7-2 Intel
®
Pentium
®
III Processor with 512KB L2 Cache Dual Processor Platform Design Guide
7.2.2 Active Voltage Positioning
The new VRM design now includes active voltage positioning. Active voltage positioning allows the VRM
to improve handling of load transients. This is accomplished by adjusting the output voltage of the VRM
as a function of the load current so the voltage is optimally positioned for system transients. In addition,
the better system transients response allows for fewer output capacitors, which reduces the VR footprint
and reduces cost. Finally, this new design should reduce the number of design changes as frequencies
increase.
In order for a platform to support AGTL compatible processors, it must meet the new VRM guidelines
outlined in the VRM 8.5 DC-DC Converter Design Guidelines. In particular, the voltage regulator must be
able to respond to the transient and static loads specified in Figure 7-2.
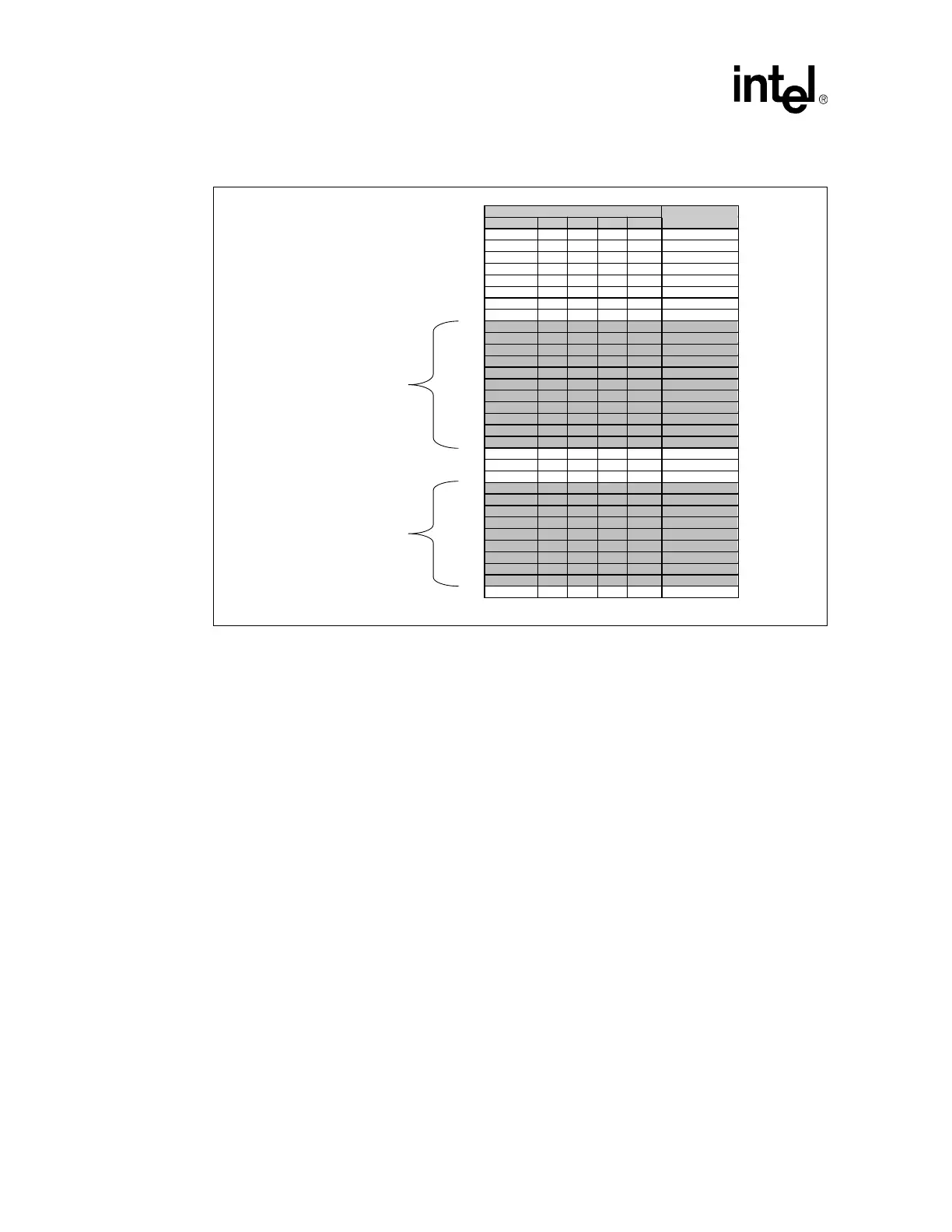
Figure 7-1. Voltage Range Comparison
Voltage Identification Code at Processor Pins Vcc
CORE
VID25mV VID3 VID2 VID1 VID0 (V
DC
)
0 010 0 1.05
1 010 0 1.075
0 001 1 1.10
1 001 1 1.125
0 001 0 1.15
1 001 0 1.175
0 000 1 1.20
1 000 1 1.225
0 0 0 0 0 1.25
1 0 0 0 0 1.275
0 1 1 1 1 1.30
1 1 1 1 1 No Core
0 1 1 1 0 1.35
1 1 1 1 0 1.375
0 1 1 0 1 1.40
1 1 1 0 1 1.425
0 1 1 0 0 1.45
1 1 1 0 0 1.475
0 1 0 1 1 1.50
1 101 1 1.525
0 101 0 1.55
1 101 0 1.575
0 1 0 0 1 1.60
1 1 0 0 1 1.625
0 1 0 0 0 1.65
1 1 0 0 0 1.675
0 0 1 1 1 1.70
1 0 1 1 1 1.725
0 0 1 1 0 1.75
1 0 1 1 0 1.775
0 0 1 0 1 1.80
1 010 1 1.825
Intel
®
Pentium
®
III
Processor with
512KB L2 Cache
Voltage Range
Intel
®
Pentium
®
III
Processor (CPUID
068xh) Voltage
Range
 Loading...
Loading...











