fitting Piston Rings:
1.
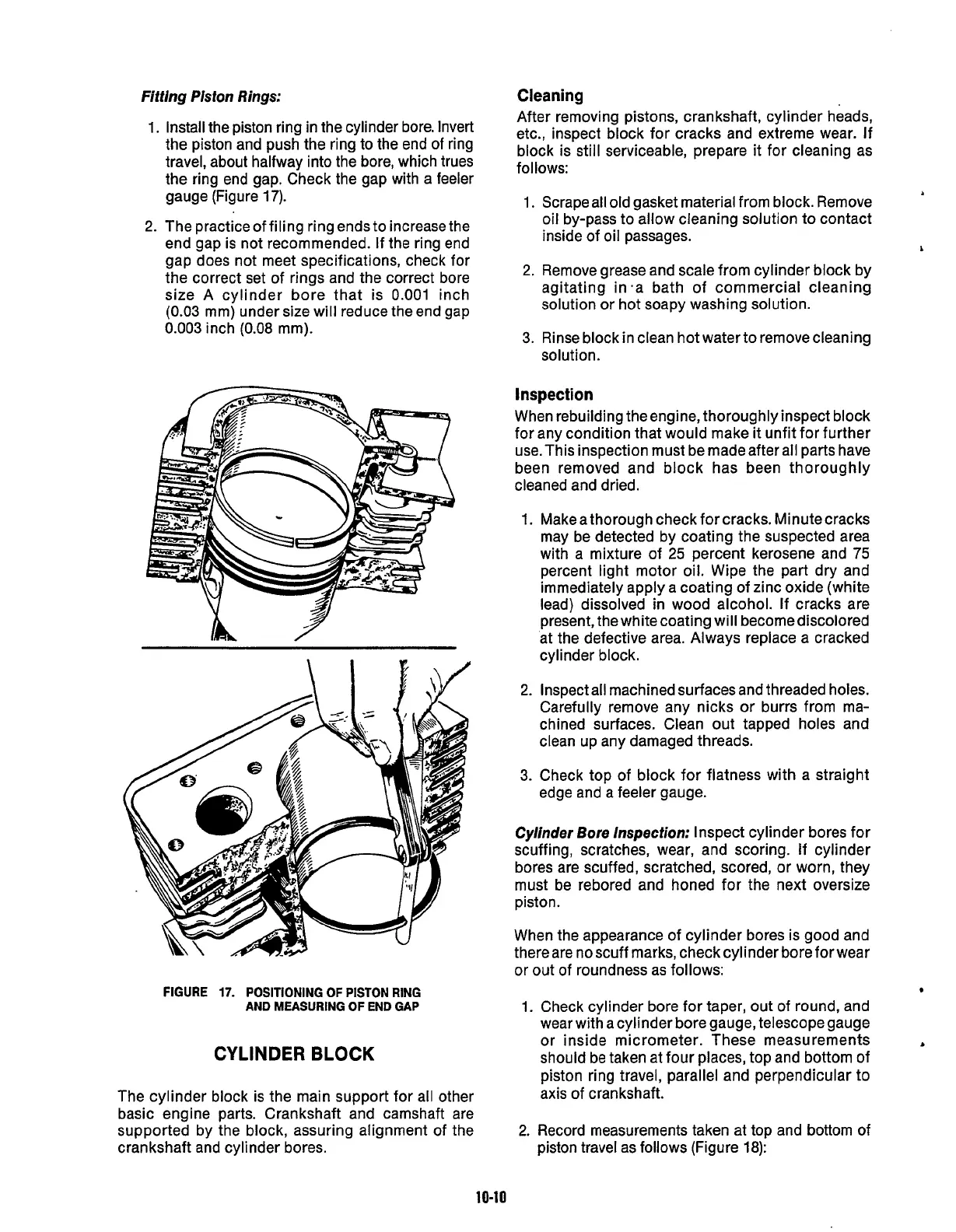
Install the piston ring in the cylinder bore. Invert
the piston and push the ring to the end of ring
travel, about halfway into the bore, which trues
the ring end gap. Check the gap with a feeler
gauge (Figure
17).
2.
The practice
of
filing ring ends to increase the
end gap
is
not recommended. If the ring end
gap does not meet specifications, check for
the correct set of rings and the correct bore
size A cylinder bore that is
0.001
inch
(0.03
mm) under size will reduce the end gap
0.003
inch
(0.08
mm).
FIGURE
17.
POSITIONING OF PISTON RING
AND MEASURING
OF
END GAP
CYLINDER
BLOCK
The cylinder block is the main support for all other
basic engine parts. Crankshaft and camshaft are
supported by the block, assuring alignment of the
crankshaft and cylinder bores.
Cleaning
After removing pistons, crankshaft, cylinder heads,
etc., inspect block for cracks and extreme wear. If
block is still serviceable, prepare
it
for cleaning as
follows:
,
1.
Scrape all old gasket material from block. Remove
oil by-pass to allow cleaning solution to contact
inside of oil passages.
2. Remove grease and scale from cylinder block by
agitating in .a bath of commercial cleaning
solution
or
hot soapy washing solution.
3.
Rinse block in clean hot water to remove cleaning
L
solution.
Inspection
When rebuilding theengine, thoroughly inspect block
for any condition that would make
it
unfit for further
use. This inspection must be made after all parts have
been removed and block has been thoroughly
cleaned and dried.
1.
Makeathorough check forcracks. Minutecracks
may be detected by coating the suspected area
with a mixture of 25 percent kerosene and 75
percent light motor oil. Wipe the part dry and
immediately apply a coating of zinc oxide (white
lead) dissolved in wood alcohol. If cracks are
present, the white coating will become discolored
at the defective area. Always replace a cracked
cylinder block.
2.
Inspect all machined surfaces and threaded holes.
Carefully remove any nicks
or
burrs from ma-
chined surfaces. Clean out tapped holes and
clean up any damaged threads.
3.
Check top of block for flatness with a straight
edge and a feeler gauge.
CyMnder Bore Inspection:
Inspect cylinder bores for
scuffing, scratches, wear, and scoring. If cylinder
bores are scuffed, scratched, scored, or worn, they
must be rebored and honed for the next oversize
piston.
When the appearance of cylinder bores is good and
thereare noscuff marks, check cylinder bore forwear
or out of roundness as follows:
1.
2.
Check cylinder bore for taper, out of round, and
wear with a cylinder bore gauge, telescope gauge
or inside micrometer. These measurements
should be taken at four places, top and bottom of
piston ring travel, parallel and perpendicular to
axis
of
crankshaft.
Record measurements taken at top and bottom of
piston travel as follows (Figure
18):
10-10
Redistribution or publication of this document,
by any means, is strictly prohibited.

 Loading...
Loading...