Lode BV Excalibur Sport
9
P (
W)
RPM
200
30 120
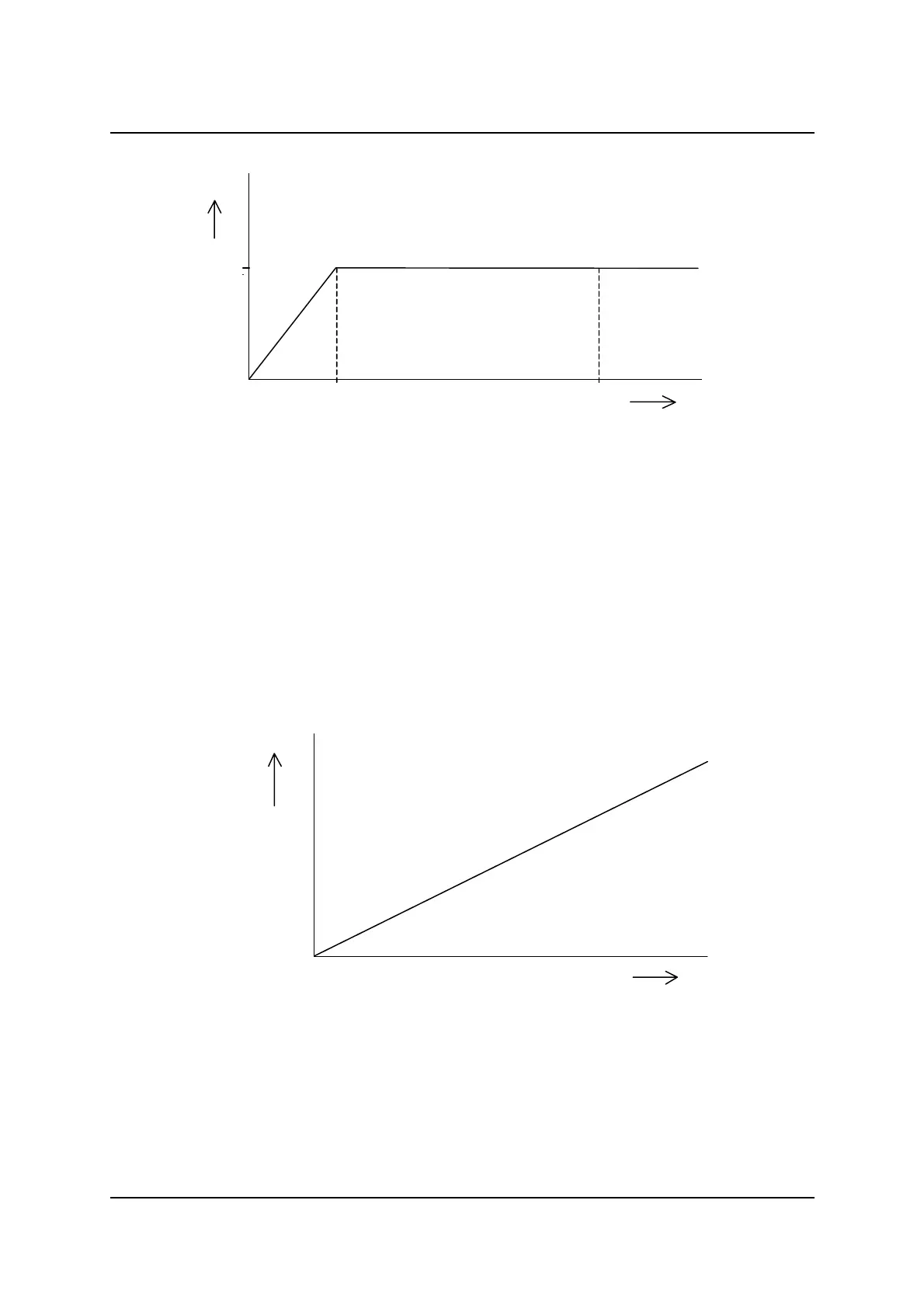
Linear Ergometry: RPM dependent ergometry. The linear relation is determined by the
relation between the torque (T) and the pedaling speed (RPM) (see Fig 3). As a result of this
linear relation the workload (W) is RPM dependent (see Fig. 4 Linear ergometry ). This
means the faster the test subject is cycling, the higher the delivered workload. The linear
braking principle is usually used in mechanical ergometers.
RPM
TORQUE
Fig 2: Hyperbolic ergometry: at a pedaling speed between
30 – 150 RPM the workload is constant 200 W.
Fig 3: Linear ergometry
 Loading...
Loading...