S
MART
AXIS P
RO
/L
ITE
U
SER
'
S
M
ANUAL
FT9Y-B1378 11-11
11: M
ODBUS
C
OMMUNICATION
Communication Protocol
This section describes the communication frame format used for Modbus RTU communication.
Communication Frame Format
Request from Modbus Master
ACK Reply from Modbus Slave
NAK Reply from Modbus Slave
Note: Note: Idle means no data flowing on the communication line.
Communication Frame Format
RTU mode requires a minimum of 3.5-character-long idle time between frames to determine the beginning of a frame. The
SmartAXIS Modbus master sends requests at idle intervals of 5ms, which can be changed in the Function Area Settings dialog box.
Slave No.
The SmartAXIS can be assigned slave numbers 1 through 247. In the 1:1 communication using RS232C, the same slave number
must be set in the master and the SmartAXIS.
Slave No. 0 is reserved for broadcast slave number and is used to write the same data to all Modbus slaves. In this case, the
Modbus slaves do not send a reply to the master.
Modbus Communication NG Reply Error Code
One of the following error codes is stored in NAK reply.
01h: Function code error (unsupported function code)
02h: Access destination error (address out of range, address+device quantity out of range)
03h: Device quantity error, 1-bit write data error
CRC
RTU mode uses CRC check codes.
• Modbus RTU Mode — Calculating the CRC-16 (cyclic redundancy checksum)
Calculate the BCC using CRC-16 for the range from the slave number to the byte immediately before the BCC. The generation
polynomial is: X
16
+ X
15
+ X
2
+ 1.
1. Take the exclusive OR (XOR) of FFFFh and the first 1-byte data at the slave number.
2. Shift the result by 1 bit to the right. When a carry occurs, take the exclusive OR (XOR) of A001h, then go to step 3.
If not, directly go to step 3.
3. Repeat step 2, shifting 8 times.
4. Take the exclusive OR (XOR) of the result and the next 1-byte data.
5. Repeat step 2 through step 4 up to the byte immediately before the BCC.
6. Swap the higher and lower bytes of the result of step 5, and store the resultant CRC-16 to the BCC (CRC) position. (Example:
1234h → 34h, 12h)
Idle
3.5 characters
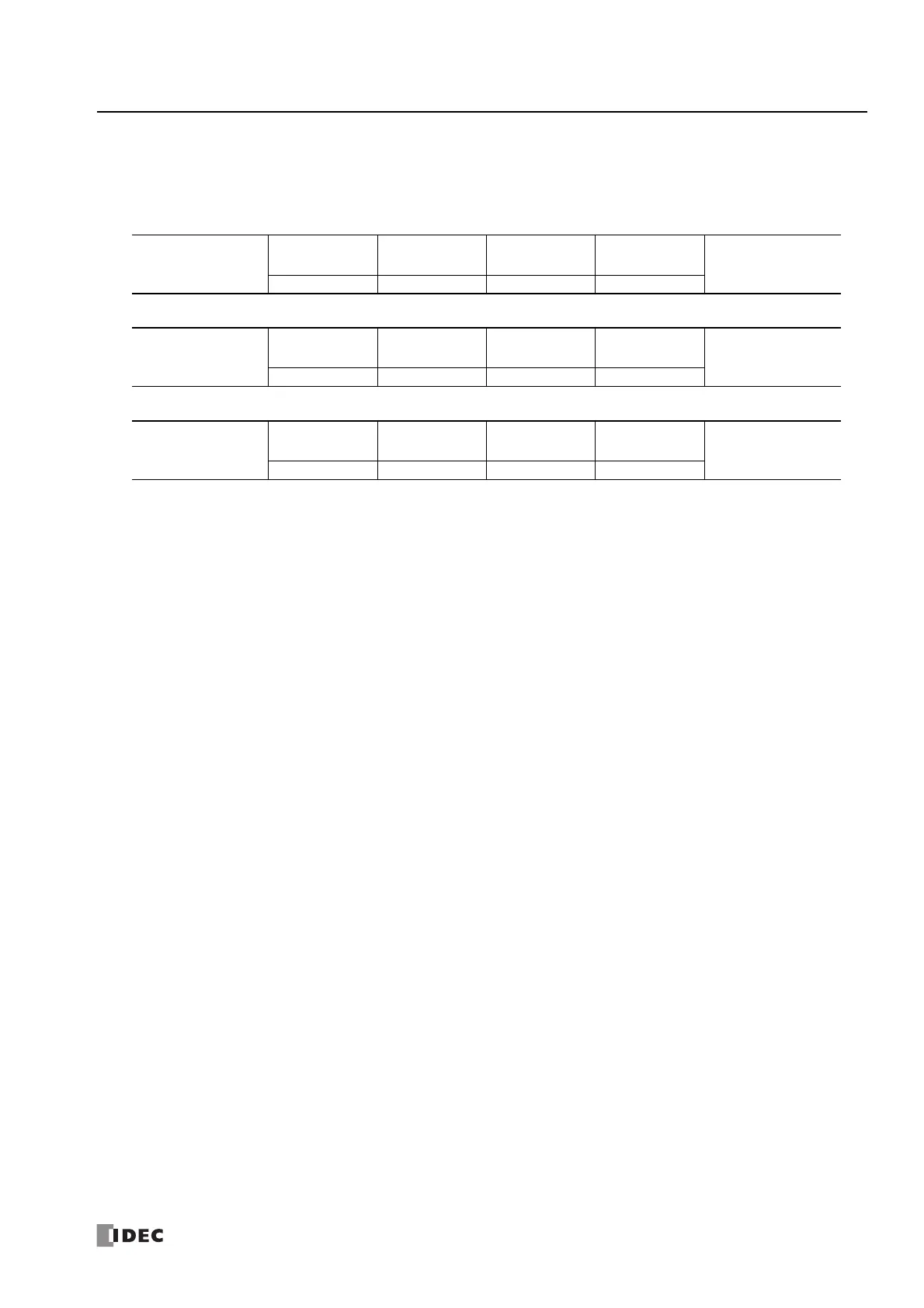
Slave No. Function Code Data CRC
Idle
3.5 characters
1 byte 1 byte 2 bytes
Idle
3.5 characters
Slave No. Function Code Data CRC
Idle
3.5 characters
1 byte 1 byte 2 bytes
Idle
3.5 characters
Slave No.
Function Code +
80H
Error Code CRC
Idle
3.5 characters
1 byte 1 byte 1 byte 2 bytes
 Loading...
Loading...