6-26 Cardiology
The LV Mass (A-L) is calculated.
If height and weight have been input already, LV Mass-I(A-L) is calculated.
LV Mass (T-E)
Study Items
Tools Descriptions Operations
LVAd sax Epi
Left Ventricular Epicardial Area at Papillary
Muscle level at end-diastole in Short-axis view
Area in 2D General
Measurements
LVAd sax Endo
Left Ventricular Endocardial Area at Papillary
Muscle level at end-diastole in Short-axis view
a
Semi-major axis from widest minor axis radius to
apex
Distance in 2D General
Measurements
d
Truncated semi-major axis from widest minor
axis radius to mitral annulus plane
Study Results
Except for values in upper table, the following results can be obtained in this study:
Tools Descriptions Formulae
LV Mass (T-E) Left Ventricular Mass *1
LV MASS-I (T-E)
Index of Left
Ventricular Mass
See LV Mass-I formula in “Left Ventricular Mass (LV
Mass)”
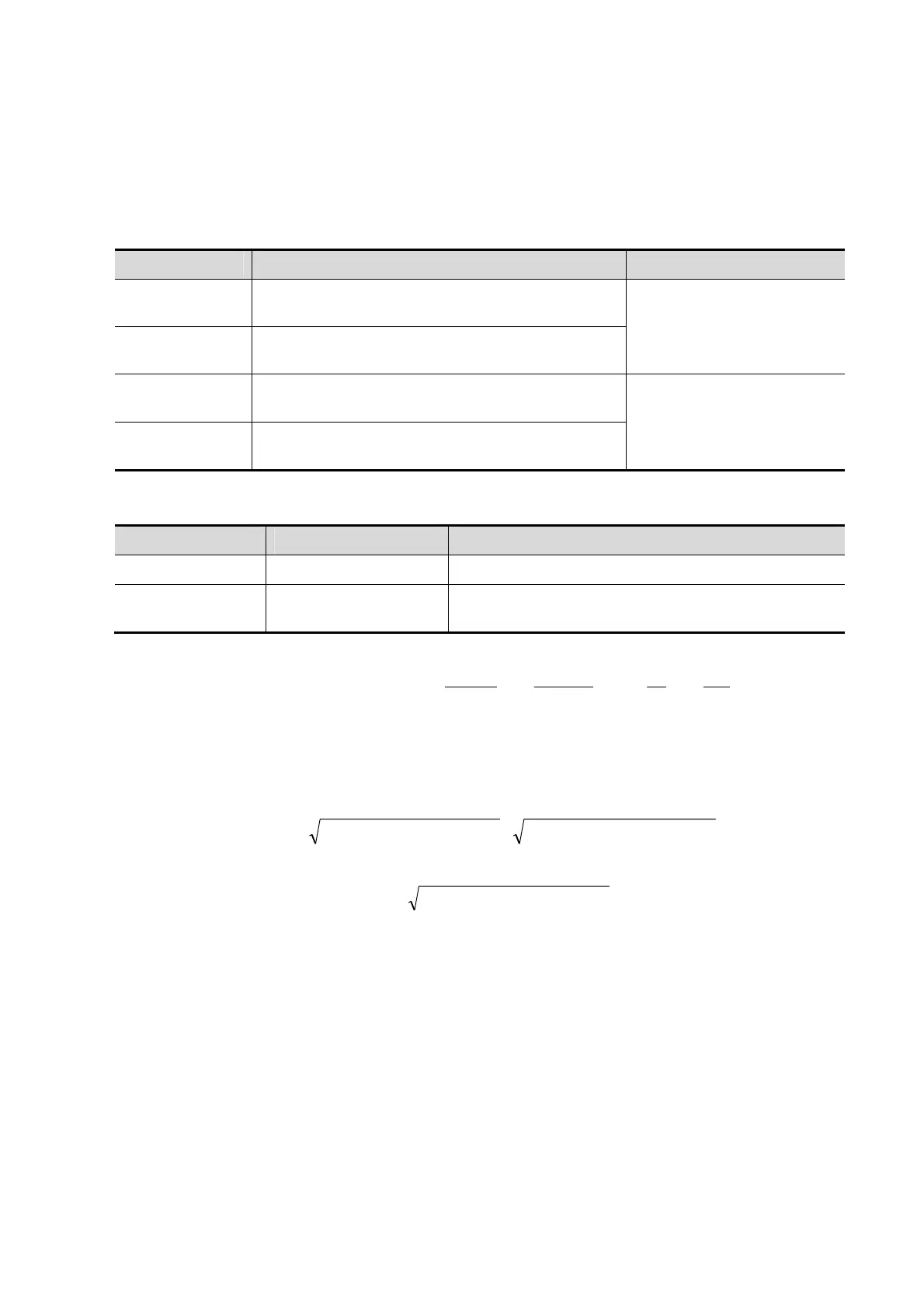
*1 means:
)}
3a
d
-d+
3
2a
(b-]
t)+3(a
d
-d+
3
t)2(a
[t)+(b{1.05 Mass(g) LV
2
3
2
2
3
2
×
+
××=
π
Where, units of a, b, d, t are cm.
a: Semi-major axis from widest minor axis radius to apex
d: Truncated semi-major axis from widest minor axis radius to mitral annulus plane
t: Thickness of the myocardium
))/Endo(cmSax (LVAd - ) /)Epi(cmsax (LVAd (cm)t
22
ππ
=
b: Short axis radius, usually measured where the radius is largest.
))/Endo(cmSax (LVAd b(cm)
2
π
=
Operating Procedures
1. Select [LV Mass(T-E)] in the measurement menu.
2. In short-axis view at papillary muscle level at end diastole, measure the following parameters:
Endocardium area: LVAd sax Endo;
Epicardium area LVAd sax Epi
3. Measure a and d.
The LV Mass(T-E) is calculated.
If height and weight have been input already, LV Mass-I(T-E) is calculated.
 Loading...
Loading...