10. Note the offset-compensated reference DMM reading, and calculate limits based on DMM6500
specifications (use the reference DMM reading as the expected value and verify the DMM6500
accuracy from the calculated reference DMM current).
11. Repeat steps 1 through 10 for all ranges (10 µA through 100 mA).
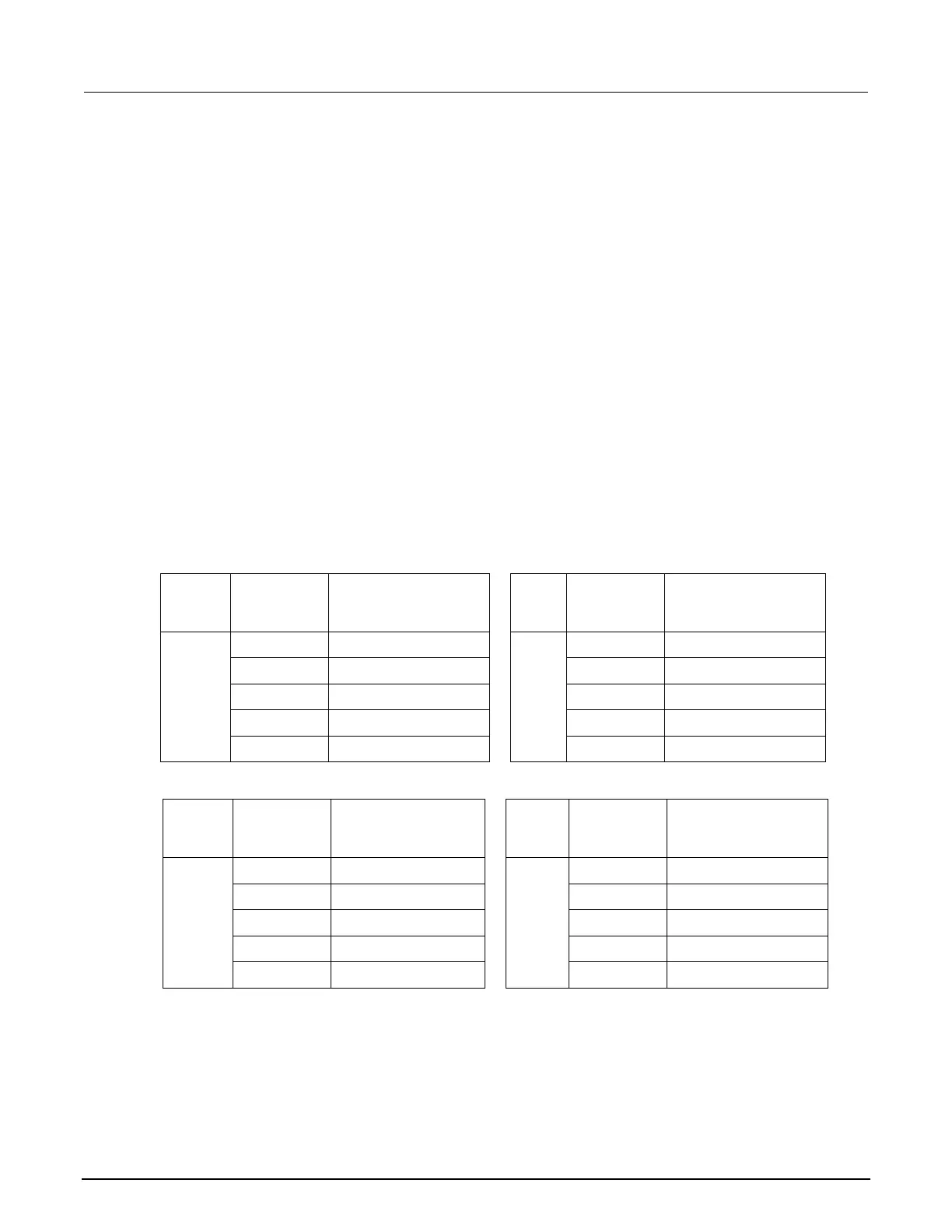
Test limit calculation for 10 µA to 100 mA ranges
The following tables list nominal test current for 10 µA to 100 mA ranges. Test limits must be
calculated relative to actual current, as determined by the reference digital multimeter (DMM)
measurement. For example, using a specification of 60 ppm of reading + 9 ppm of range on the
10 mA range, the reference DMM measures 5.00012 mA on the nominal 5 mA test.
Specification tolerance = 5.00012 (mA) 60 ppm + 10 (mA) 9 ppm = 0.000390072 mA
Lower test limit = 5.00012 – 0.000390072 = 4.999729928 mA
Upper test limit = 5.00012 + 0.000390072 = 5.000510072 mA
Although the specification tolerance calculated above from the actual test current differs slightly from
the values listed in the table (based on nominal value), this difference is generally much smaller than
the measurement uncertainty and can be ignored. As a result, the test limits can be calculated from
the table specification tolerance as:
Lower test limit = 5.00012 – 0.00039 = 4.99973 mA
Upper test limit = 5.00012 + 0.00039 = 5.00051 mA

 Loading...
Loading...