THE BLUE BOX LT TROUBLESHOOTING WITH AN OSCILLOSCOPE 65
LCDBBTSWO03Sept08
USING AN OSCILLOSCOPE TO TEST
A DIGITAL BUS (Continued)
With a partially bad device, it is sometimes hard to 6.
distinguish because it looks very similar to a good bus.
One has to carefully examine the waveform and see
if the baseline is centered at Zero.
A bad device causes the baseline to shift and become 7.
unbalanced. (Baseline is not at Zero anymore). Below
are three examples where A & B are not equal.
Use the Bus-Splitting technique to find the problem.8.
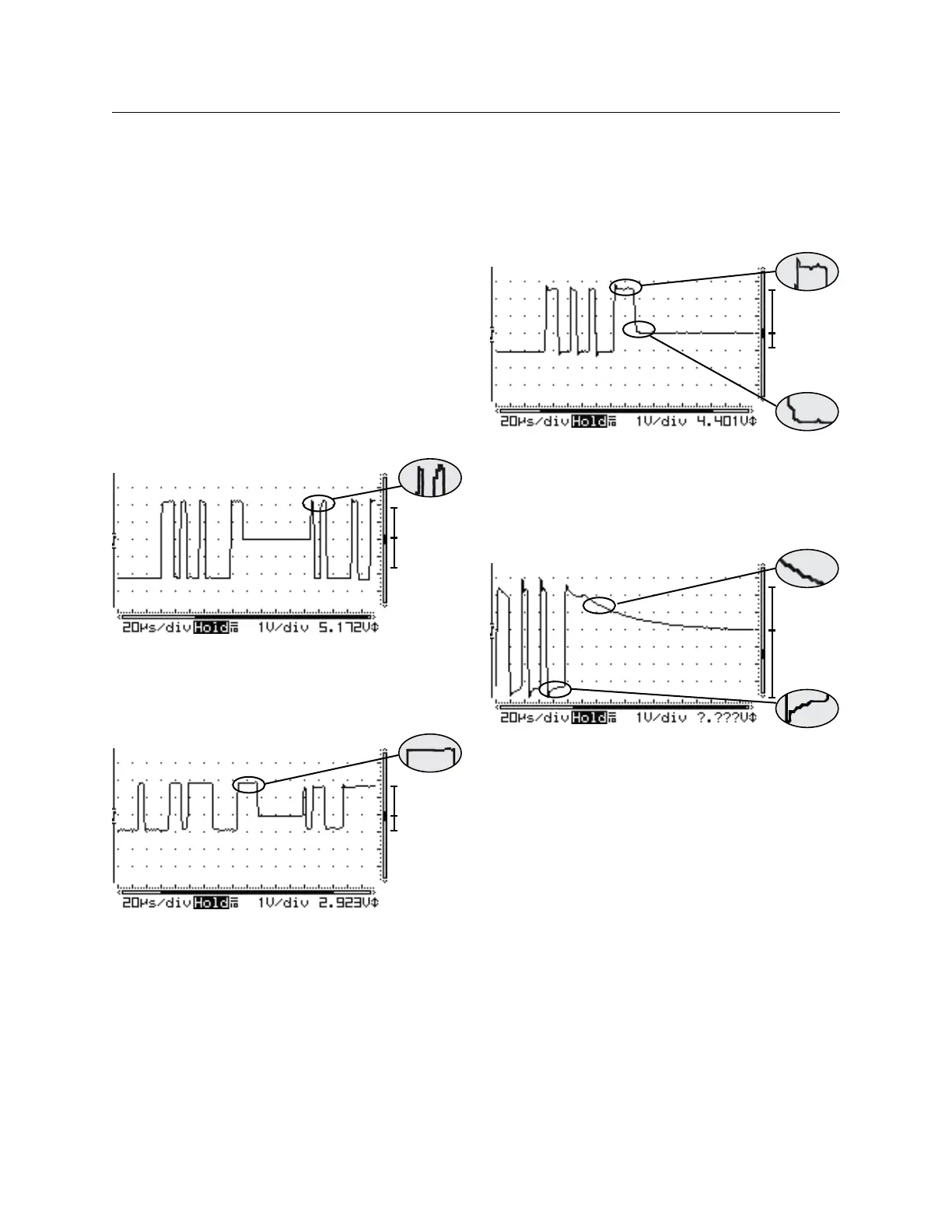
+V = -V
Problematic: Ringing on peak of square wave means the bus
is missing one or both terminators. +V = -V means no bad
devices.
+V ≠ -V
Problematic: Clean square waves mean the bus is termi-
nated. But +V ≠ -V means damaged devices. Usually caused
by over-voltage: static, lightning, or line voltage.
+V ≠ -V
Problematic: Ringing and dampened square wave means
that the bus is missing one or both terminators. +V ≠ -V
means damaged devices. Usually caused by over-voltage:
static, lightning, or line voltage.
+V ≠ -V
Problematic: Ringing and extremely dampened square wave
means the bus is missing one or both terminators. +V ≠
-V means damaged devices. Usually caused by over-voltage:
static, lightning, or line voltage.
 Loading...
Loading...