522
DEG, DEGP
Program Example
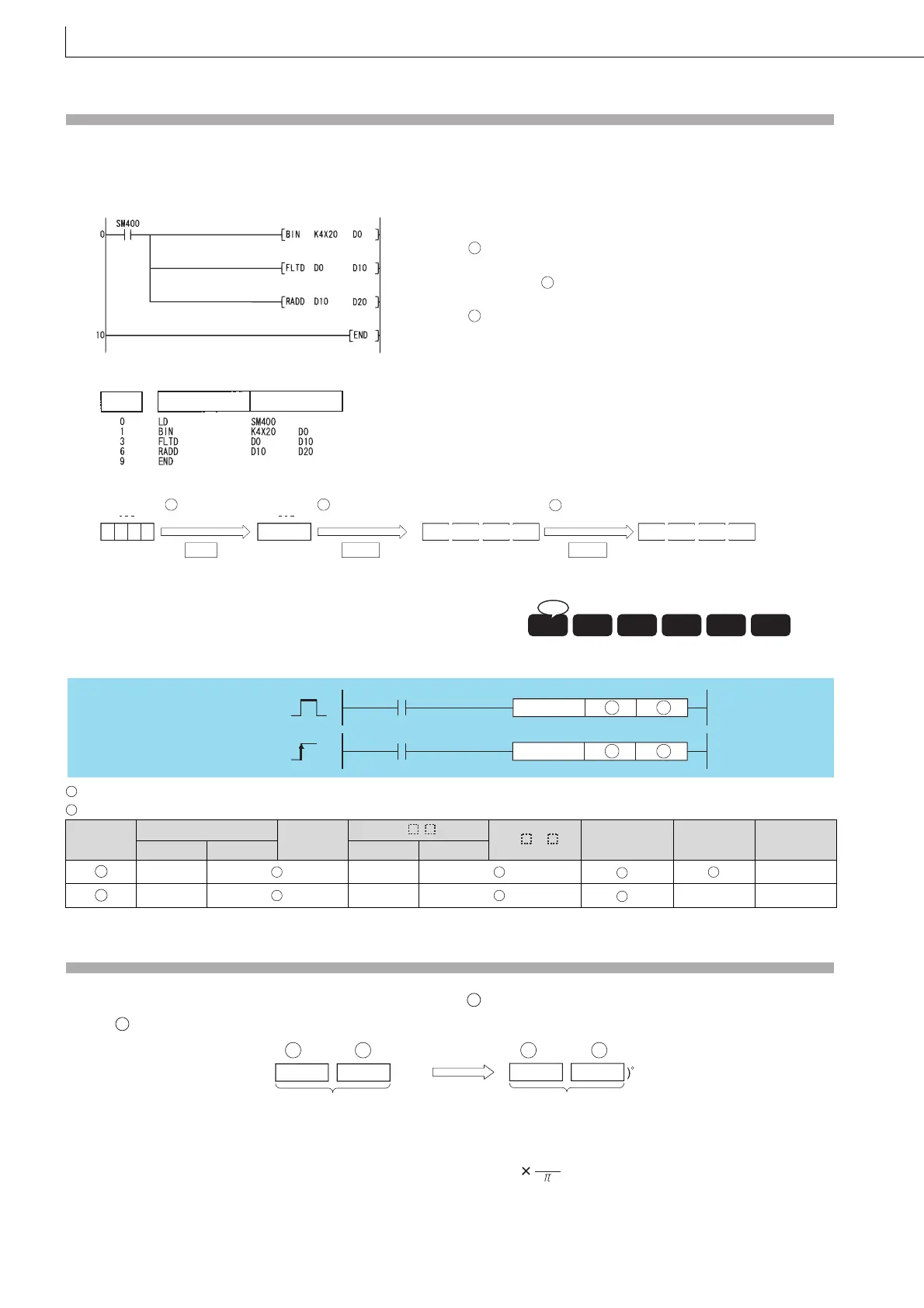
(1) The following program converts the angle set by the 4 BCD digits at X20 to X2F to radians, and stores results as 64-bit
floating decimal point type real number at D20 to D23.
[Ladder Mode]
[List Mode]
[Operations involved when X20 to X2F designate a value of 120]
: Radian angle to be converted to degrees or head number of the devices where the radian angle is stored (real number)
: Head number of the devices where the value converted in degrees will be stored (real number)
*1: Applicable for the Universal model QCPU, LCPU.
Function
(1) Converts units of angle size from radian units designated by to angles, and stores result at device number designated
by .
(2) The conversion from radians to angles is performed according to the following equation:
7.12.15 DEG, DEGP Conversion from floating-point radian to angle
(Single precisio n)
7.12.15
DEG, DEGP
• Basic model QCPU: The serial number (first five digits) is
"04122" or later.
Setting
Data
Internal Devices
R, ZR
J\
U\G
Zn
Constants
E
Other
Bit Word Bit Word
–– ––
*1
––
–– ––
*1
–– ––
Inputs an angle to be converted into a
radian value ( ).
Converts the converted angle into a
radian value ( ).
Converts the input angle into a 64-bit
floating-point real number (
).
1
2
3
Step Instruction Device
X2F
BCD value
0
D0
120
X20
Conversion
to BIN
BIN
b15 b0
BIN value
120
Conversion to
floating-point
FLTD
Conversion
to radian
RADD
D11
120
D10D13 D12
D21
2.094395···
D20D23 D22
1
3
2
Basic
Process
High
performance
Redundant
Universal
LCPU
Ver.
Command
Command
DEGP
DEG
DEGP
DEGSD
S D
S
D
S
D
S
D
+1 +1
S DS D
32-bit floating-point
real number
(
32-bit floating-point
real number
( )rad
Degree unit = Radian unit
180

 Loading...
Loading...











