: TX VCO and RX VCO. Both types control EMD22 to switch operating
status via OMAP. RX VCO is composed of the oscillator loop and Q104, to provide LO signal. TX VCO

 Loading...
Loading...