17
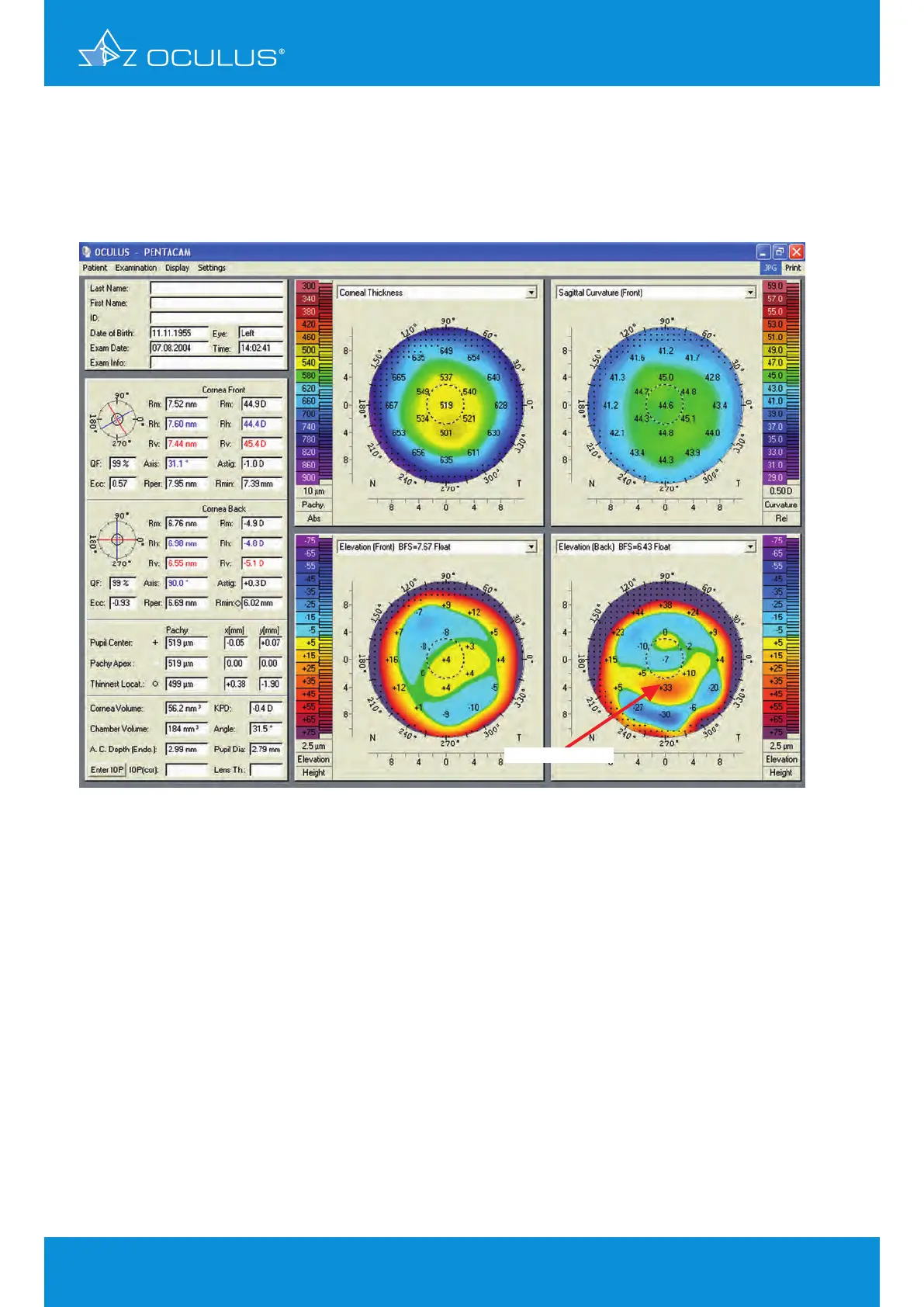
The left eye (Figure 10) indicates an inferior steepening, but a smooth anterior elevation map.
The reason for the thinning in the pachymetry map is the posterior elevation map, where there
are significant elevations of more than 30 μm. Note that the position of the thinning in the
pachymetry map and the highest spot on the elevation map are exactly at the same position.
This is an excellent example to document that topography or anterior elevation only does not
indicate keratoconus.
Figure 10: 4 Maps Selectable showing significant elevation in OS
significant elevation
5 Differences between Placido and
elevation-derived curvature maps
 Loading...
Loading...