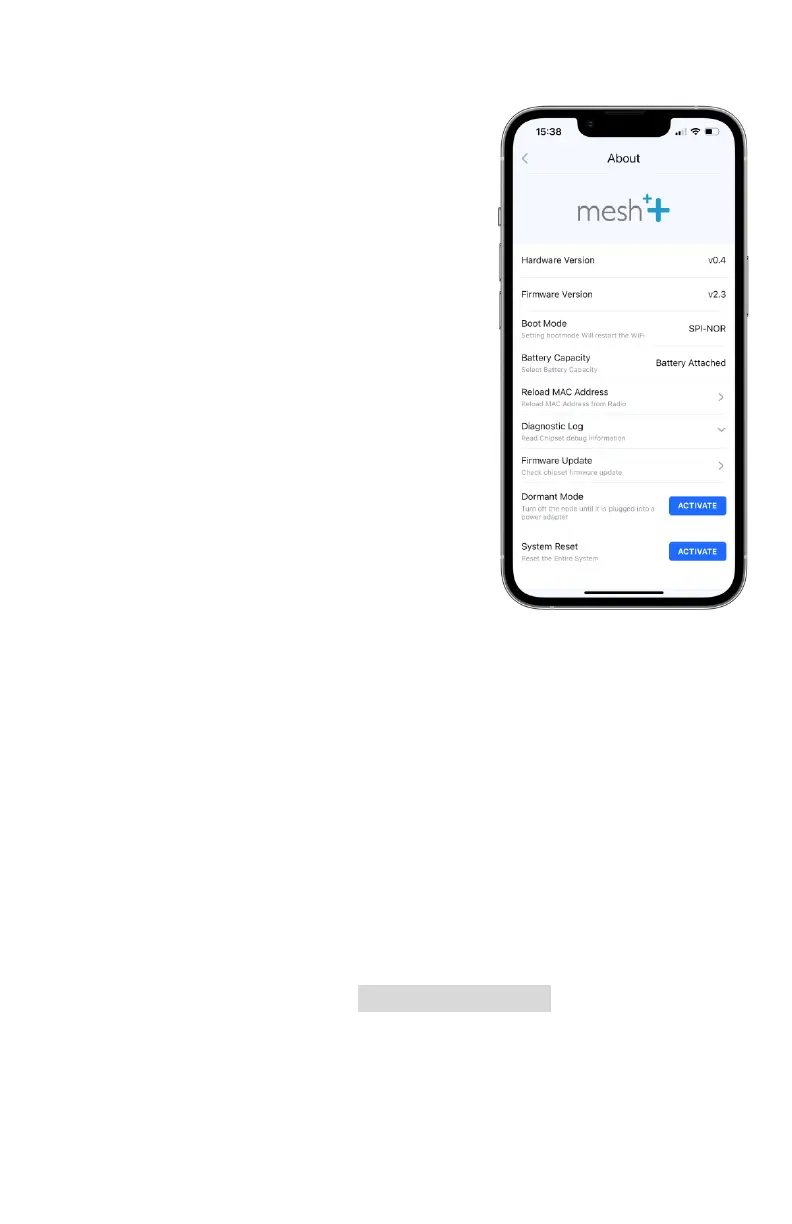
3. Boot Mode: allows the user to boot the node’s system
from an alternative source; SPI-NOR is standard
4. Battery Capacity: recalibrates
battery level readout for more
accuracy based on how many
battery packs are installed into
the node, or if it is powered
without them
5. Reload MAC address: reads the
MAC address from the onboard
flash and broadcasts that MAC
address over Bluetooth. If the
MAC address of a node is
modified on the networking
subsystem itself, this will allow
the new address to be
broadcast over Bluetooth.
6. Diagnostic Log: provides
real-time diagnostics through
various chipsets on the PCB
7. Firmware Update: updates the node’s Bluetooth firmware
to the latest version available
8. Dormant Mode: turns the node off entirely, including
Bluetooth signal, until it is plugged into any power source.
Once it receives power, it will automatically turn on. This is
used for shipping or storing nodes for long periods
9. System reset: resets the power controller and bluetooth
firmware. This includes data on battery level, various
system voltages, MAC address broadcasting, and any
power management. It can be used as a debugging step
iv. Verify that the Firmware Version is v2.1 or higher to use the
Diagnostic Log. Tap the Firmware Update button to check
for new updates. If any are available, select whether your
node is being powered via battery (default) or 12V directly.
Ensure that your mobile device stays within 3 m (10 ft) of the
node to prevent failure.
 Loading...
Loading...