Chapter 15 PID Function (Built-in function)
15 - 35
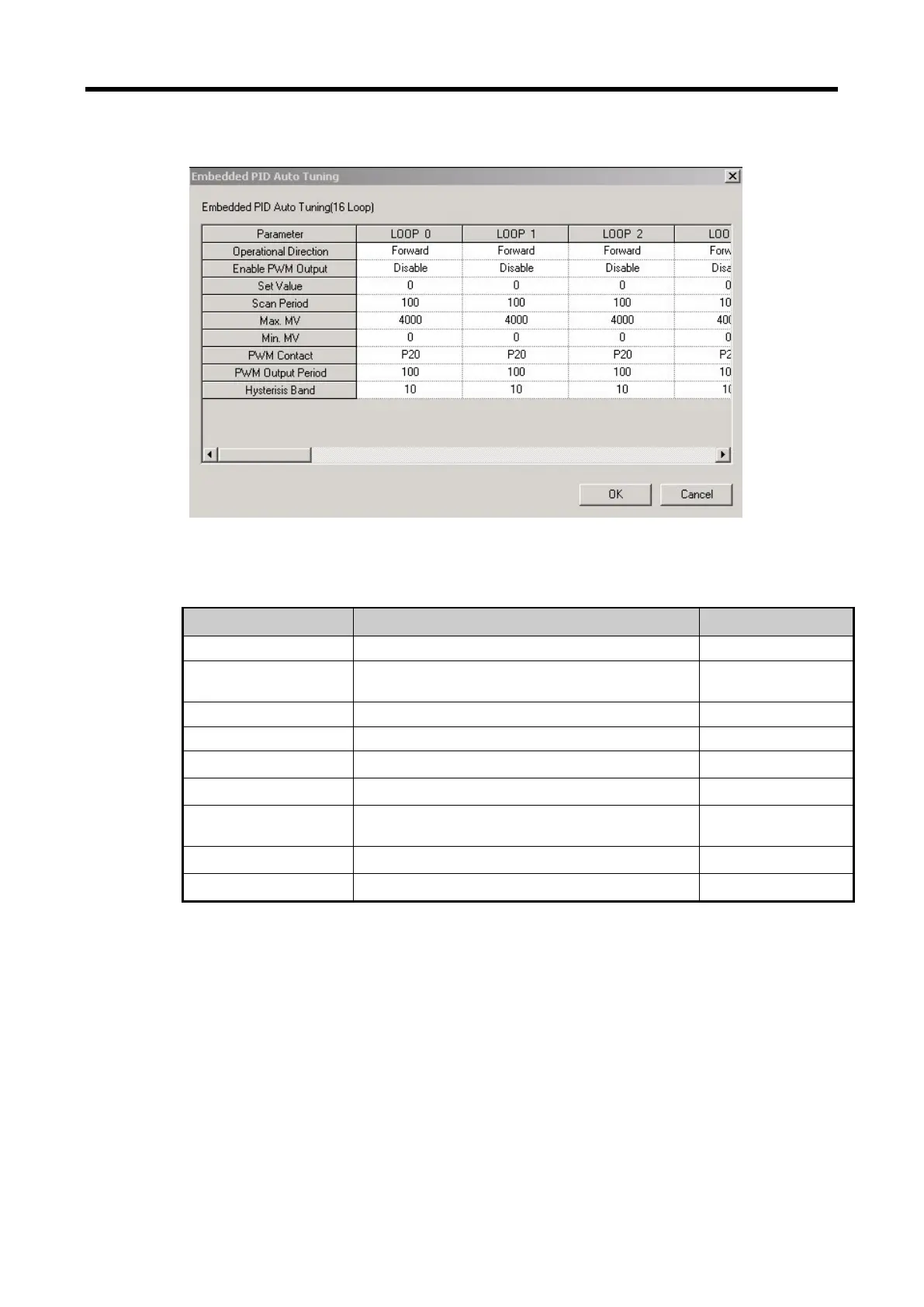
(b) If selecting auto-tuning, it shows the parameter setting window as seen in Figure 15.17.
<Figure 15.17 Built-in auto-tuning function parameter setting window>
(c) Input items
Table shows the items to set in auto-tuning parameter window and the available scopes.
Set the run direction of auto-tuning.
Set whether to set PWM output of MV enabled/
disabled.
Set auto-tuning operation time.
Set the max. MV in control.
Set the min. MV in control.
Designate the junction to which PWM output is
output.
Set the output cycle of PWM output.
Set the hysteresis of auto-tuning MV.
< Table 15.11 Auto-tuning function parameter setting items>
(2) Description of auto-tuning parameters and how to set them
(a) RUN direction
RUN direction is to set the direction of auto-tuning run of a loop. The available option is forward
or reverse. The former (forward) means that PV increase when MV increases while the latter
(reverse) means PV decreases when MV increases. For instance, a heater is a kind of forward
direction system because PV (temperature) increases when output (heating) increases. A
refrigerator is a kind of reverse direction system in which PV (temperature) decreases when
output increases.

 Loading...
Loading...