Intel
®
Core
TM
2 Duo E6400, E4300, and Intel
®
Pentium
®
Dual-Core E2160 Processor—Intel®
Reference Thermal Solution
Intel
®
Core
TM
2 Duo E6400, E4300, and Intel
®
Pentium
®
Dual-Core E2160 Processor
TDG October 2007
36 Order Number: 315279 - 003US
The performance of the heatsink could improve with more airflow. However, the final
intended thermal solution including, heatsink, airflow source, TIM and attach
mechanism must be validated by system integrators.
Developers who wish to design thermal solutions for the processor, need to ensure that
it meets the processor thermal specifications as stated in the processor datasheet and
follow the recommended motherboard component keep-out as shown in Figure 20. This
keep-out will ensure that the processor thermal solution will not interfere with the
voltage regulator components. In addition to this, a thermal solution design must meet
the maximum component heights as specified by the PICMG 1.3 (http://picmg.org/
specifications.stm). It should be noted that due to the vertical orientation of the
heatsink, there might be some stresses in the board due to the heatsink weight.
5.3 ATX/BTX form factors
For information regarding the Intel Thermal/Mechanical Reference Design thermal
solution and design criteria for the ATX and BTX form factor, refer to the Intel
®
Core™2
Duo Desktop Processor E6000 Sequence Thermal and Mechanical Design Guidelines.
5.4 Altitude
The reference heatsink solutions will be evaluated at sea level. However, many
companies design products that must function reliably at high altitude, typically 1,500
m [5,000 ft] or more. Air-cooled temperature calculations and measurements at sea
level must be adjusted to take into account altitude effects like variation in air density
and overall heat capacity. This often leads to some degradation in thermal solution
performance compared to what is obtained at sea level, with lower fan performance
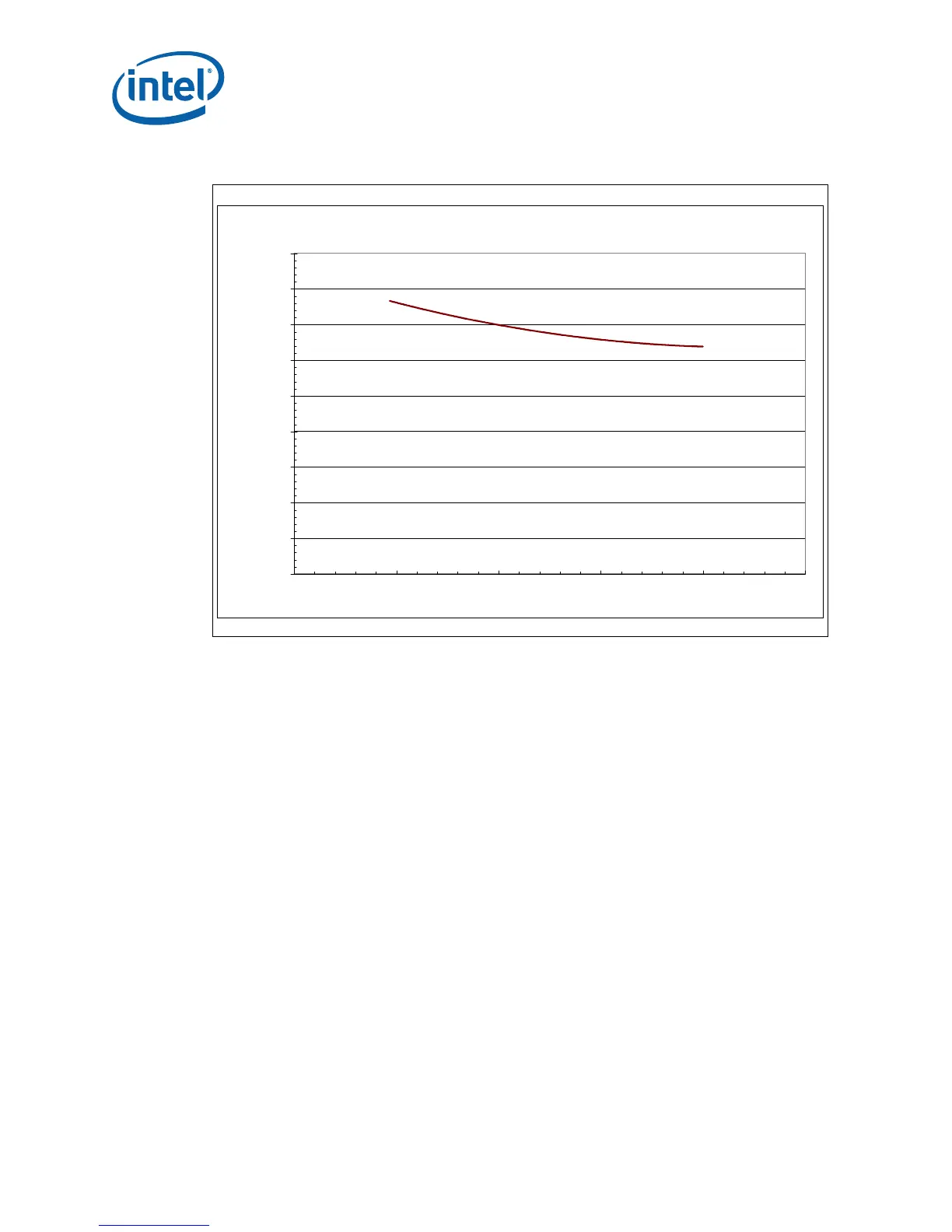
Figure 12. PICMG 1.3 Heatsink Performance
PICMG 1.3 Heatsink Psi_ca
0.000
0.050
0.100
0.150
0.200
0.250
0.300
0.350
0.400
0.450
10 15 20 25 30 35
Airflow Throught the Fins (CFM)
Thermal Resistance (
o
C/W)

 Loading...
Loading...











