Nasuni Edge Appliance Initial Configuration Guide 8.3 33
Configuring the Nasuni Edge Appliance Network Settings
4. Also in the Network Interface Settings area, to configure each Traffic Group, click Edit beside
the Traffic Group. The Network Settings page appears.
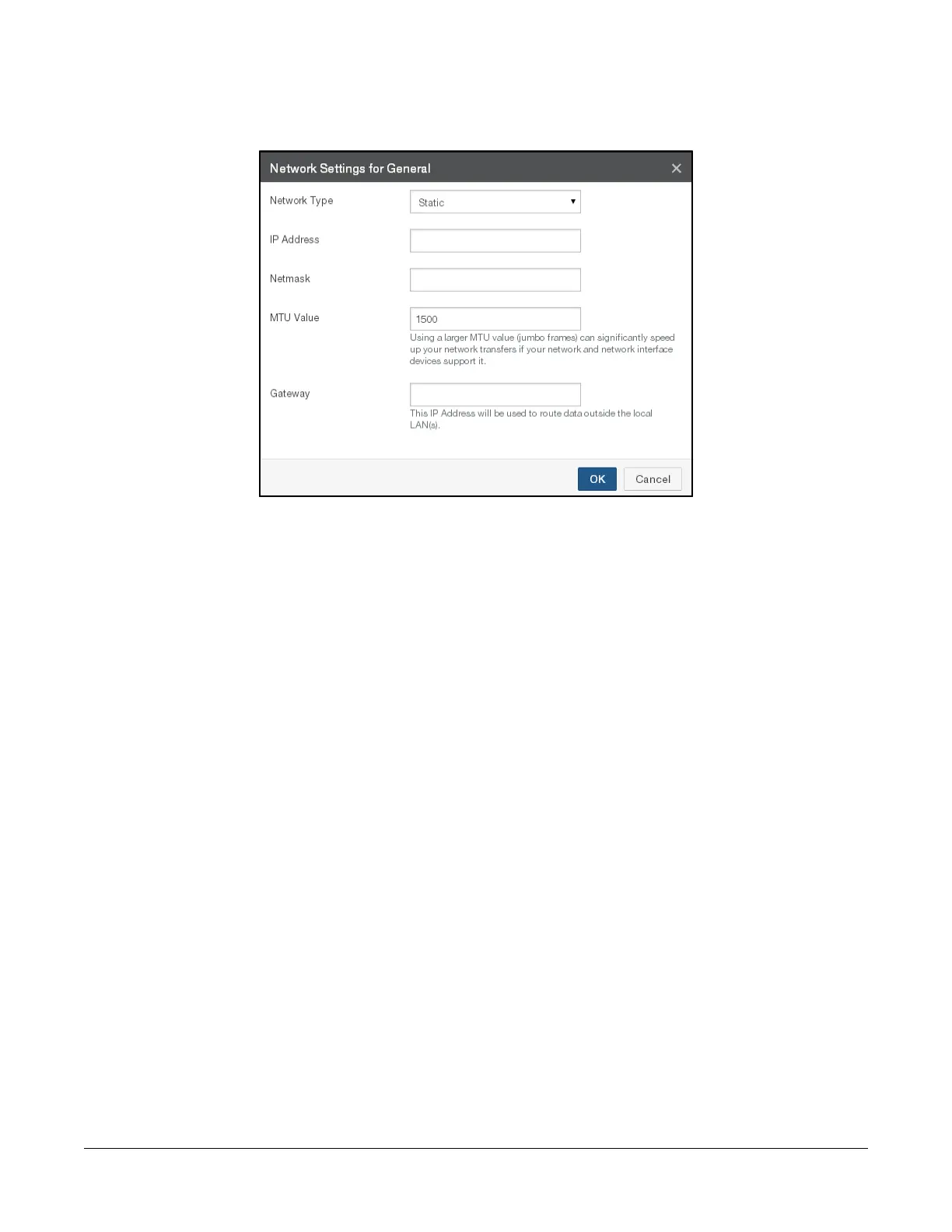
Figure 1-13: Network Settings page.
From the Network Type drop-down list, select either Static or DHCP.
Tip: For optimal performance, do not use DHCP.
If you select DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), the IP Address, Netmask, and MTU
Value fields become unavailable.
Note: DHCP may not be enabled on more than one traffic group.
If you select Static, you must provide Network Interface Settings and System Settings. See your IT
administrator for assistance. Enter the following information:
• Enter the static IP address in the IP Address text box. The address of a static device must
not already be present on the network. The Nasuni Edge Appliance verifies this and displays
an error if a collision is detected.
Note: If you define more than one static device, the Nasuni Edge Appliance checks that
the subnets specified do not appear more than once.
• Enter a netmask address in the Netmask text box.
• Enter the MTU value in the MTU Value text box.
Tip: MTU settings should not exceed 1500.
The maximum transmission unit (MTU) is the size (in bytes) of the largest protocol data unit
that the layer can pass onwards. A larger MTU brings greater efficiency, because each
packet carries more user data, while protocol overheads, such as headers, remain fixed; the
resulting higher efficiency means a slight improvement in the bulk protocol throughput. A
larger MTU also means processing fewer packets for the same amount of data. However,
large packets can occupy a slow link for some time, causing greater delays to following
packets, and increasing lag and minimum latency.
 Loading...
Loading...