526
POWD, POWDP
Program Example
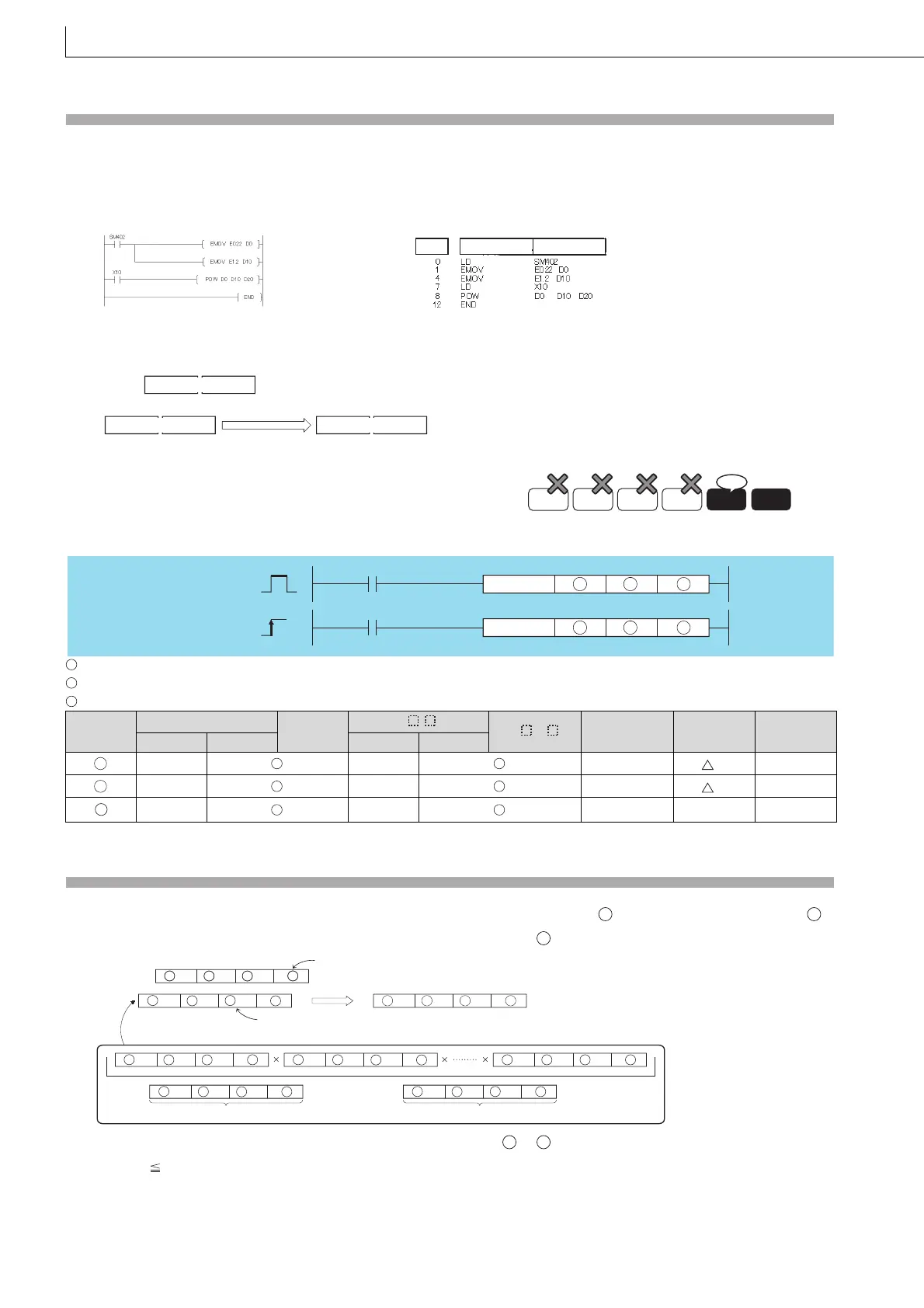
(1) The following program raises the 32-bit floating-point data type real number data specified by D0 and D1 to the data
specified by (D10 and D11)th power, when X10 is turned on. Then the program stores the operation result into D20 and
D21.
[Ladder Mode] [List Mode]
[Operation]
: Exponentiation recipient data or head number of the devices where the exponentiation recipient data are stored (real number)
: Exponentiation data or head number of the devices where the data are stored (real number)
: Head number of the devices where the operation result will be stored (real number)
*1: Available only for real number
Function
(1) This instruction raises the 64-bit floating-point data type real number specified by to the number nth specified by
power, and then stores the operation result into the device specified by .
(2) The following shows the values to be specified by and stored into or
0, 2
-1022
| Set values (Storage values) | < 2
1024
(3) If the value resulted from the operation is -0 or an underflow occurs, the result will be processed as 0.
7.12.18 POW D, POWDP Exponentiation operati on on floating-point da ta
(Double preci sion)
7.12.18
POWD, POWDP
• QnU(D)(H)CPU, QnUDE(H)CPU: The serial number (first five
digits) is "10102" or later.
Setting
Data
Internal Devices
R, ZR
J\
U\G
Zn
Constants
E
Other
Bit Word Bit Word
–– –– ––
*1
––
–– –– ––
*1
––
–– –– –– –– ––
Step
Instruction
Device
Exponentiation
operation
D21 D20D1 D0
0.22 0.163
D11 D10
1.2
Basic
High
performance
Process
Redundant
Universal
LCPU
Ver.
POWD
POWDP
S1
S2
D
S1
S2
D
POWD
POWDP
Command
Command
S1
S2
D
S1
S2
D
S1
S2
D
64-bit floating-point data type real number 64-bit floating-point data type real number
raised to the power of is carried out.
Exponentiation recipient data
Exponentiation data
DDDD
+3 +2 +1
+3 +2 +1
+3 +2 +1+3 +2 +1
+3 +2 +1 +3 +2 +1
+3 +2 +1
+3 +2 +1
S1
S2
S2
S2
S2
S2
S1
S1
S1
S1
S1
S1
S1
S1
S1
S1
S1
S1
S1
S2 S2
S2
S1
S1
S1 S1 S1 S1
S1
S2

 Loading...
Loading...











