74 / 174
Service Manual Mitsubishi SQ-Series diesel engines
Version 08/2004
ENGLISH
PISTONS, CONNECTING RODS,
CRANKSHAFT AND CRANKCASE ENGINE MAIN PARTS
10.2.4 Crankcase
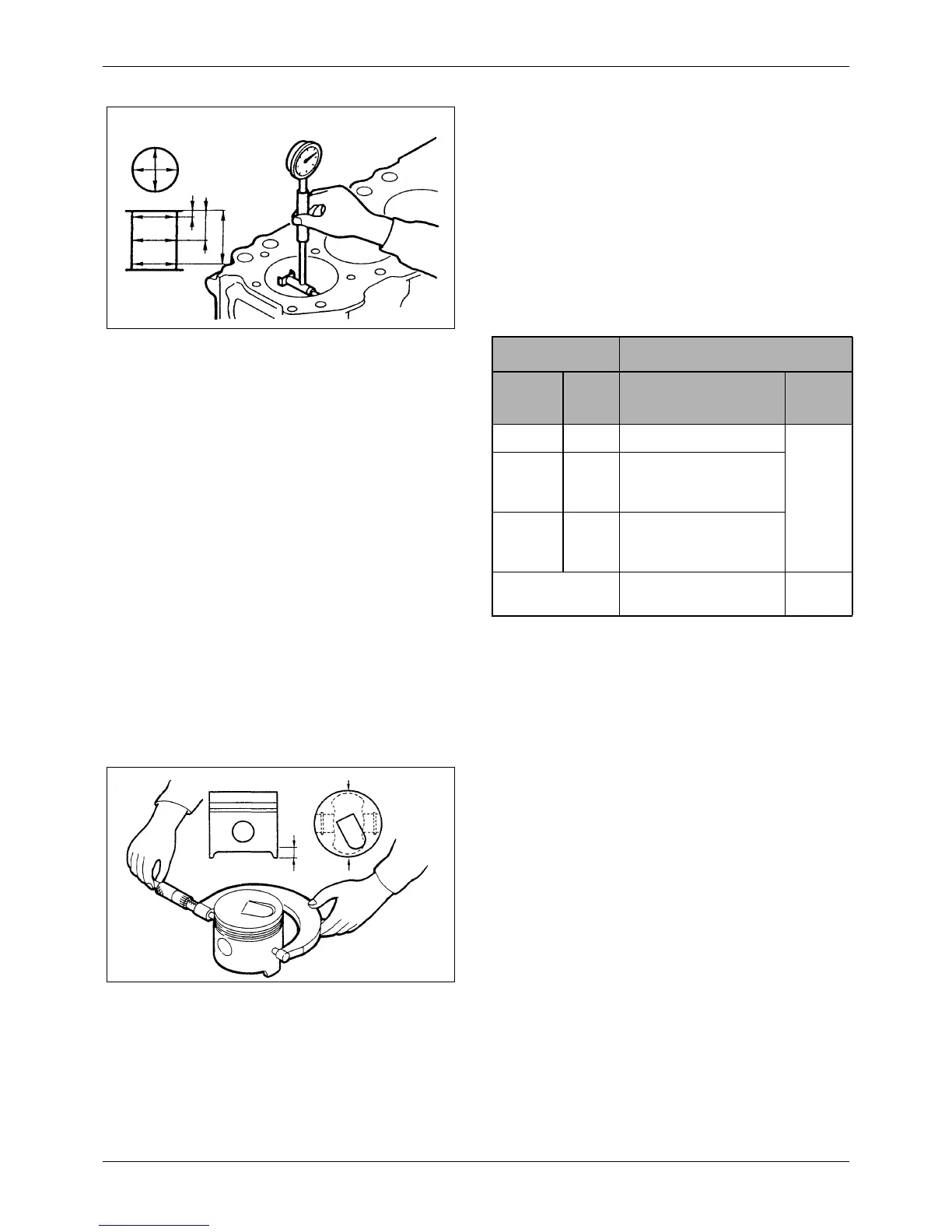
1. Checking crankcase bore
1) Measure the entire bore with a cylinder bore
gage having a dial indicator. Take
measurements at A, B and C positions in the
bore on axes 90° apart, as shown in the
illustration, to check the diameter, out-of-
round and taper. If the bores exceeds the
service limit for diameter, out-of-round and
taper, increase them for oversize pistons.
Unit: mm [in.]
2) Boring of cylinders
a There are two piston oversizes (0.25 mm
[0.0098 in.] and 0.50 mm [0.0197 in.] over
standard size) as listed above. Determine the
piston size to be used based on the largest
bore diameter of the cylinders.
b Measure the outside diameter of the piston to
be used.
c Based on the measurement of the piston
outside diameter, calculate the finishing
dimension to be achieved by boring.
A : Measured piston outside diameter selected
oversized piston) mm
B : Clearance between piston and cylinder
(standard value) 0.03 mm [0.0012 in.]
C : Honing allowance 0.04 mm [0.0016 in.] or
less
Finishing dimension = A + B - C
Figure 131 Checking crankcase bore
Measuring
points
Measuring
directions
Piston available Bore Diameter
Size
Size
Code
Assembly Standard
Service
Limit
Standard STD 88 [3.46 ]
+0.2
[+0.008]
0.25
[0.0098]
oversize
25 88.25 [3.4744 ]
0.50
[0.0197]
oversize
50 88.50 [3.4842 ]
Out-of-round and
taper of bores
0.015 [0.0006] or less __
+0.035
0
+0.0014
0
+0.035
0
+0.0014
0
+0.035
0
+0.0014
0
Figure 132 Measuring piston diameter
14 mm
[0.55 in.]
Perpendicular
to piston pin

 Loading...
Loading...