7
C. The refractive index
For historical reasons, most Placido topographers and keratometers use the refractive index of 1.3375
for calculating corneal refractive power. However, this refractive index is actually incorrect even for
the untreated eye (n ≈ 1.332). It assumes the ratio between the anterior and posterior curvature of
the cornea to be constant. Many intraocular lens (IOL) power calculation formulas use the incorrect
‘K-reading’, necessitating empirical correction to obtain the correct IOL power even in normal cases.
Care should also be taken when using ‘K-readings’ from post-LASIK corneas or based on True Net
Power or ray tracing, as the resultant D readings will be out of range for the applied IOL calculation
formulas unless they are corrected for or converted into equivalent keratometer readings (EKR). Some
modern formulas are able to deal with the rather measured curvatures of the front and back surface
of the cornea, however.
D. Location of the principal planes
Calculation of corneal power by ray tracing involves sending parallel light through the cornea.
It must take into account that each light beam is refracted according to the refractive index
(1.376/1.336), the slope of the surfaces, and the exact location of refraction. This is necessary
because the principal planes of the anterior and posterior surface differ slightly from one another due
tocorneal thickness. The Pentacam® is able to measure the anterior as well as the posterior surface of
the cornea. This allows further corrections to be made. The Pentacam® provides a number of different
maps for predicting corneal power.
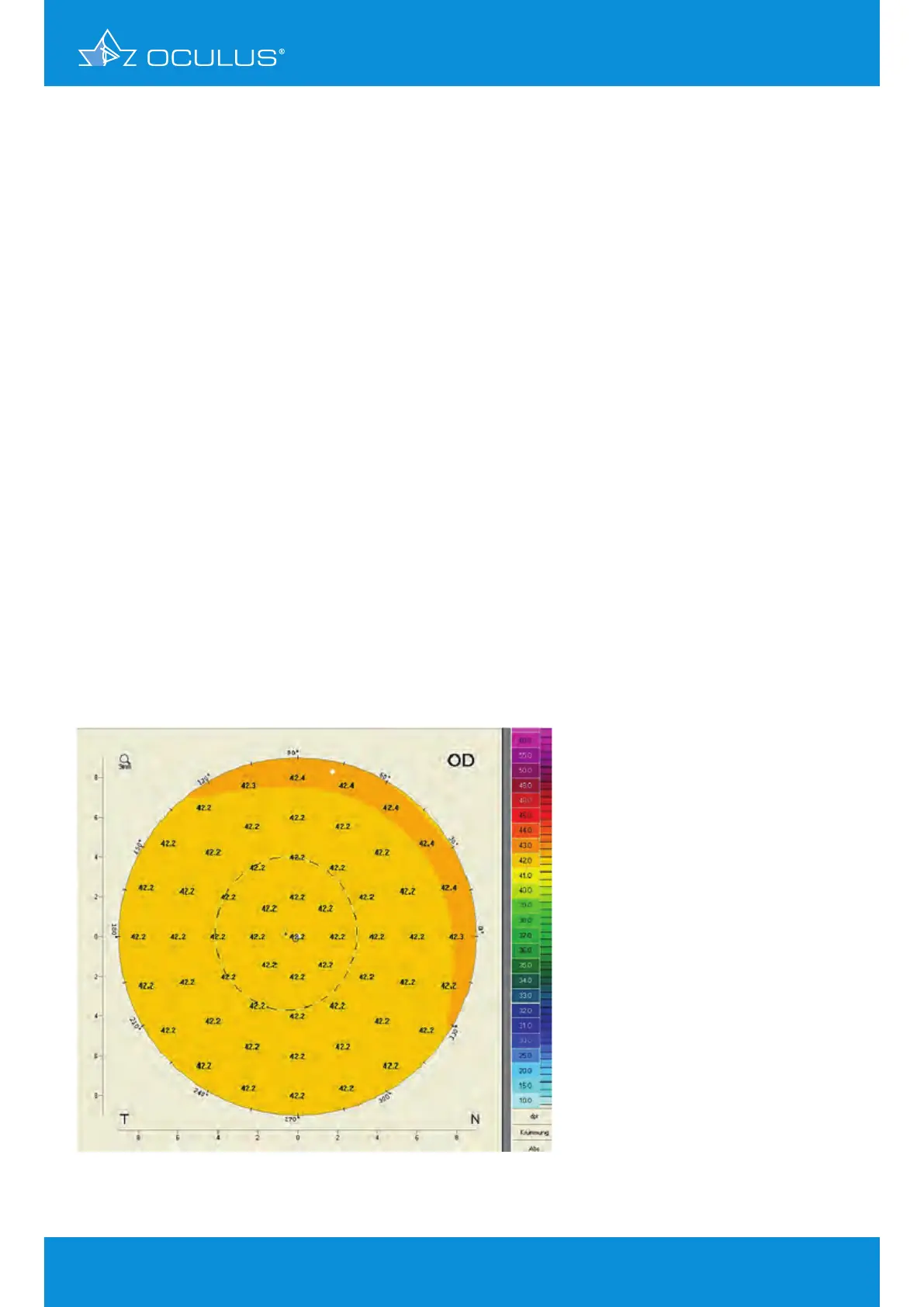
3.2 Sagittal power map (also called axial power map)
This is the common Placido style map with corneal power calculated using a refractive index of
1.3375 and the simple formula D = (1.3375-1)*(1000)/Rmm. It shows power values (Figure 1) similar
to those of other Placido topographers.
3 Differences between the various topography maps of Pentacam
®
Figure 1: Sagittal power map of a sphere, r= 8 mm
 Loading...
Loading...